Abstract
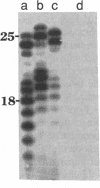
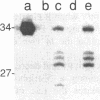
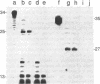
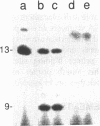
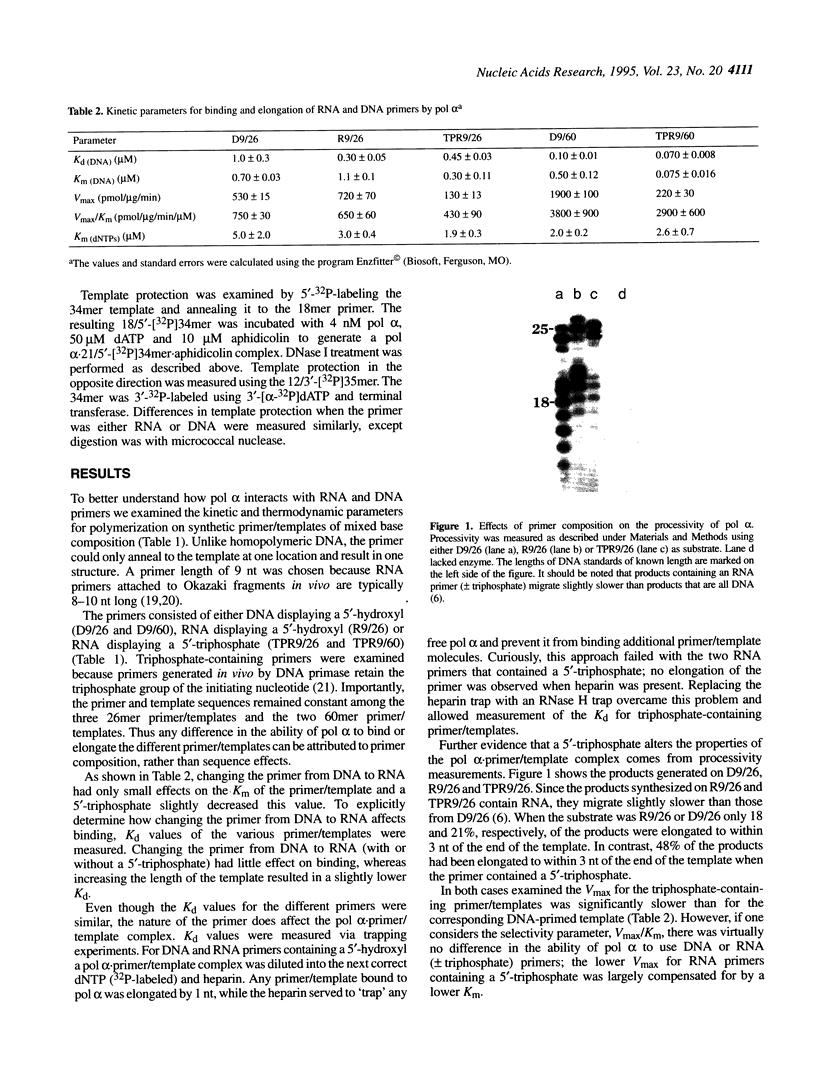
The interactions of calf thymus DNA polymerase alpha (pol alpha) with primer/templates were examined. Simply changing the primer from DNA to RNA had little effect on primer/template binding or dNTP polymerization (Km, Vmax and processivity). Surprisingly, however, adding a 5'-triphosphate to the primer greatly changed its interactions with pol alpha (binding, Vmax and Km and processivity). While changing the primer from DNA to RNA greatly altered the abilit of pol alpha to discriminate against nucleotide analogs, it did not compromise the ability of pol alpha to discriminate against non-cognate dNTPs. Thus the nature of the primer appears to affect 'sugar fidelity', without altering 'base fidelity'. DNase protection assays showed that pol alpha strongly protected 9 nt of the primer strand, 13 nt of the duplex template strand and 14 nt of the single-stranded template from hydrolysis by DNase I and weakly protected several bases outside this core region. This large DNA binding domain may account for the ability of a 5'-triphosphate on RNA primers to alter the catalytic properties of pol alpha.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boosalis M. S., Petruska J., Goodman M. F. DNA polymerase insertion fidelity. Gel assay for site-specific kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14689–14696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant F. R., Johnson K. A., Benkovic S. J. Elementary steps in the DNA polymerase I reaction pathway. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3537–3546. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. H., Kuchta R. D. DNA polymerase epsilon: aphidicolin inhibition and the relationship between polymerase and exonuclease activity. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 24;32(33):8568–8574. doi: 10.1021/bi00084a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland W. C., Wang T. S. Mutational analysis of the human DNA polymerase alpha. The most conserved region in alpha-like DNA polymerases is involved in metal-specific catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11028–11040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detera S. D., Becerra S. P., Swack J. A., Wilson S. H. Studies on the mechanism of DNA polymerase alpha. Nascent chain elongation, steady state kinetics, and the initiation phase of DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6933–6943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Korn D. Properties of the primer-binding site and the role of magnesium ion in primer-template recognition by KB cell DNA polymerase alpha. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4570–4578. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosse F., Krauss G. The primase activity of DNA polymerase alpha from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1881–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., Hendrickson E. A., DePamphilis M. L. Sequence specificity for the initiation of RNA-primed simian virus 40 DNA synthesis in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 15;175(2):131–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn K. T., Grosse F. Processivity of the DNA polymerase alpha-primase complex from calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2870–2878. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. Z., Wang T. S., Korn D. DNA primase from KB cells. Evidence for a novel model of primase catalysis by a highly purified primase/polymerase-alpha complex. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2602–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilsley D. D., Lee S. H., Miller W. H., Kuchta R. D. Acyclic guanosine analogs inhibit DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon with very different potencies and have unique mechanisms of action. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 28;34(8):2504–2510. doi: 10.1021/bi00008a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Rossignol J. M., Conaway R. C., Banks G. R., Lehman I. R. Association of DNA primase with the beta/gamma subunits of DNA polymerase alpha from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9037–9039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitani T., Yoda K., Okazaki T. Discontinuous DNA replication of Drosophila melanogaster is primed by octaribonucleotide primer. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1591–1596. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchta R. D., Ilsley D., Kravig K. D., Schubert S., Harris B. Inhibition of DNA primase and polymerase alpha by arabinofuranosylnucleoside triphosphates and related compounds. Biochemistry. 1992 May 19;31(19):4720–4728. doi: 10.1021/bi00134a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesner L. D., Hockensmith J. W. Probing the energetics of oligo(dT).poly(dA) by laser cross-linking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2521–2525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn M. M., Alberts B. M. DNA footprinting studies of the complex formed by the T4 DNA polymerase holoenzyme at a primer-template junction. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20034–20044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier H., Sawaya M. R., Kumar A., Wilson S. H., Kraut J. Structures of ternary complexes of rat DNA polymerase beta, a DNA template-primer, and ddCTP. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1891–1903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podust V. N., Vladimirova O. V., Manakova E. N., Lavrik O. I. Eukaryotic DNA primase appears to act as oligomer in DNA-polymerase-alpha--primase complex. Eur J Biochem. 1992 May 15;206(1):7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. G., Weaver D. T., Baril E. F., DePamphilis M. L. DNA polymerase alpha cofactors C1C2 function as primer recognition proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9810–9819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Nguyen D., Kunkel T. A. Frameshift fidelity during replication of double-stranded DNA in HeLa cell extracts. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 20;32(15):4083–4089. doi: 10.1021/bi00066a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar M., Fedoroff O. Y., Miller J. M., Ribeiro N. S., Reid B. R. The DNA strand in DNA.RNA hybrid duplexes is neither B-form nor A-form in solution. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4207–4215. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheaff R. J., Kuchta R. D., Ilsley D. Calf thymus DNA polymerase alpha-primase: "communication" and primer-template movement between the two active sites. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 1;33(8):2247–2254. doi: 10.1021/bi00174a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheaff R. J., Kuchta R. D. Mechanism of calf thymus DNA primase: slow initiation, rapid polymerization, and intelligent termination. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):3027–3037. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheaff R., Ilsley D., Kuchta R. Mechanism of DNA polymerase alpha inhibition by aphidicolin. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8590–8597. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng B. Y., Ahlem C. N. A DNA primase from mouse cells. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9845–9849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Replication factors required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. I. DNA structure-specific recognition of a primer-template junction by eukaryotic DNA polymerases and their accessory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1950–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser T., Gassmann M., Thömmes P., Ferrari E., Hafkemeyer P., Hübscher U. Biochemical and functional comparison of DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10420–10428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]