Abstract
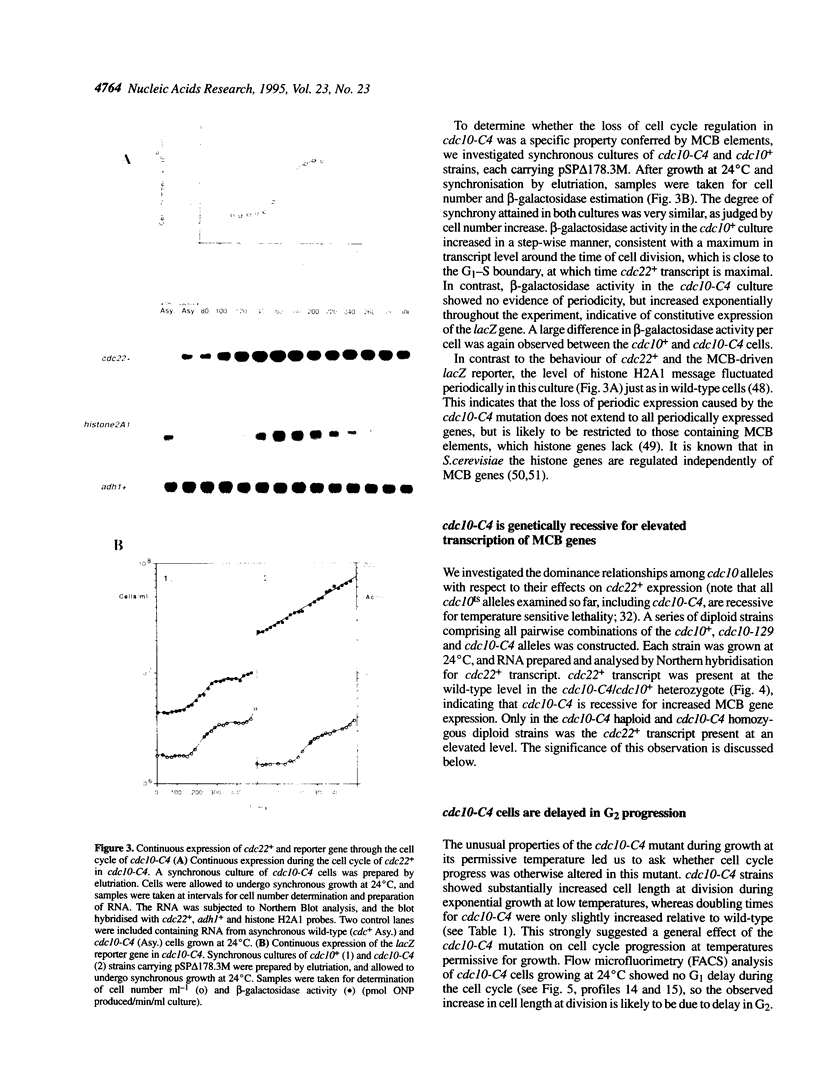
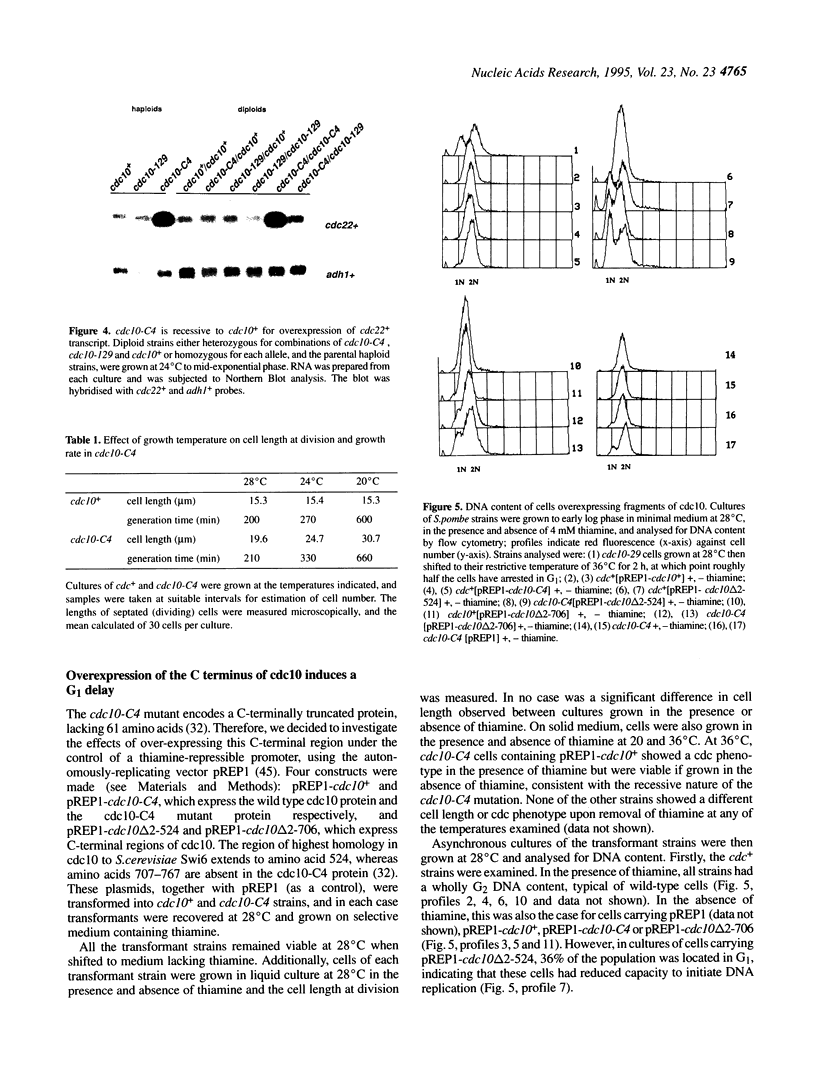
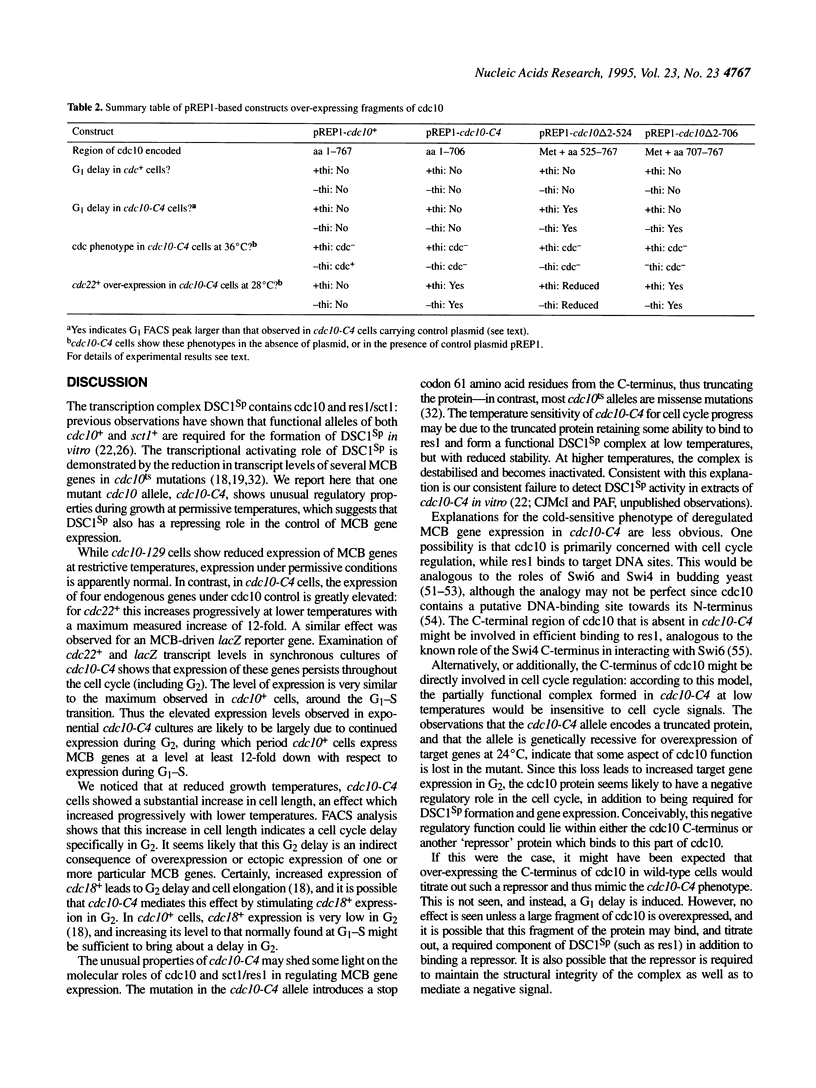
In this paper we describe properties of the cdc10-C4 mutant of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. The cdc10+ gene encodes a component of the DSC1Sp/MBF transcription complex, which is required for cell-cycle regulated expression at G1-S of several genes via cis-acting MCB (MIuI cell cycle box) elements. At permissive temperatures cdc10-C4 causes expression of MCB-regulated genes through the whole cell cycle, which in asynchronously dividing cells is manifested in overall higher expression levels. This overexpression phenotype is cold sensitive: in cdc10-C4 cells, MCB genes are expressed offprogressively higher levels at lower temperatures. In heterozygous cdc10-C4/cdc10+ diploid strains, MCB-regulated genes are not overexpressed, suggesting that loss, rather than alteration, of function of the cdc10-C4 gene product is the reason for unregulated target gene expression. Consistent with this, the cdc10-C4 mutant allele is known to encode a truncated protein. We have also overexpressed the region of the cdc10 protein absent in cdc10-C4 under the control of an inducible promoter. This induces a G1 delay, and additionally causes a reduction of the overexpression of MCB genes in cdc10-C4 strains. These results suggest that DSC1Sp/MBF represses, as well as activates, MCB gene expression during the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Tyers M., Futcher B., Nasmyth K. Mechanisms that help the yeast cell cycle clock tick: G2 cyclins transcriptionally activate G2 cyclins and repress G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):993–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90722-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. J., Herskowitz I. Identification of a DNA binding factor involved in cell-cycle control of the yeast HO gene. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. J., Herskowitz I. The yeast SWI4 protein contains a motif present in developmental regulators and is part of a complex involved in cell-cycle-dependent transcription. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):830–833. doi: 10.1038/342830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. J., Moore L. A. Interaction of the yeast Swi4 and Swi6 cell cycle regulatory proteins in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11852–11856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aves S. J., Durkacz B. W., Carr A., Nurse P. Cloning, sequencing and transcriptional control of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc10 'start' gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):457–463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayté J., Leis J. F., Herrera A., Tang E., Yang H., DeCaprio J. A. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe MBF complex requires heterodimerization for entry into S phase. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2589–2599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Similarity between cell-cycle genes of budding yeast and fission yeast and the Notch gene of Drosophila. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):651–654. doi: 10.1038/329651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caligiuri M., Beach D. Sct1 functions in partnership with Cdc10 in a transcription complex that activates cell cycle START and inhibits differentiation. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):607–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T., Beach D. Interaction between the Cig1 and Cig2 B-type cyclins in the fission yeast cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):768–776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirick L., Moll T., Auer H., Nasmyth K. A central role for SWI6 in modulating cell cycle Start-specific transcription in yeast. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):508–513. doi: 10.1038/357508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirick L., Moll T., Auer H., Nasmyth K. A central role for SWI6 in modulating cell cycle Start-specific transcription in yeast. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):508–513. doi: 10.1038/357508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L. Cell cycle. In and out of the cell cycle. Curr Biol. 1994 Sep 1;4(9):828–830. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C. B., Fantes P. A. The cdc22 gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe encodes a cell cycle-regulated transcript. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2981–2985. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm C., Kohli J., Murray J., Maundrell K. Genetic engineering of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: a system for gene disruption and replacement using the ura4 gene as a selectable marker. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00331307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Beach D. cdt1 is an essential target of the Cdc10/Sct1 transcription factor: requirement for DNA replication and inhibition of mitosis. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):425–434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H. Cell cycle control of gene expression in yeast. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;2(12):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90041-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., Lowndes N. F. Cell cycle control of DNA synthesis in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2403–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Moll T., Neuberg M., Ahorn H., Nasmyth K. A role for the transcription factors Mbp1 and Swi4 in progression from G1 to S phase. Science. 1993 Sep 17;261(5128):1551–1557. doi: 10.1126/science.8372350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohli J., Hottinger H., Munz P., Strauss A., Thuriaux P. Genetic Mapping in SCHIZOSACCHAROMYCES POMBE by Mitotic and Meiotic Analysis and Induced Haploidization. Genetics. 1977 Nov;87(3):471–489. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Simanis V., Nurse P. Fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe correctly excises a mammalian RNA transcript intervening sequence. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):78–80. doi: 10.1038/318078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B., Taylor W. R. A structural similarity between mammalian and yeast transcription factors for cell-cycle-regulated genes. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;3(3):75–76. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90067-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J., Wu C. Protein traffic on the heat shock promoter: parking, stalling, and trucking along. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90286-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowndes N. F., Johnson A. L., Breeden L., Johnston L. H. SWI6 protein is required for transcription of the periodically expressed DNA synthesis genes in budding yeast. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):505–508. doi: 10.1038/357505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowndes N. F., Johnson A. L., Johnston L. H. Coordination of expression of DNA synthesis genes in budding yeast by a cell-cycle regulated trans factor. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):247–250. doi: 10.1038/350247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowndes N. F., McInerny C. J., Johnson A. L., Fantes P. A., Johnston L. H. Control of DNA synthesis genes in fission yeast by the cell-cycle gene cdc10+. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):449–453. doi: 10.1038/355449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Yanagida M. Histone gene organization of fission yeast: a common upstream sequence. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3531–3538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Yanagida M., Nurse P. Histone transcription in cell cycle mutants of fission yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1093–1097. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. Thiamine-repressible expression vectors pREP and pRIP for fission yeast. Gene. 1993 Jan 15;123(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90551-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Tanaka K., Okayama H. res2+, a new member of the cdc10+/SWI4 family, controls the 'start' of mitotic and meiotic cycles in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1873–1880. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Klar A., Nurse P. Molecular genetic analysis of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:795–823. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94059-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A repetitive DNA sequence that confers cell-cycle START (CDC28)-dependent transcription of the HO gene in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. Control of the yeast cell cycle by the Cdc28 protein kinase. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):166–179. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90099-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Clear as crystal? Curr Biol. 1993 Aug 1;3(8):544–547. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90053-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond A., Marks J., Simanis V. The activity of S.pombe DSC-1-like factor is cell cycle regulated and dependent on the activity of p34cdc2. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4325–4334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond A., Schmidt S., Simanis V. Mutations in the cdc10 start gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe implicate the region of homology between cdc10 and SWI6 as important for p85cdc10 function. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Sep;234(3):449–456. doi: 10.1007/BF00538705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond A., Simanis V. Domains of p85cdc10 required for function of the fission yeast DSC-1 factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3615–3621. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. R., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saka Y., Fantes P., Sutani T., McInerny C., Creanor J., Yanagida M. Fission yeast cut5 links nuclear chromatin and M phase regulator in the replication checkpoint control. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 15;13(22):5319–5329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06866.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saka Y., Yanagida M. Fission yeast cut5+, required for S phase onset and M phase restraint, is identical to the radiation-damage repair gene rad4+. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90428-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sazer S., Sherwood S. W. Mitochondrial growth and DNA synthesis occur in the absence of nuclear DNA replication in fission yeast. J Cell Sci. 1990 Nov;97(Pt 3):509–516. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taba M. R., Muroff I., Lydall D., Tebb G., Nasmyth K. Changes in a SWI4,6-DNA-binding complex occur at the time of HO gene activation in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2000–2013. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Okazaki K., Okazaki N., Ueda T., Sugiyama A., Nojima H., Okayama H. A new cdc gene required for S phase entry of Schizosaccharomyces pombe encodes a protein similar to the cdc 10+ and SWI4 gene products. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4923–4932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05599.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y., Takeda T., Nasmyth K., Jones N. pct1+, which encodes a new DNA-binding partner of p85cdc10, is required for meiosis in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 15;8(8):885–898. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]