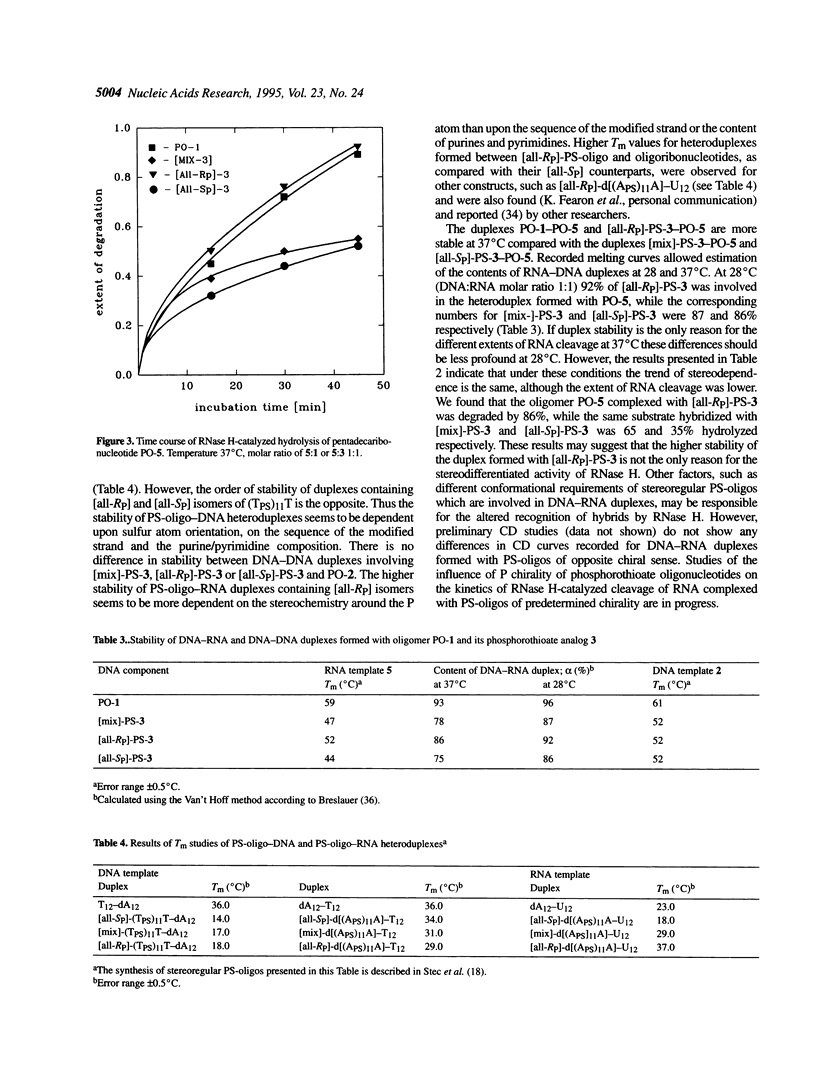
Abstract
P stereoregular phosphorothioate analogs of pentadecamer 5'-d(AGATGTTTGAGCTCT)-3' were synthesized by the oxathiaphospholane method. Their diastereomeric purity was assigned by means of enzymatic degradation with nuclease P1 and, independently, with snake venom phosphodiesterase. DNA-RNA hybrids formed by phosphorothioate oligonucleotides (PS-oligos) with the corresponding complementary pentadecaribonucleotide were treated with bacterial RNase H. The DNA-RNA complex containing the PS-oligo of [all-RP] configuration was found to be more susceptible to RNase H-dependent degradation of the pentadecaribonucleotide compared with hybrids containing either the [all-SP] counterpart or the so called 'random mixture of diastereomers' of the pentadeca(nucleoside phosphorothioate). This stereodependence of RNase H action was also observed for a polyribonucleotide (475 nt) hybridized with these phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. The results of melting studies of PS-oligo-RNA hybrids allowed a rationalization of the observed stereodifferentiation in terms of the higher stability of heterodimers formed between oligoribonucleotides and [all-RP]-oligo(nucleoside phosphorothioates), compared with the less stable heterodimers formed with [all-SP]-oligo(nucleoside phosphorothioates) or the random mixture of diastereomers.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botelho L. H., Webster L. C., Rothermel J. D., Baraniak J., Stec W. J. Inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by adenosine cyclic 3'-, 5'-phosphorodithioate, a second cAMP antagonist. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5301–5305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J. Extracting thermodynamic data from equilibrium melting curves for oligonucleotide order-disorder transitions. Methods Mol Biol. 1994;26:347–372. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59259-513-6_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant F. R., Benkovic S. J. Stereochemical course of the reaction catalyzed by 5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase from snake venom. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2825–2828. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M., Eckstein F., Hunneman D. H. Stereochemistry of hydrolysis by snake venom phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7476–7478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey P. A., Sammons R. D. Bond order and charge localization in nucleoside phosphorothioates. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):541–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2984773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furdon P. J., Dominski Z., Kole R. RNase H cleavage of RNA hybridized to oligonucleotides containing methylphosphonate, phosphorothioate and phosphodiester bonds. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9193–9204. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaroszewski J. W., Syi J. L., Maizel J., Cohen J. S. Towards rational design of antisense DNA: molecular modelling of phosphorothioate DNA analogues. Anticancer Drug Des. 1992 Jun;7(3):253–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall W. S., Caruthers M. H. Phosphorodithioate DNA as a potential therapeutic drug. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.7681216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami A., Tamura Y., Wada H., Makino K. Separation and characterization of diastereoisomers of antisense oligodeoxyribonucleoside phosphorothioates. Anal Biochem. 1994 Dec;223(2):285–290. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter B. V., Connolly B. A., Eckstein F. Synthesis and configurational analysis of a dinucleoside phosphate isotopically chiral at phosphorus. Stereochemical course of Penicillium citrum nuclease P1 reaction. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 15;22(6):1369–1377. doi: 10.1021/bi00275a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosolen A., Kyle E., Chavany C., Bergan R., Kalman E. T., Crouch R., Neckers L. Effect of over-expression of bacterial ribonuclease H on the utility of antisense MYC oligodeoxynucleotides in the monocytic leukemia cell line U937. Biochimie. 1993;75(1-2):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90028-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Cantin E. M., Chang P. S., Zaia J. A., Ladne P. A., Stephens D. A., Rossi J. J. Ribozymes as potential anti-HIV-1 therapeutic agents. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1222–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.2107573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stec W. J., Grajkowski A., Koziolkiewicz M., Uznanski B. Novel route to oligo(deoxyribonucleoside phosphorothioates). Stereocontrolled synthesis of P-chiral oligo(deoxyribonucleoside phosphorothioates). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5883–5888. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stec W. J. Novel method of synthesis of oligo(deoxyribonucleoside phosphorothioates). Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1991;(25):171–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cheng Y. C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents--is the bullet really magical? Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1004–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.8351515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder R. Y., Walder J. A. Role of RNase H in hybrid-arrested translation by antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5011–5015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk A., Stec W. J. Analysis of oligo(deoxynucleoside phosphorothioate)s and their diastereomeric composition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 11;23(3):530–534. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.3.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W., Hendrickson W. A., Crouch R. J., Satow Y. Structure of ribonuclease H phased at 2 A resolution by MAD analysis of the selenomethionyl protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1398–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2169648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon G. Oligonucleotide analogues as potential chemotherapeutic agents. Pharm Res. 1988 Sep;5(9):539–549. doi: 10.1023/a:1015985728434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]