Abstract
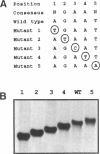
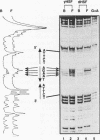
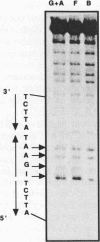
Heat shock genes are activated by the binding of the heat shock transcription factor (HSF) to heat shock elements (HSEs), consisting of arrays of the 5-bp unit NGAAN arranged as inverted repeats. Here, we have investigated the interaction of the 5-bp unit with HSFs of Drosophila and Saccharomyces. Mutations within the conserved, central trinucleotide GAA reduce the relative binding affinity of both HSFs. In addition, the base at position 1 (N1) also influences binding, with a strong preference for an A at this position. Methylation interference initially indicated that HSF contacts A1 in the minor groove, but interacts with the immediately adjacent base G2 in the major groove. Further characterization of this apparently abrupt minor to major groove transition by substitution of A1 with an inosine, shows that HSF contacts A1 in the major groove. We offer an explanation for this apparent contradiction and propose that HSF recognizes the HSE primarily through contacts within the major groove of the DNA helix. Finally, based on these observations and a re-evaluation of the base frequencies and criteria for consensus sequence assignment, we propose that the sequence AGAAN more accurately represents the consensus HSE motif.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Jun;13(6):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boorstein W. R., Craig E. A. Structure and regulation of the SSA4 HSP70 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18912–18921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R., Ray S. C. Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3185–3192. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Westwood J. T., Becker P. B., Wilson S., Lambert K., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a hexameric Drosophila heat shock factor subject to negative regulation. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1085–1097. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90511-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunniff N. F., Morgan W. D. Analysis of heat shock element recognition by saturation mutagenesis of the human HSP70.1 gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8317–8324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunniff N. F., Wagner J., Morgan W. D. Modular recognition of 5-base-pair DNA sequence motifs by human heat shock transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3504–3514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. J., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Regulation of heat shock factor in Schizosaccharomyces pombe more closely resembles regulation in mammals than in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Diethyl pyrocarbonate: a chemical probe for secondary structure in negatively supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8009–8013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger P. E., Sarge K. D., Morimoto R. I. Mouse heat shock transcription factors 1 and 2 prefer a trimeric binding site but interact differently with the HSP70 heat shock element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3370–3383. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWLEY P. D., BROOKES P. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE ALKYLATION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS AND THEIR CONSTITUENT NUCLEOTIDES. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:127–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0890127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. L., Jack W. E., Modrich P. DNA determinants important in sequence recognition by Eco RI endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13200–13206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. D., Theodorakis N. G., Morimoto R. I. Coordinate changes in heat shock element-binding activity and HSP70 gene transcription rates in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4736–4744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Xiao H., Lis J. T. Stable binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to head-to-head and tail-to-tail repeats of a conserved 5 bp recognition unit. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peteranderl R., Nelson H. C. Trimerization of the heat shock transcription factor by a triple-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coil. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):12272–12276. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Giorgi G., Clos J., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a human heat shock factor, HSF1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6906–6910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarge K. D., Zimarino V., Holm K., Wu C., Morimoto R. I. Cloning and characterization of two mouse heat shock factors with distinct inducible and constitutive DNA-binding ability. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1902–1911. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf K. D., Rose S., Zott W., Schöffl F., Nover L., Schöff F. Three tomato genes code for heat stress transcription factors with a region of remarkable homology to the DNA-binding domain of the yeast HSF. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4495–4501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheit K. H., Holy A. Die Methylierung von Inosin und Uridylyl-(3'-5')inosin durch Dimethylsulfat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Dec 19;149(2):344–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz T. J., Gallo G. J., Sheldon L., Tempst P., Kingston R. E. Isolation of a cDNA for HSF2: evidence for two heat shock factor genes in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6911–6915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluka J. P., Horvath S. J., Glasgow A. C., Simon M. I., Dervan P. B. Importance of minor-groove contacts for recognition of DNA by the binding domain of Hin recombinase. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6551–6561. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K. Heat shock factor and the heat shock response. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Nelson H. C. Trimerization of a yeast transcriptional activator via a coiled-coil motif. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr D. B., Hawley D. K. TFIID binds in the minor groove of the TATA box. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90299-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwood J. T., Wu C. Activation of Drosophila heat shock factor: conformational change associated with a monomer-to-trimer transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3481–3486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Seto D., Parker C. S. Isolation of the gene encoding the S. cerevisiae heat shock transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):841–853. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Germline transformation used to define key features of heat-shock response elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.3125608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Perisic O., Lis J. T. Cooperative binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to arrays of a conserved 5 bp unit. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90242-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]