Abstract
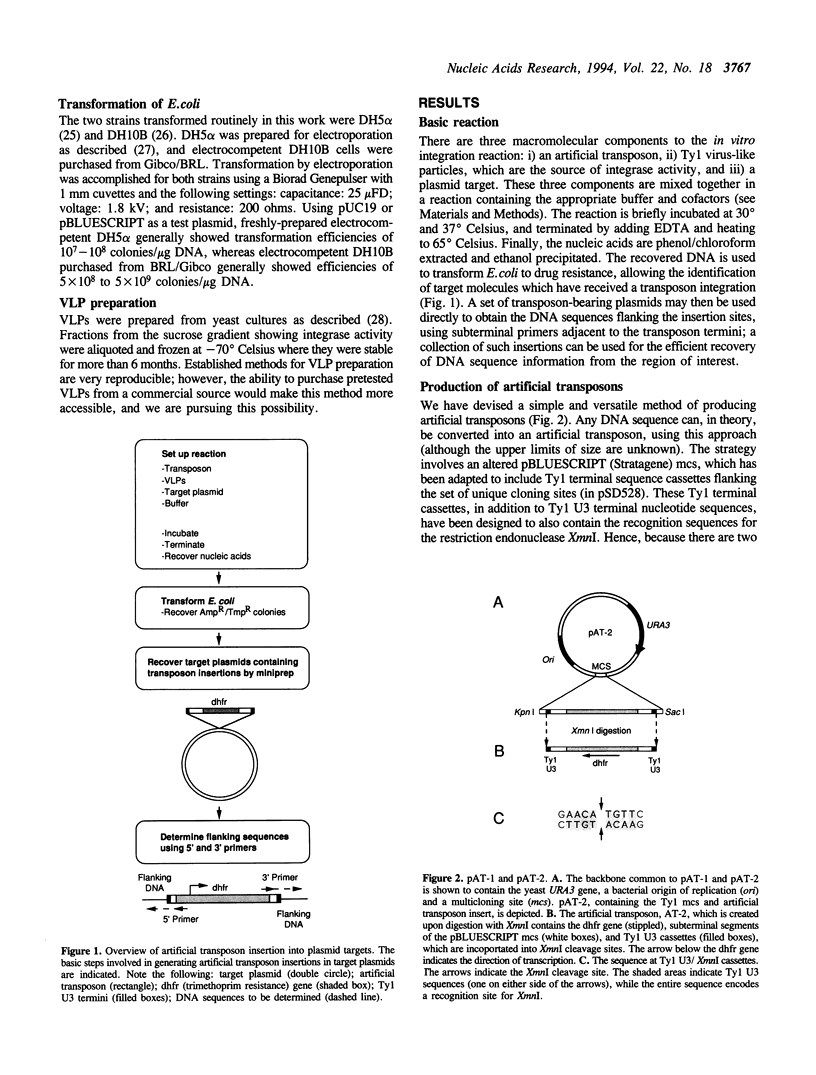
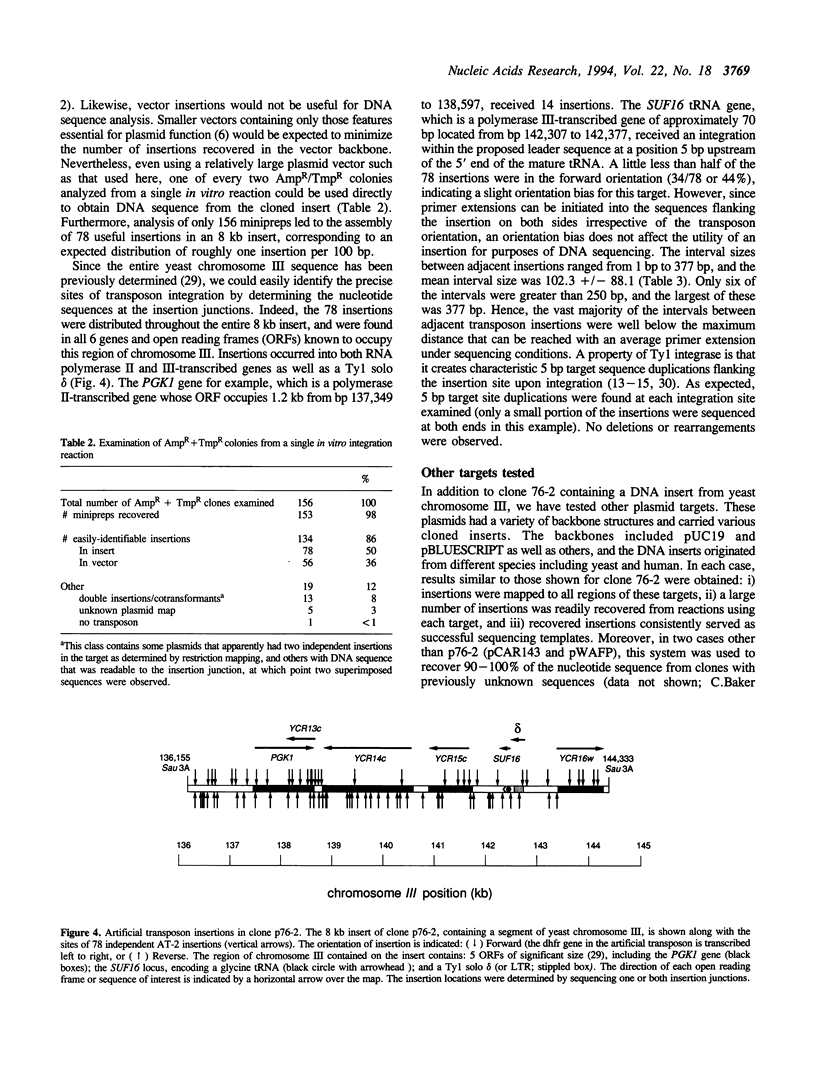
We have developed efficient methods for creating artificial transposons and inserting these transposons into plasmid targets in vitro, primarily for the purpose of DNA mapping and sequencing. A novel plasmid has been engineered to convert virtually any DNA sequence, or combination of sequences, into an artificial transposon; hence, custom transposons containing any desired feature can be easily designed and constructed. Such transposons are then efficiently inserted into plasmid targets, in vitro, using the integrase activity present in yeast Ty1 virus-like particles. A single in vitro integration reaction, which resembles a simple restriction digestion in the complexity of the reaction, gives rise to thousands of recoverable insertion events within DNA target molecules; this frequency approaches one insertion per phosphodiester bond in typical plasmids. Importantly, transposon insertions are recovered from all regions of DNA inserts carried on plasmid targets, indicating that integration is a random or nearly-random process. Because of its versatility, this technology offers a generalized method of generating recombinant DNA molecules of a desired structure. We have adapted this system for DNA sequencing by developing a customized artificial transposon to insert new primer binding sites into internal regions of DNA inserts carried on cloning vectors. Transposon insertions have been generated throughout several different yeast and human DNA inserts carried on plasmids, allowing the efficient recovery of sequence information from these inserts. Our results demonstrate the overall utility of this method for both small and large-scale DNA sequencing, as well as general DNA restructuring, and indicate that it could be adapted for use with a number of additional applications including functional genetic analysis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Mizuuchi M., Robinson E. A., Appella E., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M., Mizuuchi K. DNA sequence of the E. coli gyrB gene: application of a new sequencing strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):771–784. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed A. A rapid procedure for DNA sequencing using transposon-promoted deletions in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;39(2-3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton R. J., Kubo K. M., Feng J. N., Craig N. L. Tn7 transposition: target DNA recognition is mediated by multiple Tn7-encoded proteins in a purified in vitro system. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):931–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90581-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. PCR amplification of up to 35-kb DNA with high fidelity and high yield from lambda bacteriophage templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2216–2220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiterman L. T., Monokian G. M., Eichinger D. J., Merbs S. L., Gabriel A., Boeke J. D. In-frame linker insertion mutagenesis of yeast transposon Ty1: phenotypic analysis. Gene. 1994 Feb 11;139(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90518-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1339–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin N. M., Hanawalt P. C. High-efficiency transformation of bacterial cells by electroporation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2796–2801. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2796-2801.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger D. J., Boeke J. D. A specific terminal structure is required for Ty1 transposition. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):324–330. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger D. J., Boeke J. D. The DNA intermediate in yeast Ty1 element transposition copurifies with virus-like particles: cell-free Ty1 transposition. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):955–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Rossi J. J., Wallace R. B. Synthesis and use of synthetic oligonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:323–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji H., Moore D. P., Blomberg M. A., Braiterman L. T., Voytas D. F., Natsoulis G., Boeke J. D. Hotspots for unselected Ty1 transposition events on yeast chromosome III are near tRNA genes and LTR sequences. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Bender J., Gottesman S. Uses of transposons with emphasis on Tn10. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:139–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04009-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Butler D., Kleckner N. Efficient Tn10 transposition into a DNA insertion hot spot in vivo requires the 5-methyl groups of symmetrically disposed thymines within the hot-spot consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7876–7880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. P., Garfinkel D. J. Expression and partial purification of enzymatically active recombinant Ty1 integrase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., van der Aart Q. J., Agostoni-Carbone M. L., Aigle M., Alberghina L., Alexandraki D., Antoine G., Anwar R., Ballesta J. P., Benit P. The complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome III. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):38–46. doi: 10.1038/357038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phadnis S. H., Huang H. V., Berg D. E. Tn5supF, a 264-base-pair transposon derived from Tn5 for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing DNAs cloned in phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5908–5912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Boeke J. D. In vitro mutagenesis and plasmid shuffling: from cloned gene to mutant yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:302–318. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M. The future of DNA sequencing. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):530–532. doi: 10.1126/science.8211178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Hamilton B. A., Mayeda C. A., Simon M. I., Meyerowitz E. M., Palazzolo M. J. Transposon-facilitated DNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1247–1250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


