Abstract
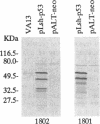
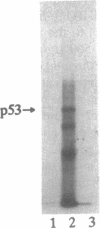
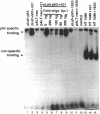
We have investigated the use of Leishmania cells as a novel eukaryotic expression system for the production of recombinant protein. These cells are easy to maintain, requiring no CO2 incubator or shaker, and can be grown in standard tissue culture media. Leishmania cells can be readily transfected with plasmid DNA by electroporation and transformants selected with antibiotic resistance. Recent studies have shown that it is possible to express foreign genes in Leishmania for the purpose of understanding the biology of this protozoan cell. In the present study we report the use of this system as a means of producing a biologically functional human p53 protein. The conformation of the p53 protein is critical for its ability to bind specific DNA sequences. It is demonstrated that Leishmania-synthesized human p53 is phosphorylated and can bind specifically to its enhancer DNA sequence. These data demonstrate that Leishmania may represent a simple eukaryotic expression system for the production of biologically active recombinant proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N. Trans splicing of nuclear pre-mRNAs. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1157–1160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest H., Matlashewski G. Developmental gene expression in Leishmania donovani: differential cloning and analysis of an amastigote-stage-specific gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):2975–2984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E. The molecular biology of the Kinetoplastidae. Genet Eng. 1988;(7):1–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox L. S., Lane D. P. Tumour suppressors, kinases and clamps: how p53 regulates the cell cycle in response to DNA damage. Bioessays. 1995 Jun;17(6):501–508. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz A., Beverley S. M. Gene replacement in parasitic protozoa. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):171–173. doi: 10.1038/348171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Pim D., Labrecque S., Banks L., Matlashewski G. DNA damage induced p53 mediated transcription is inhibited by human papillomavirus type 18 E6. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):629–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Activation of the cryptic DNA binding function of mutant forms of p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3167–3174. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laban A., Tobin J. F., Curotto de Lafaille M. A., Wirth D. F. Stable expression of the bacterial neor gene in Leishmania enriettii. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):572–574. doi: 10.1038/343572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Coburn C. M., McMahon-Pratt D., Beverley S. M. Development of a stable Leishmania expression vector and application to the study of parasite surface antigen genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9736–9740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Smith H. Q., Rusche L., Beverley S. M. Coupling of poly(A) site selection and trans-splicing in Leishmania. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):996–1007. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G. J., Tuck S., Pim D., Lamb P., Schneider J., Crawford L. V. Primary structure polymorphism at amino acid residue 72 of human p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):961–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Banks L., Pim D., Crawford L. Analysis of human p53 proteins and mRNA levels in normal and transformed cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou B., Roy G., Ouellette M. A novel antifolate resistance gene on the amplified H circle of Leishmania. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3601–3608. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou B., Roy G., Ouellette M. Autonomous replication of bacterial DNA plasmid oligomers in Leishmania. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 May;65(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou B., Roy G., Ouellette M. Frequent amplification of a short chain dehydrogenase gene as part of circular and linear amplicons in methotrexate resistant Leishmania. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4305–4312. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G., Talamas-Rohana P. Leishmania and the macrophage: a marriage of inconvenience. Immunol Today. 1989 Oct;10(10):328–333. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan K. A., Garraway L. A., Descoteaux A., Turco S. J., Beverley S. M. Isolation of virulence genes directing surface glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol synthesis by functional complementation of Leishmania. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8609–8613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarunina M., Jenkins J. R. Human p53 binds DNA as a protein homodimer but monomeric variants retain full transcription transactivation activity. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):3165–3173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. F., Reiner S. L., Hatam F., Zheng S., Leptak C. L., Wirth D. F., Locksley R. M. Transfected Leishmania expressing biologically active IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):5059–5069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]