Abstract
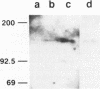
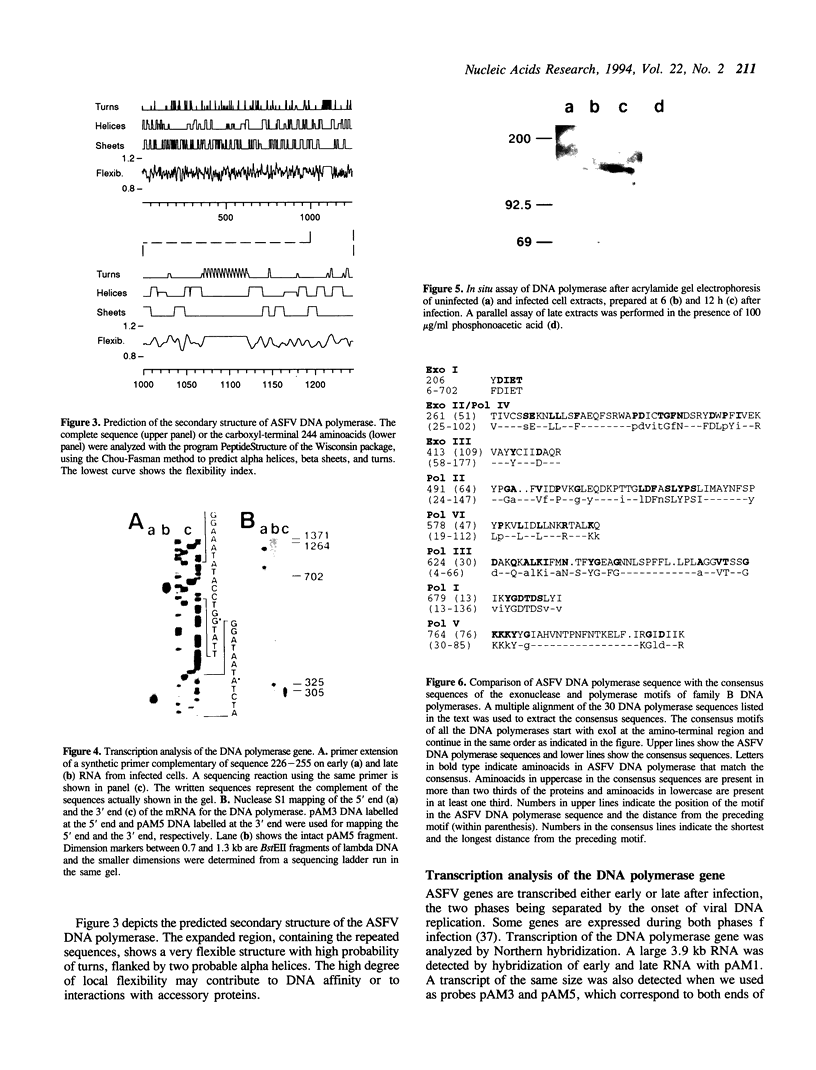
The DNA polymerase gene of African swine fever virus (ASFV) was mapped by marker rescue experiments using a phosphonoacetic acid-resistant mutant and hybridization with an oligonucleotide probe designed from the most conserved motif of family B DNA polymerases. Viral DNA fragments mapping in this region were cloned and sequenced. An open reading frame coding for a 1244 amino acid long peptide with a molecular mass of 142.5 kDa was determined from the sequence. A unique feature of ASFV DNA polymerase is the presence of 13 tandem repeats of the sequence Ala-Gly-Asp-Pro near the carboxyl end of the molecule. Comparison with 30 sequences of alpha-like DNA polymerases of cellular and viral origin showed that ASFV DNA polymerase has all the conserved motifs of family B DNA polymerases. A 3.9 kb transcript was detected by Northern hybridization and the transcription initiation and termination sites were mapped by S1 analysis and primer extension. Late transcription was initiated at a site different from the early transcription initiation site. A 145 kDa protein, consistent with the size of the gene, was identified by an in situ enzyme assay after gel electrophoresis of infected cell extracts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almazán F., Rodríguez J. M., Andrés G., Pérez R., Viñuela E., Rodriguez J. F. Transcriptional analysis of multigene family 110 of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6655–6667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6655-6667.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernad A., Blanco L., Lázaro J. M., Martín G., Salas M. A conserved 3'----5' exonuclease active site in prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90883-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernad A., Lázaro J. M., Salas M., Blanco L. The highly conserved amino acid sequence motif Tyr-Gly-Asp-Thr-Asp-Ser in alpha-like DNA polymerases is required by phage phi 29 DNA polymerase for protein-primed initiation and polymerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4610–4614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns M. M., Stenzler L., Tomley F. M., Campbell J., Boursnell M. E. Identification by a random sequencing strategy of the fowlpoxvirus DNA polymerase gene, its nucleotide sequence and comparison with other viral DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6563–6573. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson R. M., Glocker B., Rohrmann G. F. Characterization of the nucleotide sequence of the Lymantria dispar nuclear polyhedrosis virus DNA polymerase gene region. J Gen Virol. 1992 Dec;73(Pt 12):3177–3183. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-12-3177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Zhang J. A., Tan C. K., Davie E. W., So A. G., Downey K. M. Primary structure of the catalytic subunit of human DNA polymerase delta and chromosomal location of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11197–11201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L., Cadena D. L., Ahearn J. M., Jr, Dahmus M. E. A unique structure at the carboxyl terminus of the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damagnez V., Tillit J., de Recondo A. M., Baldacci G. The POL1 gene from the fission yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, shows conserved amino acid blocks specific for eukaryotic DNA polymerases alpha. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):182–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00273602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digard P., Bebrin W. R., Weisshart K., Coen D. M. The extreme C terminus of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase is crucial for functional interaction with processivity factor UL42 and for viral replication. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):398–406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.398-406.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Jones E. V., Moss B. Homology between DNA polymerases of poxviruses, herpesviruses, and adenoviruses: nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteves A., Marques M. I., Costa J. V. Two-dimensional analysis of African swine fever virus proteins and proteins induced in infected cells. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):192–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Hall J. D., Mount D. W., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Coen D. M. Sequence and mapping analyses of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene predict a C-terminal substrate binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7969–7973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Sciaky D., Gelinas R. E., Bing-Dong J., Yen C. E., Kelly M. M., Bullock P. A., Parsons B. L., O'Neill K. E., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequences from the adenovirus-2 genome. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13475–13491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabherr R., Strasser P., Van Etten J. L. The DNA polymerase gene from chlorella viruses PBCV-1 and NY-2A contains an intron with nuclear splicing sequences. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):721–731. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90527-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose F., Yamaguchi M., Nishida Y., Masutani M., Miyazawa H., Hanaoka F., Matsukage A. Structure and expression during development of Drosophila melanogaster gene for DNA polymerase alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4991–4998. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J., Braithwaite D. K. Compilation and alignment of DNA polymerase sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4045–4057. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki H., Ishino Y., Toh H., Nakata A., Shinagawa H. Escherichia coli DNA polymerase II is homologous to alpha-like DNA polymerases. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):24–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00273583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G. H., Leavitt M. C., Hsieh J. C., Ito J. Bacteriophage PRD1 DNA polymerase: evolution of DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8287–8291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempken F., Meinhardt F., Esser K. In organello replication and viral affinity of linear, extrachromosomal DNA of the ascomycete Ascobolus immersus. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):523–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00332419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S. C., Weston K., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. G. Sequence and transcription analysis of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.125-133.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznar J., Salas M. L., Viñuela E. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in African swine fever virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leegwater P. A., Strating M., Murphy N. B., Kooy R. F., van der Vliet P. C., Overdulve J. P. The Trypanosoma brucei DNA polymerase alpha core subunit gene is developmentally regulated and linked to a constitutively expressed open reading frame. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6441–6447. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcy A. I., Hwang C. B., Ruffner K. L., Coen D. M. Engineered herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase point mutants: the most highly conserved region shared among alpha-like DNA polymerases is involved in substrate recognition. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5883–5890. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5883-5890.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques M. I., Costa J. V. African swine fever virus-induced DNA polymerase is resistant to aphidicolin. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):498–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90219-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Takano H., Kim C. I., Hirokawa H. Primary structure of bacteriophage M2 DNA polymerase: conserved segments within protein-priming DNA polymerases and DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Araki H., Clark A. B., Hamatake R. K., Sugino A. A third essential DNA polymerase in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1143–1151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90391-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Christensen R. B., Alley J., Beck A. K., Bernstine E. G., Lemontt J. F., Lawrence C. W. REV3, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene whose function is required for induced mutagenesis, is predicted to encode a nonessential DNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5659–5667. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5659-5667.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Sugino A. Nucleotide sequence of the POL3 gene encoding DNA polymerase III (delta) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):375–375. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeser B., Tudzynski P. The linear mitochondrial plasmid pClK1 of the phytopathogenic fungus Claviceps purpurea may code for a DNA polymerase and an RNA polymerase. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):132–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00330952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paillard M., Sederoff R. R., Levings C. S. Nucleotide sequence of the S-1 mitochondrial DNA from the S cytoplasm of maize. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1125–1128. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisani F. M., De Martino C., Rossi M. A DNA polymerase from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus shows sequence similarity to family B DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2711–2716. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzagalli A., Valsasnini P., Plevani P., Lucchini G. DNA polymerase I gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence, mapping of a temperature-sensitive mutation, and protein homology with other DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3772–3776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Hess W. R. Increased deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity in African swine fever virus-infected culture cells. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;38(4):383–385. doi: 10.1007/BF01262828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. M., Salas M. L., Viñuela E. Genes homologous to ubiquitin-conjugating proteins and eukaryotic transcription factor SII in African swine fever virus. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):40–52. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M. L., Kuznar J., Viñuela E. Polyadenylation, methylation, and capping of the RNA synthesized in vitro by African swine fever virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanos A., Sedgwick S. G., Yarranton G. T., Hübscher U., Banks G. R. Detection of the catalytic activities of DNA polymerases and their associated exonucleases following SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1825–1839. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Rush J., Fung C., Reha-Krantz L. J., Karam J. D., Konigsberg W. H. Primary structure of T4 DNA polymerase. Evolutionary relatedness to eucaryotic and other procaryotic DNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7478–7486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Mileham A. J., Romanos M. A., Boyd A. Nucleotide sequence and transcription analysis of a linear DNA plasmid associated with the killer character of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6011–6030. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomalski M. D., Wu J. G., Miller L. K. The location, sequence, transcription, and regulation of a baculovirus DNA polymerase gene. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):591–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommasino M., Ricci S., Galeotti C. L. Genome organization of the killer plasmid pGK12 from Kluyveromyces lactis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5863–5878. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Wahl A. F., Yuan P. M., Arai N., Pearson B. E., Arai K., Korn D., Hunkapiller M. W., Wang T. S. Human DNA polymerase alpha gene expression is cell proliferation dependent and its primary structure is similar to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic replicative DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):37–47. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Ito J. Nucleotide sequence of the major early region of bacteriophage phi 29. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Chung D. W., Tan C. K., Downey K. M., Davie E. W., So A. G. Primary structure of the catalytic subunit of calf thymus DNA polymerase delta: sequence similarities with other DNA polymerases. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 24;30(51):11742–11750. doi: 10.1021/bi00115a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]