Abstract
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnau J., Housego A. P., Oliver R. P. The use of RAPD markers in the genetic analysis of the plant pathogenic fungus Cladosporium fulvum. Curr Genet. 1994 May;25(5):438–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00351783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
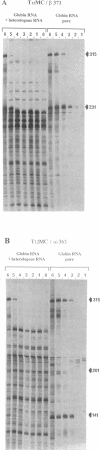
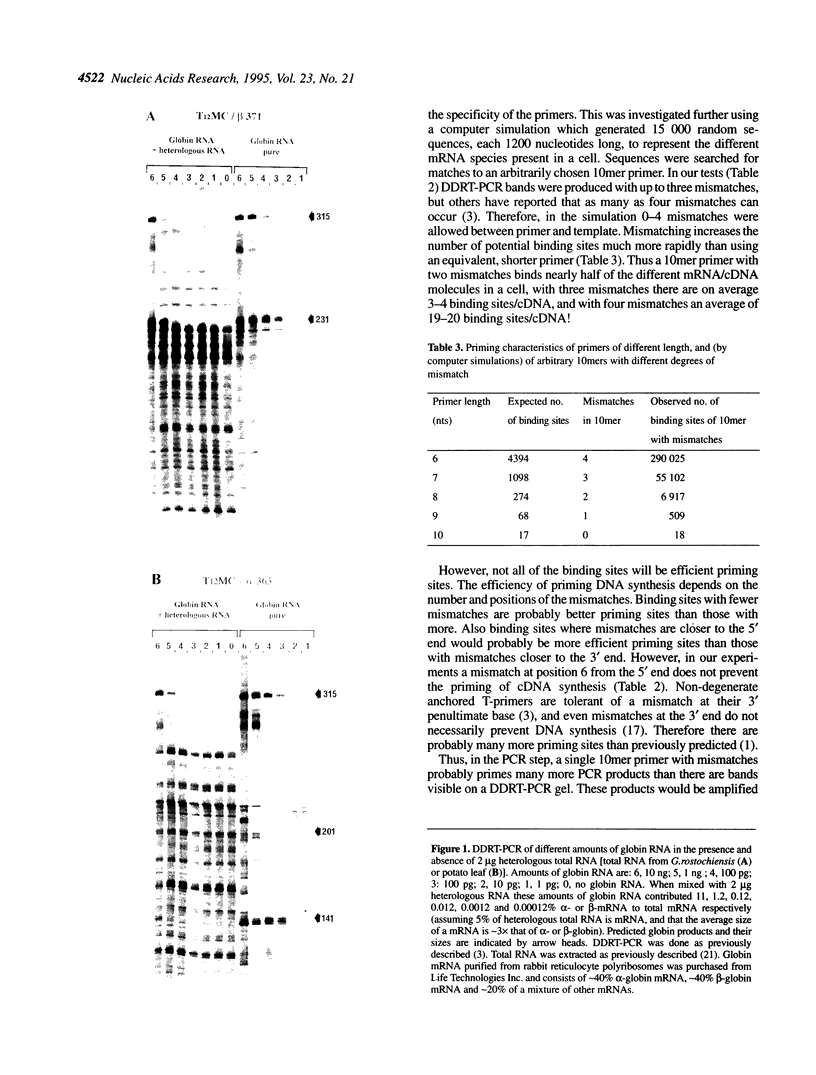
- Bauer D., Müller H., Reich J., Riedel H., Ahrenkiel V., Warthoe P., Strauss M. Identification of differentially expressed mRNA species by an improved display technique (DDRT-PCR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4272–4280. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffard D., Vaillant V., Esnault R. Complexity of polysomal polyadenylated RNAs in Vicia faba meristematic root cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):129–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Q., Russell M., Birch D. E., Raymond J., Bloch W. Prevention of pre-PCR mis-priming and primer dimerization improves low-copy-number amplifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1717–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conkling M. A., Cheng C. L., Yamamoto Y. T., Goodman H. M. Isolation of transcriptionally regulated root-specific genes from tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jul;93(3):1203–1211. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.3.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddijn O. J., Lindsey K., van der Lee F. M., Klap J. C., Sijmons P. C. Differential gene expression in nematode-induced feeding structures of transgenic plants harbouring promoter-gusA fusion constructs. Plant J. 1993 Nov;4(5):863–873. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.04050863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Cornelissen B. J., van Loon L. C., van Boom J. H., Tromp M., Bol J. F. Virus-induced synthesis of messenger RNAs for precursors of pathogenesis-related proteins in tobacco. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2167–2171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamalay J. C., Goldberg R. B. Regulation of structural gene expression in tobacco. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):935–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Kellogg D. E., McKinney N., Spasic D., Goda L., Levenson C., Sninsky J. J. Effects of primer-template mismatches on the polymerase chain reaction: human immunodeficiency virus type 1 model studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):999–1005. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Averboukh L., Pardee A. B. Distribution and cloning of eukaryotic mRNAs by means of differential display: refinements and optimization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3269–3275. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Pardee A. B. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1354393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J., Schell J., Willmitzer L. Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Mathieu-Daude F., Welsh J. RNA fingerprinting and differential display using arbitrarily primed PCR. Trends Genet. 1995 Jun;11(6):242–246. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzner U. M., Goodman H. M. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding pathogenesis-related proteins from tobacco mosaic virus infected tobacco plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4449–4465. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph D., McClelland M., Welsh J. RNA fingerprinting using arbitrarily primed PCR identifies differentially regulated RNAs in mink lung (Mv1Lu) cells growth arrested by transforming growth factor beta 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10710–10714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Chada K., Dalal S. S., Cheng R., Ralph D., McClelland M. Arbitrarily primed PCR fingerprinting of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):4965–4970. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.4965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]