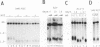Abstract
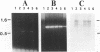
The ribonucleoprotein enzyme telomerase is a specialized type of cellular reverse transcriptase which synthesizes one strand of telomeric DNA, using as the template a sequence in the RNA moiety of telomerase. We analyzed the effects of various nucleoside analogs, known to be chain-terminating inhibitors of retroviral reverse transcriptases, on Tetrahymena thermophila telomerase activity in vitro. We also analyzed the effects of such analogs on telomere length and maintenance in vivo, and on vegetative growth and mating of Tetrahymena cells. Arabinofuranyl-guanosine triphosphate (Ara-GTP) and ddGTP both efficiently inhibited telomerase activity in vitro, while azidothymidine triphosphate (AZT-TP), dideoxyinosine triphosphate (ddITP) or ddTTP were less efficient inhibitors. All of these nucleoside triphosphate analogs, however, produced analog-specific alterations of the normal banding patterns seen upon gel electrophoresis of the synthesis products of telomerase, suggesting that their chain terminating and/or competitive actions differ at different positions along the RNA template. The analogs AZT, 3'-deoxy-2',3'-didehydrothymidine (d4T) and Ara-G in nucleoside form caused consistent and rapid telomere shortening in vegetatively growing Tetrahymena. In contrast, ddG or ddI had no effect on telomere length or cell growth rates. AZT caused growth rates and viability to decrease in a fraction of cells, while Ara-G had no such effects even after several weeks in culture. Neither AZT, Ara-G, acycloguanosine (Acyclo-G), ddG nor ddI had any detectable effect on cell mating, as assayed by quantitation of the efficiency of formation of progeny from mated cells. However, AZT decreased the efficiency of programmed de novo telomere addition during macronuclear development in mating cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsopp R. C., Vaziri H., Patterson C., Goldstein S., Younglai E. V., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W., Harley C. B. Telomere length predicts replicative capacity of human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10114–10118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Greider C. W., Henderson E., Lee M. S., Shampay J., Shippen-Lentz D. Recognition and elongation of telomeres by telomerase. Genome. 1989;31(2):553–560. doi: 10.1139/g89-104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:113–129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres and their synthesis. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):489–490. doi: 10.1126/science.2200120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challoner P. B., Blackburn E. H. Conservation of sequences adjacent to the telomeric C4A2 repeats of ciliate macronuclear ribosomal RNA gene molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6299–6311. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C. M., Avilion A. A., LeFeuvre C. E., Stewart N. G., Greider C. W., Harley C. B., Bacchetti S. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1921–1929. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapler G. M., Blackburn E. H. A weak germ-line excision mutation blocks developmentally controlled amplification of the rDNA minichromosome of Tetrahymena thermophila. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):84–95. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapler G. M. Developmentally regulated processing and replication of the Tetrahymena rDNA minichromosome. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Oct;3(5):730–735. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King B. O., Yao M. C. Tandemly repeated hexanucleotide at Tetrahymena rDNA free end is generated from a single copy during development. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. D., Spangler E. A., Blackburn E. H. Dynamics of telomere length variation in Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90501-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Blackburn E. H. Sequence-specific DNA primer effects on telomerase polymerization activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6586–6599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Blackburn E. H. An alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues est1- senescence. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90234-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Szostak J. W. A mutant with a defect in telomere elongation leads to senescence in yeast. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan W. C., Blackburn E. H. Single extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA gene copies are synthesized during amplification of the rDNA in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. E., Miller W. H. Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Substrate and inhibitor kinetics with thymidine 5'-triphosphate and 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20302–20307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Blackburn E. H. Generation of telomere-length heterogeneity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):534–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shippen-Lentz D., Blackburn E. H. Functional evidence for an RNA template in telomerase. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):546–552. doi: 10.1126/science.1689074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Blackburn E. H. Developmentally programmed healing of chromosomes by telomerase in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):823–832. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90077-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Bradley J. D., Attardi L. D., Blackburn E. H. In vivo alteration of telomere sequences and senescence caused by mutated Tetrahymena telomerase RNAs. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):126–132. doi: 10.1038/344126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Prescott D. M. Telomere terminal transferase activity in the hypotrichous ciliate Oxytricha nova and a model for replication of the ends of linear DNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6953–6972. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]