Abstract
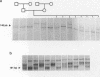
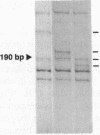
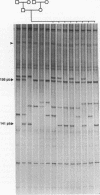
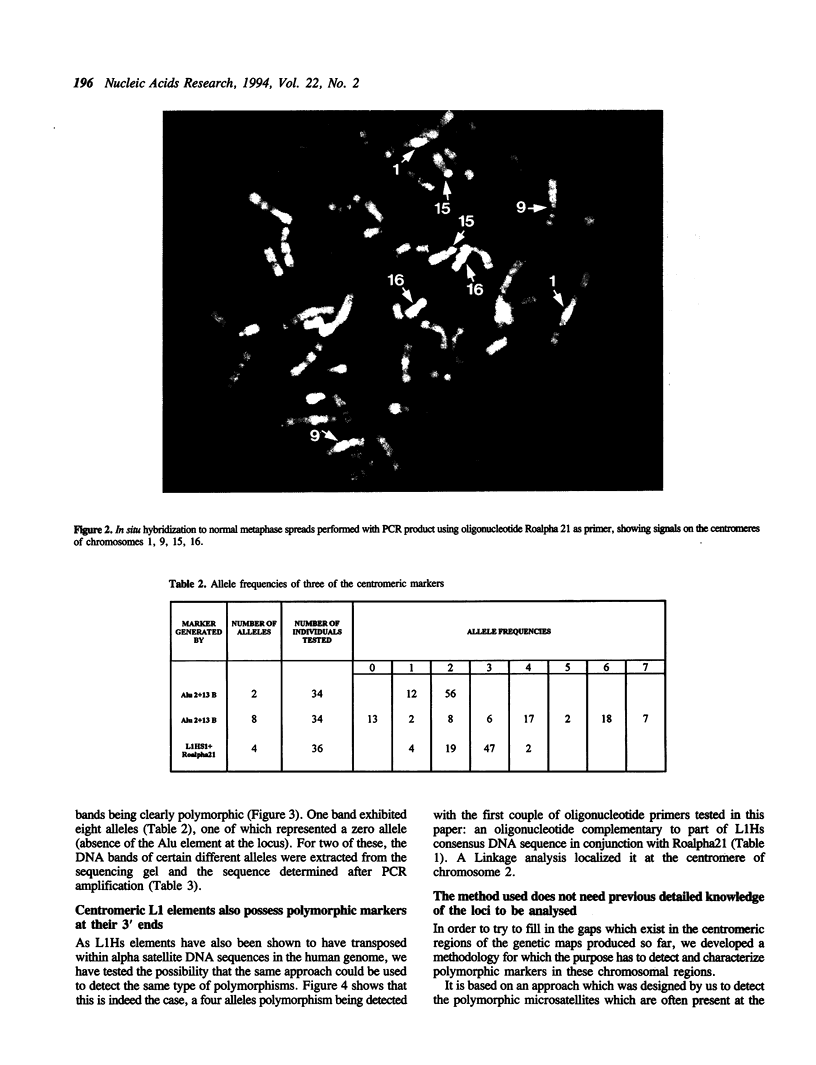
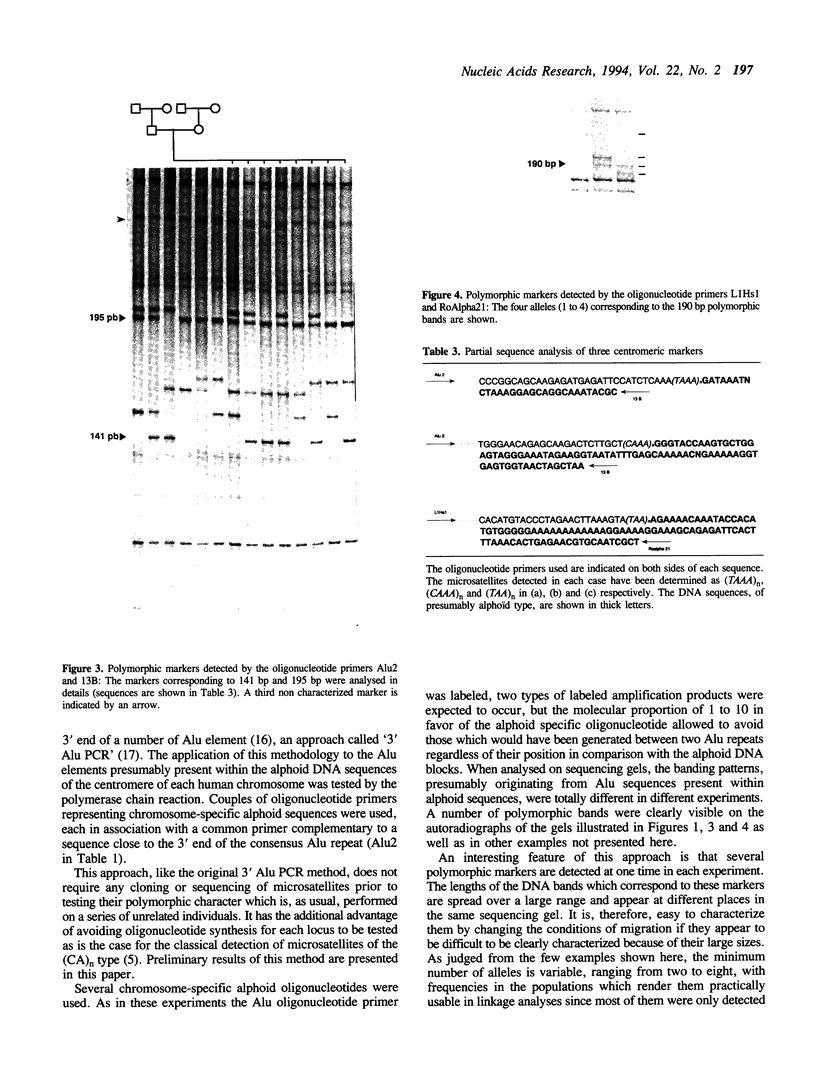
Using oligonucleotide primers complementary to the 3' ends of either the Alu or the L1Hs consensus sequences in conjunction with a primer complementary to alpha satellite subsets specific to different human chromosomes, it was possible to detect and characterize polymorphisms originating from the microsatellites which are often present downstream these repetitive elements. The methodology does not require cloning, sequencing or synthesis of specific primers. Centromeric location was confirmed by linkage analysis, in situ hybridization and sequencing. The method is proposed for the generation of polymorphic markers from all centromeric regions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casanova J. L., Pannetier C., Jaulin C., Kourilsky P. Optimal conditions for directly sequencing double-stranded PCR products with sequenase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4028–4028. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlieu J. P., Laurent A. M., Carter D. A., Bellis M., Roizès G. 3' Alu PCR: a simple and rapid method to isolate human polymorphic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1333–1337. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlieu J. P., Murgue B., Laurent A. M., Marçais B., Bellis M., Roizès G. Discrimination between alpha-satellite DNA sequences from chromosomes 21 and 13 by using polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1992 Oct;14(2):515–516. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Vissel B., Nagy A., Earle E., Kalitsis P. A survey of the genomic distribution of alpha satellite DNA on all the human chromosomes, and derivation of a new consensus sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1179–1182. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. Members of the KpnI family of long interspersed repeated sequences join and interrupt alpha-satellite in the monkey genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):321–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. J., Wang H. S., Shtromas I., Haliotis T., Roder J. C., Holden J. J., White B. N. Organization of a repetitive human 1.8 kb KpnI sequence localized in the heterochromatin of chromosome 15. Chromosoma. 1985;93(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01259449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Warren A. C., Taylor E. W., Colyer C. R., Meyers D. A., Antonarakis S. E. Alphoid DNA polymorphisms for chromosome 21 can be distinguished from those of chromosome 13 using probes homologous to both. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen A. L., Bostock C. J., Bak A. L. Homologous subfamilies of human alphoid repetitive DNA on different nucleolus organizing chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1075–1079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux N., Dutrillaux B., Viegas-Péquignot E. A simple method for simultaneous R- or G-banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization of small single-copy genes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;59(4):311–312. doi: 10.1159/000133277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Luty J. A. A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):397–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marçais B., Bellis M., Gérard A., Pagès M., Boublik Y., Roizès G. Structural organization and polymorphism of the alpha satellite DNA sequences of chromosomes 13 and 21 as revealed by pulse field gel electrophoresis. Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;86(3):311–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00202418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marçais B., Gérard A., Bellis M., Roizès G. TaqI reveals two independent alphoid polymorphisms on human chromosomes 13 and 21. Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;86(3):307–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00202417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneveri R., Agresti A., Della Valle G., Talarico D., Siccardi A. G., Ginelli E. Identification of a human clustered G + C-rich DNA family of repeats (Sau3A family). J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. DNA sequence polymorphisms in Alu repeats. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90282-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perna N. T., Batzer M. A., Deininger P. L., Stoneking M. Alu insertion polymorphism: a new type of marker for human population studies. Hum Biol. 1992 Oct;64(5):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. Rearranged sequences of a human Kpn I element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser J., Frommer M., Paul C., Vincent P. C. Sequence relationships of three human satellite DNAs. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]