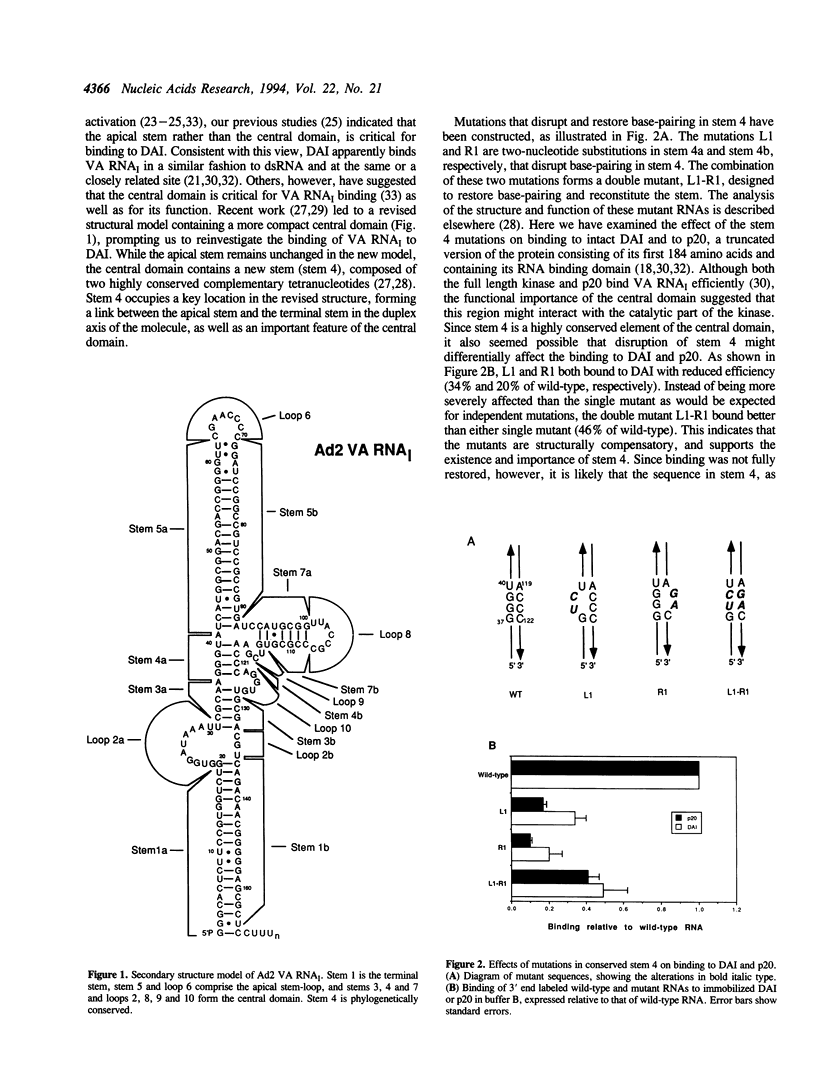
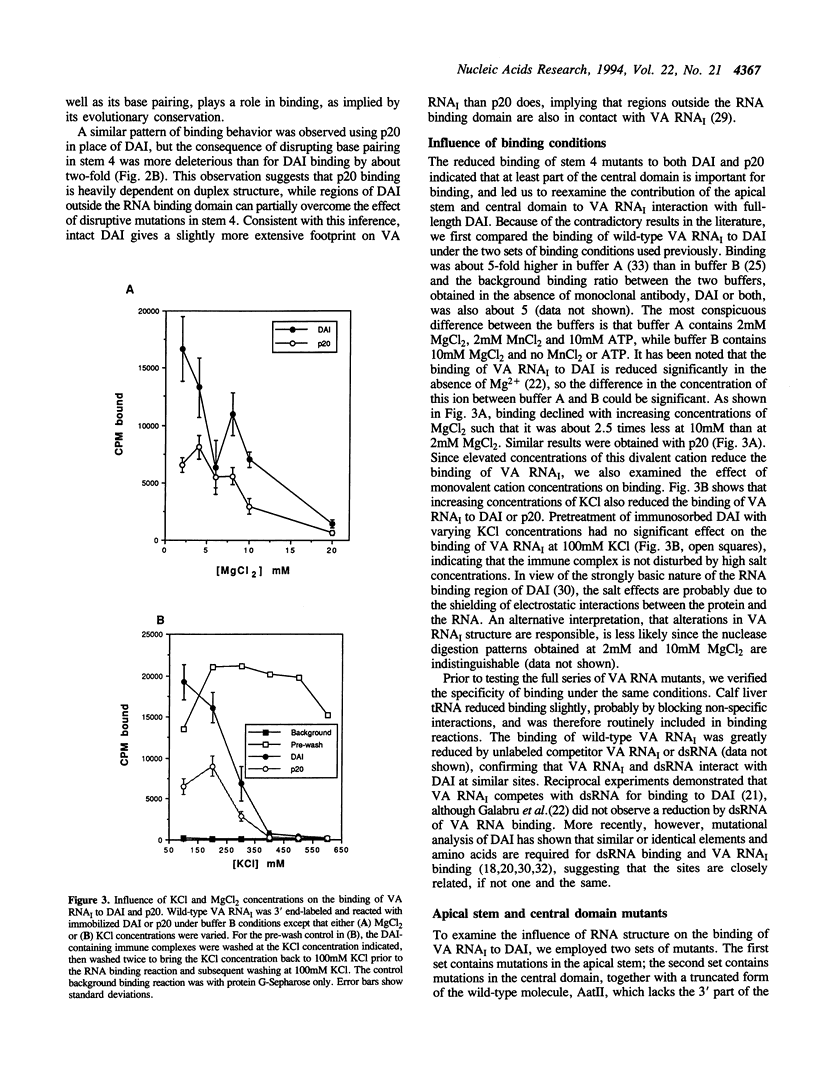
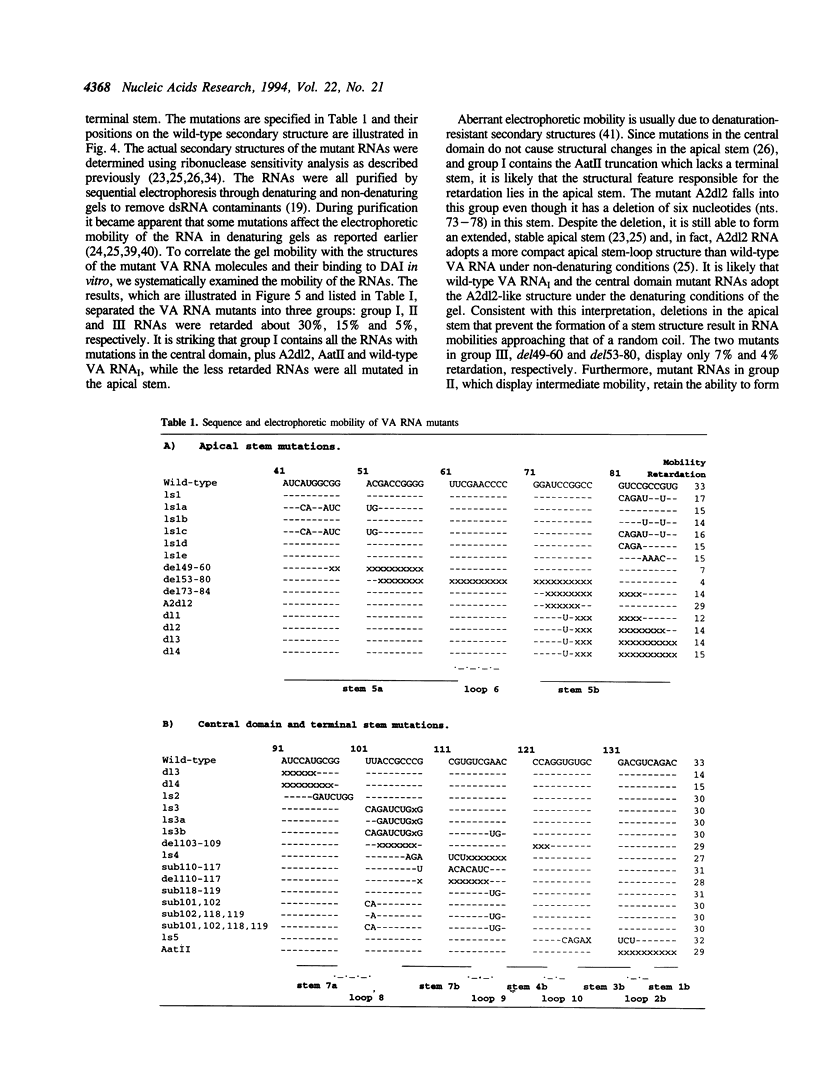
Abstract
The double-stranded RNA activated protein kinase DAI contains an RNA binding domain consisting of two copies of a double-stranded RNA binding motif. We have investigated the role of RNA structure in the interaction between DAI and the structured single-stranded RNA, adenovirus VA RNAI, which inhibits DAI activation. Mutations in the apical stem, terminal stem, and central domain of the RNA were tested to assess the contribution of these elements to DAI binding in vitro. The data demonstrate that over half a turn of intact apical stem is required for the interaction and that there is a correlation between the binding of apical stem mutants and their ability to function both in vivo and in vitro. There was also evidence of preference for GC-rich sequence in the proximal region of the apical stem. In the central domain the correlation between binding and function of mutant RNAs was poor, suggesting that at least some of this region plays no direct role in binding to DAI, despite its functional importance. Exceptionally, central domain mutations that encroached on the phylogenetically conserved stem 4 of VA RNA disrupted binding, and complementary mutations in this sequence partially restored binding. Measurement of the binding of wild-type VA RNAI to DAI and p20, a truncated form of the protein containing the RNA binding domains alone, under various ionic conditions imply that the major interactions are electrostatic and occur via the protein's RNA binding domain. However, differences between full-length DAI and p20 in their binding to mutants in the conserved stem suggest that regions outside the RNA binding domain also participate in the binding. The additional interactions are likely to be non-ionic, and may be important for preventing DAI activation during virus infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhat R. A., Thimmappaya B. Construction and analysis of additional adenovirus substitution mutants confirm the complementation of VAI RNA function by two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.750-756.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furtado M. R., Subramanian S., Bhat R. A., Fowlkes D. M., Safer B., Thimmappaya B. Functional dissection of adenovirus VAI RNA. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3423–3434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3423-3434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Katze M. G., Robert N., Hovanessian A. G. The binding of double-stranded RNA and adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):581–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatignol A., Buckler C., Jeang K. T. Relatedness of an RNA-binding motif in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR RNA-binding protein TRBP to human P1/dsI kinase and Drosophila staufen. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2193–2202. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadge G. D., Malhotra P., Furtado M. R., Dhar R., Thimmapaya B. In vitro analysis of virus-associated RNA I (VAI RNA): inhibition of the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase PKR by VAI RNA mutants correlates with the in vivo phenotype and the structural integrity of the central domain. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4137–4151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4137-4151.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadge G. D., Swaminathan S., Katze M. G., Thimmapaya B. Binding of the adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced 68-kDa protein kinase correlates with function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7140–7144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. R., Mathews M. B. Two RNA-binding motifs in the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, DAI. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2478–2490. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegg L. A., Thurlow D. L. Residual tRNA secondary structure in 'denaturing' 8M urea/TBE polyacrylamide gels: effects on electrophoretic mobility and dependency on prior chemical modification of the tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2993–3000. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Protein phosphorylation controls translation rates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20823–20826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., DeCorato D., Safer B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Adenovirus VAI RNA complexes with the 68 000 Mr protein kinase to regulate its autophosphorylation and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):689–697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Wambach M., Wong M. L., Garfinkel M., Meurs E., Chong K., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G., Barber G. N. Functional expression and RNA binding analysis of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated, 68,000-Mr protein kinase in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5497–5505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Purification and activation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2 kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1576–1586. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer F. R., Mills D. R. RNA sequencing with radioactive chain-terminating ribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5334–5338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent A. G., Krust B., Galabru J., Svab J., Hovanessian A. G. Monoclonal antibodies to an interferon-induced Mr 68,000 protein and their use for the detection of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., deHaseth P. L., Record M. T., Jr Pentalysine-deoxyribonucleic acid interactions: a model for the general effects of ion concentrations on the interactions of proteins with nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3522–3530. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y., Mathews M. B. Comparative analysis of the structure and function of adenovirus virus-associated RNAs. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6605–6617. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6605-6617.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manche L., Green S. R., Schmedt C., Mathews M. B. Interactions between double-stranded RNA regulators and the protein kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5238–5248. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maran A., Mathews M. B. Characterization of the double-stranded RNA implicated in the inhibition of protein synthesis in cells infected with a mutant adenovirus defective for VA RNA. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack S. J., Thomis D. C., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: identification of a RNA binding domain within the N-terminal region of the human RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Interaction of adenovirus VA RNAl with the protein kinase DAI: nonequivalence of binding and function. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):843–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90194-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Mathews M. B. Effects of mutations in stem and loop regions on the structure and function of adenovirus VA RNAI. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2849–2859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Pe'ery T., Manche L., Robertson H. D., Mathews M. B. Removal of double-stranded contaminants from RNA transcripts: synthesis of adenovirus VA RNAI from a T7 vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5401–5406. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Pe'ery T., Mathews M. B. Role of the apical stem in maintaining the structure and function of adenovirus virus-associated RNA. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2369–2377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2369-2377.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E., Chong K., Galabru J., Thomas N. S., Kerr I. M., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90374-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minks M. A., West D. K., Benvin S., Baglioni C. Structural requirements of double-stranded RNA for the activation of 2',5'-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10180–10183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K. Eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1109–1149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W., Mathews M. B. Modification of protein synthesis initiation factors and the shut-off of host protein synthesis in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pe'ery T., Mellits K. H., Mathews M. B. Mutational analysis of the central domain of adenovirus virus-associated RNA mandates a revision of the proposed secondary structure. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3534–3543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3534-3543.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Lohman M. L., De Haseth P. Ion effects on ligand-nucleic acid interactions. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 25;107(2):145–158. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohan R. M., Ketner G. A comprehensive collection of point mutations in the internal promoter of the adenoviral VAI gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8500–8507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mariano T. M., Reichel P. A., Mathews M. B. Translational control by adenovirus: lack of virus-associated RNAI during adenovirus infection results in phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2 and inhibition of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Brown N. H., Gall J. G., Jantsch M. A conserved double-stranded RNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10979–10983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]