Abstract
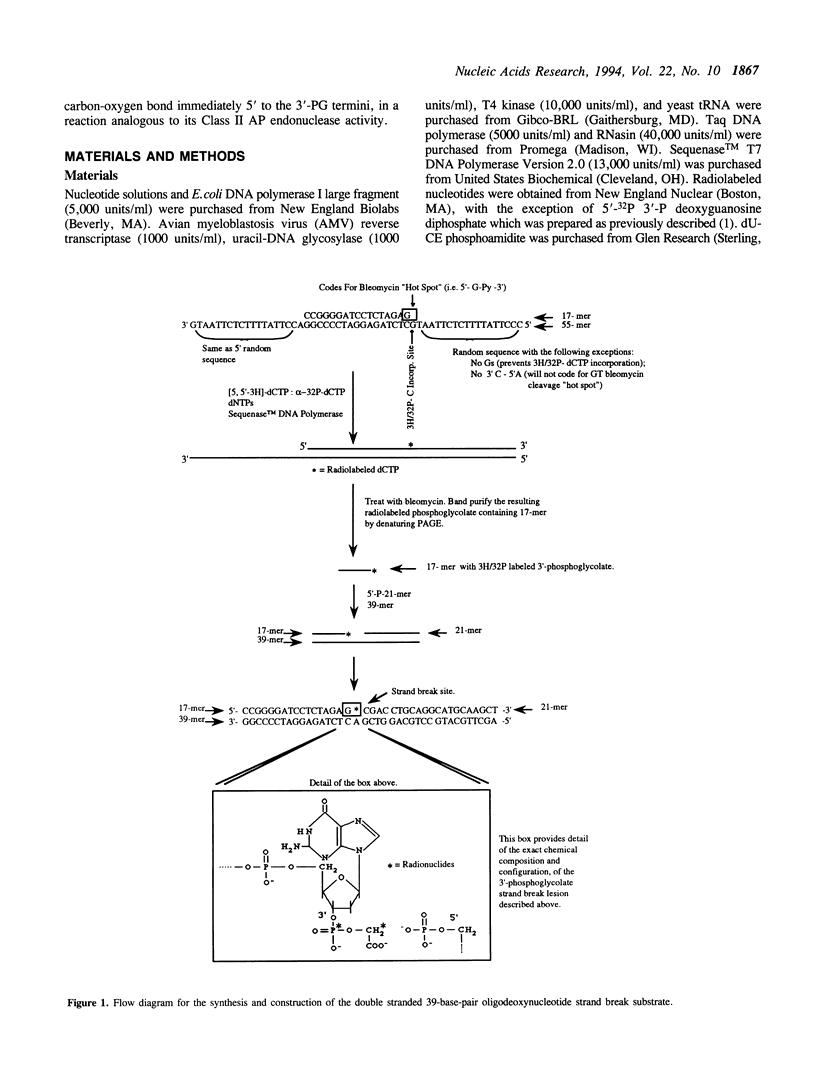
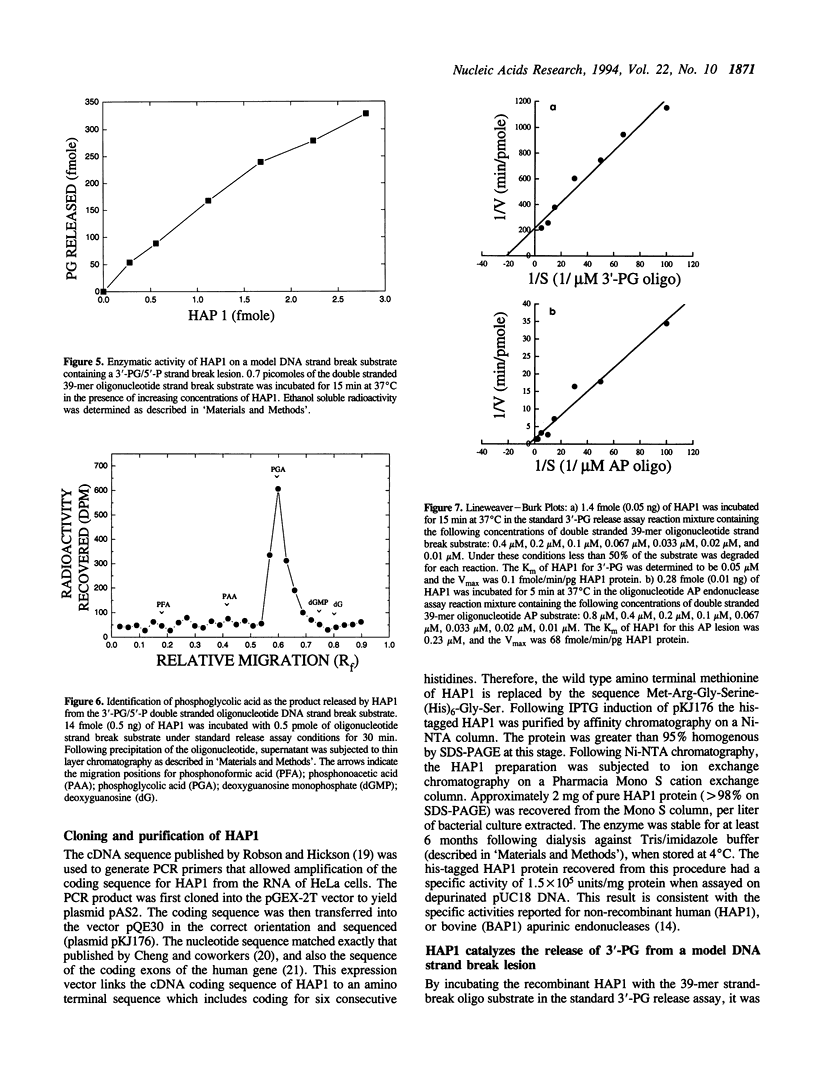
A recombinant human AP endonuclease, HAP1, was constructed and characterized with respect to its ability to recognize and act upon a model double-stranded 39-mer oligodeoxyribonucleotide substrate containing a strand break site with 3'-phosphoglycolate and 5'-phosphate end-group chemistries. This oligodeoxyribonucleotide substrate exactly duplicates the chemistry and configuration of a major DNA lesion produced by ionizing radiation. HAP1 was found to recognize the strand break, and catalyze the release of the 3'-phosphoglycolate as free phosphoglycolic acid. The enzyme had a Vmax of 0.1 fmole/min/pg of HAP1 protein, and a Km of 0.05 microM for the 3'-phosphoglycolate strand break lesion. The mechanism of catalysis was hydrolysis of the phosphate ester bond between the 3'-phosphoglycolate moiety and the 3'-carbon of the adjacent dGMP moiety within the oligonucleotide. The resulting DNA contained a 3'-hydroxyl which supported nucleotide incorporation by E. coli DNA polymerase I large fragment. AP endonucleolytic activity of HAP1 was examined using an analogous double-stranded 39-mer oligodeoxyribonucleotide substrate, in which the strand break site was replaced by an apyrimidinic site. The Vmax and Km for the AP endonuclease reaction were 68 fmole/min/pg of HAP1 protein and 0.23 microM, respectively.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. S., Herman T., Demple B. Two distinct human DNA diesterases that hydrolyze 3'-blocking deoxyribose fragments from oxidized DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5907–5914. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng X. B., Bunville J., Patterson T. A. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for an apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):370–370. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decuyper J., Piette J., Merville M. P., Van de Vorst A. Termini generated at the site of the DNA breakage mediated by photoexcited promazines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 15;35(8):1345–1350. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedon P. C., Jiang Z. W., Goldberg I. H. Neocarzinostatin-mediated DNA damage in a model AGT.ACT site: mechanistic studies of thiol-sensitive partitioning of C4' DNA damage products. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):1917–1927. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Herman T., Chen D. S. Cloning and expression of APE, the cDNA encoding the major human apurinic endonuclease: definition of a family of DNA repair enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11450–11454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizdaroglu M., Holwitt E., Hagan M. P., Blakely W. F. Formation of cytosine glycol and 5,6-dihydroxycytosine in deoxyribonucleic acid on treatment with osmium tetroxide. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):531–536. doi: 10.1042/bj2350531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner W. D., Kiker N. P., Jorgensen T. J., Munck J. N. Purification and amino-terminal amino acid sequence of an apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease from calf thymus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5529–5544. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner W. D., Rodriguez L. O., Hecht S. M., Haseltine W. A. gamma Ray induced deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks. 3' Glycolate termini. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):711–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kow Y. W., Faundez G., Melamede R. J., Wallace S. S. Processing of model single-strand breaks in phi X-174 RF transfecting DNA by Escherichia coli. Radiat Res. 1991 Jun;126(3):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. D., Demple B. Analysis of class II (hydrolytic) and class I (beta-lyase) apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases with a synthetic DNA substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5069–5075. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa O., Moses R. E. Synthesis by DNA polymerase I on bleomycin-treated deoxyribonucleic acid: a requirement for exonuclease III. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):238–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Austin M. J. Genotoxicity of bleomycin. Mutat Res. 1991 Mar;257(2):127–143. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(91)90022-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson C. N., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding a human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease that corrects DNA repair and mutagenesis defects in E. coli xth (exonuclease III) mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5519–5523. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson B. J., Chang C. N., Grollman A. P., Henner W. D. Mechanism of DNA cleavage and substrate recognition by a bovine apurinic endonuclease. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3894–3901. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanScoy M., Loghman-Adham M., Onsgard M., Szczepanska-Konkel M., Homma S., Knox F. G., Dousa T. P. Mechanism of phosphaturia elicited by administration of phosphonoformate in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 2):F984–F994. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.5.F984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinfeld M., Soderlind K. J. 32P-postlabeling detection of radiation-induced DNA damage: identification and estimation of thymine glycols and phosphoglycolate termini. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):1091–1097. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters T. A., Weinfeld M., Jorgensen T. J. Human HeLa cell enzymes that remove phosphoglycolate 3'-end groups from DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2573–2580. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B., Grandy D. K., Hagerup J. M., Magenis R. E., Smith L., Chauhan B. C., Henner W. D. The human gene for apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease (HAP1): sequence and localization to chromosome 14 band q12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4097–4098. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]