Abstract
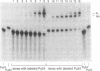
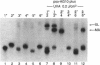
A polypurine tract in the supF gene of bacteriophage lambda (base pairs 167-176) was selected as the target for triple helix formation and targeted mutagenesis by an oligopurine (5'-AGGAAGGGGG-3') containing a chemically linked psoralen derivative (4'-hydroxymethyl-4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen) at its 5' terminus (psoAG10). The thymines at base pairs 166 and 167, a 5'ApT site, were targeted for photomodification. Exposure of the triple helical complex to long wavelength ultraviolet radiation led to the covalent binding of psoAG10 to the targeted region in the supF gene and to the induction of site-specific mutations. We report here experiments to characterize the photomodification of the targeted region of the supF gene in the context of triple helix formation. An electrophoretic mobility-shift assay showed that, at low radiation doses, monoadducts at base pair 166 were the major photoadducts. At higher doses the monoadducts were converted to crosslinks between base pairs 166 and 167. HPLC analysis of enzymatically hydrolyzed photoreaction mixtures was used to confirm the electrophoresis results. A strong strand preference for specific photoadduct formation was also detected.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan P., Miller P. S. Photo-cross-linking of psoralen-derivatized oligonucleoside methylphosphonates to single-stranded DNA. Bioconjug Chem. 1990 Jan-Feb;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1021/bc00001a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Gamper H. B., Isaacs S. T., Hearst J. E. Psoralens as photoactive probes of nucleic acid structure and function: organic chemistry, photochemistry, and biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1151–1193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Shi Y. B., Hearst J. E. Wavelength dependence for the photoreversal of a psoralen-DNA cross-link. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):3013–3020. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparro F. P., Edelson R. L., O'Malley M. E., Ugent S. J., Wong H. H. Photoactivatable antisense DNA: suppression of ampicillin resistance in normally resistant Escherichia coli. Antisense Res Dev. 1991 Summer;1(2):117–140. doi: 10.1089/ard.1991.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparro F. P., Gattolin P., Olack G. A., Deckelbaum L. I., Sumpio B. E. The excitation of 8-methoxypsoralen with visible light: reversed phase HPLC quantitation of monoadducts and cross-links. Photochem Photobiol. 1993 Jun;57(6):1007–1010. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1993.tb02963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparro F. P., Saffran W. A., Cantor C. R., Edelson R. L. Wavelength dependence for AMT crosslinking of pBR322 DNA. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Aug;40(2):215–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb04578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer P. M., Sarkar S. N., Summers W. C. Detection and analysis of UV-induced mutations in mammalian cell DNA using a lambda phage shuttle vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1041–1044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Guieysse A. L., Robin P., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. Inhibition of gene expression by triple helix-directed DNA cross-linking at specific sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3501–3505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havre P. A., Glazer P. M. Targeted mutagenesis of simian virus 40 DNA mediated by a triple helix-forming oligonucleotide. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7324–7331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7324-7331.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havre P. A., Gunther E. J., Gasparro F. P., Glazer P. M. Targeted mutagenesis of DNA using triple helix-forming oligonucleotides linked to psoralen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7879–7883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Montenay-Garestier T., Saison T., Takasugi M., Toulmé J. J., Asseline U., Lancelot G., Maurizot J. C., Toulmé F., Thuong N. T. Oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to intercalating agents: a new class of gene regulatory substances. Biochimie. 1985 Jul-Aug;67(7-8):777–783. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C. Sequence-selective recognition and cleavage of double-helical DNA. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1993 Feb;4(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(93)90028-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing N. H., Beekman J. M., Kessler D. J., Murphy M., Jayaraman K., Zendegui J. G., Hogan M. E., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. In vivo transcription of a progesterone-responsive gene is specifically inhibited by a triplex-forming oligonucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2789–2796. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetter M. C., Hobbs F. W. 7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoadenine as a replacement for cytosine in the third strand of triple helices. Triplex formation without hypochromicity. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3249–3254. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. L., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Lin S. B., Miller P. S. Interaction of psoralen-derivatized oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates with single-stranded DNA. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3197–3203. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. J. Kinetic analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation on DNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8820–8826. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olack G., Gattolin P., Gasparro F. P. Improved high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of 8-methoxypsoralen monoadducts and cross-links in polynucleotide, DNA, and cellular systems: analysis of split-dose protocols. Photochem Photobiol. 1993 Jun;57(6):941–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1993.tb02953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Evidence that a triplex-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotide binds to the c-myc promoter in HeLa cells, thereby reducing c-myc mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. Inhibition of gene transcription by purine rich triplex forming oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2845–2852. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage E., Moustacchi E. Sequence context effects on 8-methoxypsoralen photobinding to defined DNA fragments. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3307–3314. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Hearst J. E. Wavelength dependence for the photoreactions of DNA-psoralen monoadducts. 2. Photo-cross-linking of monoadducts. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):3792–3798. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stilz H. U., Dervan P. B. Specific recognition of CG base pairs by 2-deoxynebularine within the purine.purine.pyrimidine triple-helix motif. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 9;32(9):2177–2185. doi: 10.1021/bi00060a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Doucette-Stamm L. A., Riba L., Housman D. E., Dervan P. B. Site-specific cleavage of human chromosome 4 mediated by triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1639–1642. doi: 10.1126/science.1836279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Guendouz A., Chassignol M., Decout J. L., Lhomme J., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific photo-induced cross-linking of the two strands of double-helical DNA by a psoralen covalently linked to a triple helix-forming oligonucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5602–5606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman J. W., Isaacs S. T., Hearst J. E. Photochemistry of the furan-side 8-methoxypsoralen-thymidine monoadduct inside the DNA helix. Conversion to diadduct and to pyrone-side monoadduct. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 26;24(7):1669–1676. doi: 10.1021/bi00328a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]