Abstract
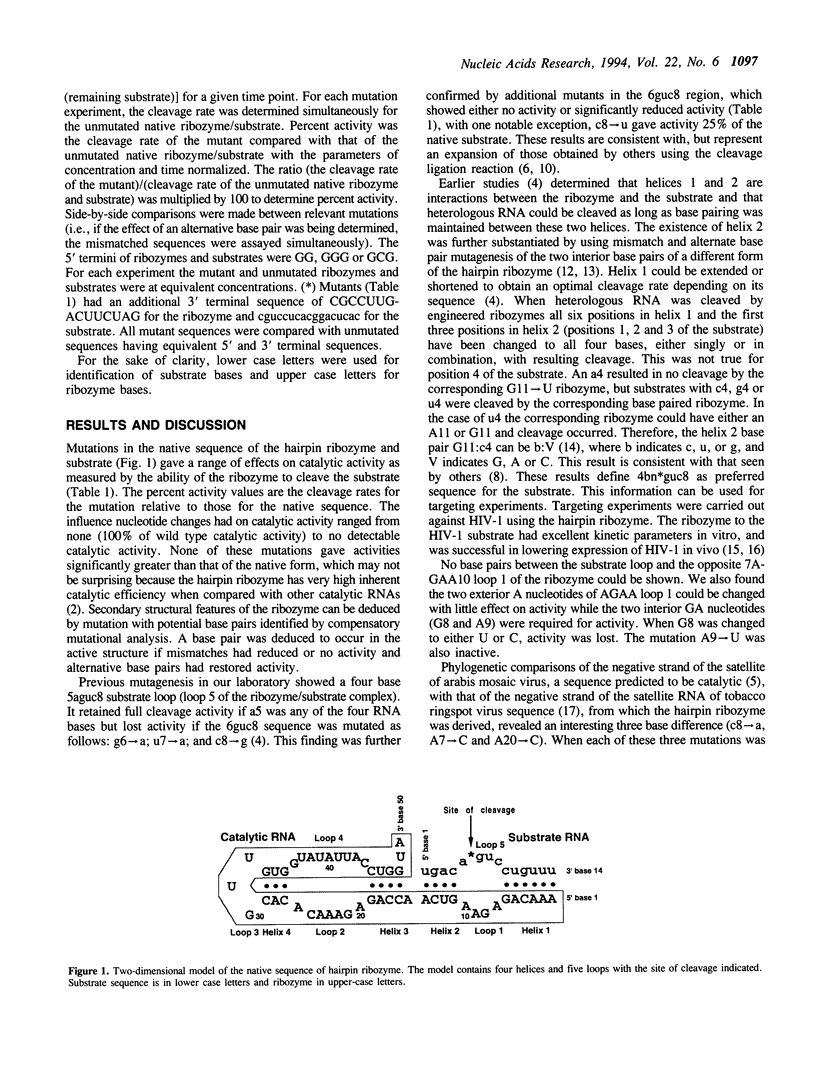
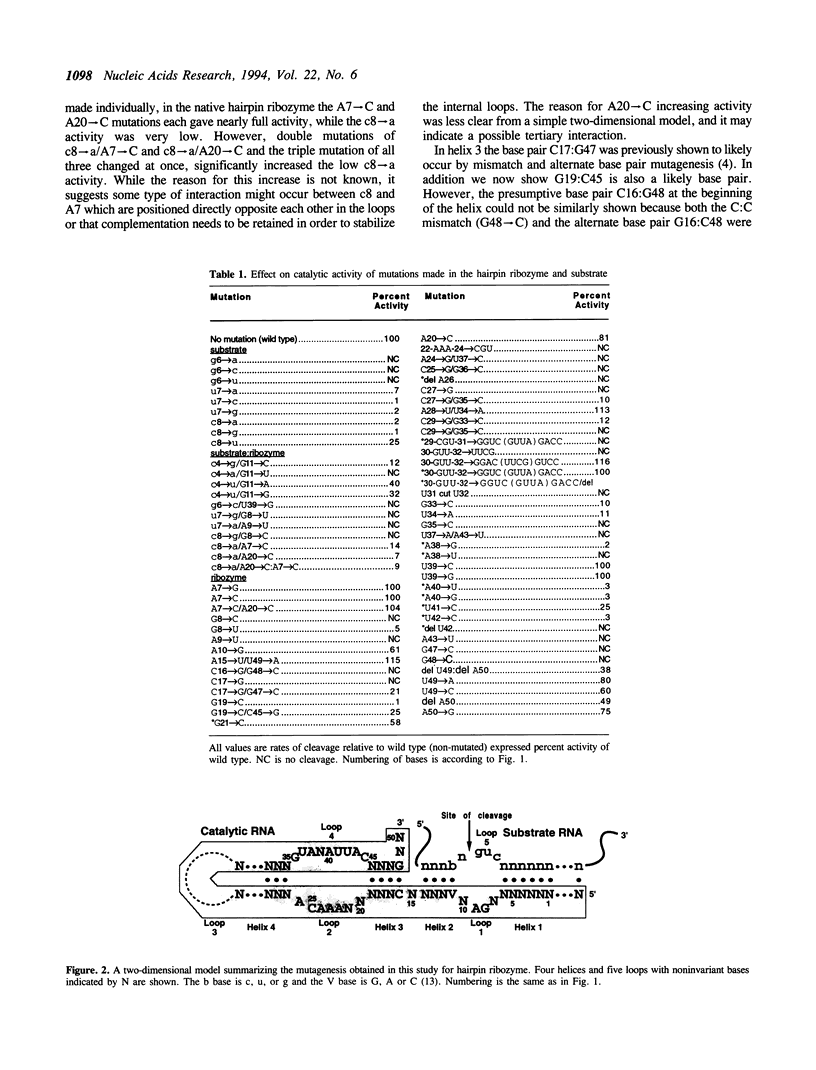
Extensive in vitro mutagenesis studies have been performed on the hairpin ribozyme and substrate in an effort to refine the overall secondary structure of the molecule and provide further insight into what elements are essential for activity. A secondary structure consisting of four helices and five loop regions remains the basic model as originally proposed. Two helices, helix 1 and 2, form between the substrate and ribozyme while helices 3 and 4 are within the ribozyme itself. Our results suggest that helices 3 and 4 are smaller than previously proposed, consisting of four base pairs and three base pairs respectively. Helix 4 can be extended without loss of activity and loop 3 at the closed end of the hairpin model can be varied in sequence with retention of activity. There is an unpaired nucleotide between helices 2 and 3 consisting of a single A base, suggesting the opportunity for flexibility within the tertiary structure at this point. Comparisons are made between the new data and previously published mutagenesis and phylogenetic data. Substrate targeting rules require base pairing between helices 1 and 2 with cleavage (*) occurring in a preferred 5'(g/c/u)n*guc3' sequence of the substrate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berzal-Herranz A., Joseph S., Burke J. M. In vitro selection of active hairpin ribozymes by sequential RNA-catalyzed cleavage and ligation reactions. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):129–134. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzal-Herranz A., Joseph S., Chowrira B. M., Butcher S. E., Burke J. M. Essential nucleotide sequences and secondary structure elements of the hairpin ribozyme. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2567–2573. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowrira B. M., Berzal-Herranz A., Burke J. M. Novel guanosine requirement for catalysis by the hairpin ribozyme. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):320–322. doi: 10.1038/354320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein P. A., Buzayan J. M., Bruening G. Two sequences participating in the autolytic processing of satellite tobacco ringspot virus complementary RNA. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein P. A., Buzayan J. M., van Tol H., deBear J., Gough G. R., Gilham P. T., Bruening G. Specific association between an endoribonucleolytic sequence from a satellite RNA and a substrate analogue containing a 2'-5' phosphodiester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel A., Tritz R., Hicks M., Cruz P. 'Hairpin' catalytic RNA model: evidence for helices and sequence requirement for substrate RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):299–304. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel A., Tritz R. RNA catalytic properties of the minimum (-)sTRSV sequence. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):4929–4933. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J., Gerlach W. L. Sequences required for self-catalysed cleavage of the satellite RNA of tobacco ringspot virus. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S., Berzal-Herranz A., Chowrira B. M., Butcher S. E., Burke J. M. Substrate selection rules for the hairpin ribozyme determined by in vitro selection, mutation, and analysis of mismatched substrates. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):130–138. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. M., Tousignant M. E., Steger G. Nucleotide sequence predicts circularity and self-cleavage of 300-ribonucleotide satellite of arabis mosaic virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):318–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90687-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojwang J. O., Hampel A., Looney D. J., Wong-Staal F., Rappaport J. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression by a hairpin ribozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10802–10806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubino L., Tousignant M. E., Steger G., Kaper J. M. Nucleotide sequence and structural analysis of two satellite RNAs associated with chicory yellow mottle virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Sep;71(Pt 9):1897–1903. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-9-1897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi A., Komatsu Y., Koizumi M., Ohtsuka E. Mutagenesis and self-ligation of the self-cleavage domain of the satellite RNA minus strand of tobacco ringspot virus and its binding to polyamines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6833–6838. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H., Buzayan J. M., Bruening G. Evidence for spontaneous circle formation in the replication of the satellite RNA of tobacco ringspot virus. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90005-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M., Ojwang J., Yamada O., Hampel A., Rapapport J., Looney D., Wong-Staal F. A hairpin ribozyme inhibits expression of diverse strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6340–6344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]