Abstract
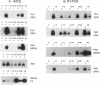
During macromolecular development in the ciliated protozoan, Euplotes crassus, > 105 Tec elements are precisely eliminated from the genome in a 2-4 h time interval, generating extrachromosomal circular forms of the elements. Various models have proposed a transposition-based mechanism for this excision. We have tested this hypothesis by determining the abundance of transcripts of Tec element open reading frames (ORFs) and the timing of their appearance. Transcripts are very low in abundance and are only detected by PCR amplification techniques. Thus, the low levels of transcripts argue against the participation of element-encoded functions in the Tec element elimination process. The element transcripts are only detected in RNA samples from mated cells, indicating that the micronucleus and/or developing macronucleus are transcriptionally active during the sexual phase of the life cycle. The transcription detected could allow a low level of germline-specific transposition for these elements.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allis C. D., Wiggins J. C. Histone rearrangements accompany nuclear differentiation and dedifferentiation in Tetrahymena. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):282–294. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird S. E., Fino G. M., Tausta S. L., Klobutcher L. A. Micronuclear genome organization in Euplotes crassus: a transposonlike element is removed during macronuclear development. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3793–3807. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Kleckner N. Intramolecular transposition by Tn10. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Egner C., Lowe J. B. Mechanism of F factor-enhanced excision of transposon Tn5. Gene. 1983 Apr;22(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicoine L. G., Wenkert D., Richman R., Wiggins J. C., Allis C. D. Modulation of linker histones during development in Tetrahymena: selective elimination of linker histone during the differentiation of new macronuclei. Dev Biol. 1985 May;109(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Volckaert G., Nevers P. Precise and nearly-precise excision of the symmetrical inverted repeats of Tn5; common features of recA-independent deletion events in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doak T. G., Doerder F. P., Jahn C. L., Herrick G. A proposed superfamily of transposase genes: transposon-like elements in ciliated protozoa and a common "D35E" motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):942–946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egner C., Berg D. E. Excision of transposon Tn5 is dependent on the inverted repeats but not on the transposase function of Tn5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley K. P., Leonard M. W., Engel J. D. Quantitation of RNA using the polymerase chain reaction. Trends Genet. 1993 Nov;9(11):380–385. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Lundblad V., Hanley-Way S., Halling S. M., Kleckner N. Three Tn10-associated excision events: relationship to transposition and role of direct and inverted repeats. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fusswinkel H., Schein S., Courage U., Starlinger P., Kunze R. Detection and abundance of mRNA and protein encoded by transposable element activator (Ac) in maize. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Feb;225(2):186–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00269846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Jaraczewski J. W., Klobutcher L. A., Jahn C. L. Characterization of transcription initiation, translation initiation, and poly(A) addition sites in the gene-sized macronuclear DNA molecules of Euplotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jan 25;22(2):214–221. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordenin D. A., Lobachev K. S., Degtyareva N. P., Malkova A. L., Perkins E., Resnick M. A. Inverted DNA repeats: a source of eukaryotic genomic instability. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5315–5322. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordenin D. A., Malkova A. L., Peterzen A., Kulikov V. N., Pavlov Y. I., Perkins E., Resnick M. A. Transposon Tn5 excision in yeast: influence of DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon and repair genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3785–3789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
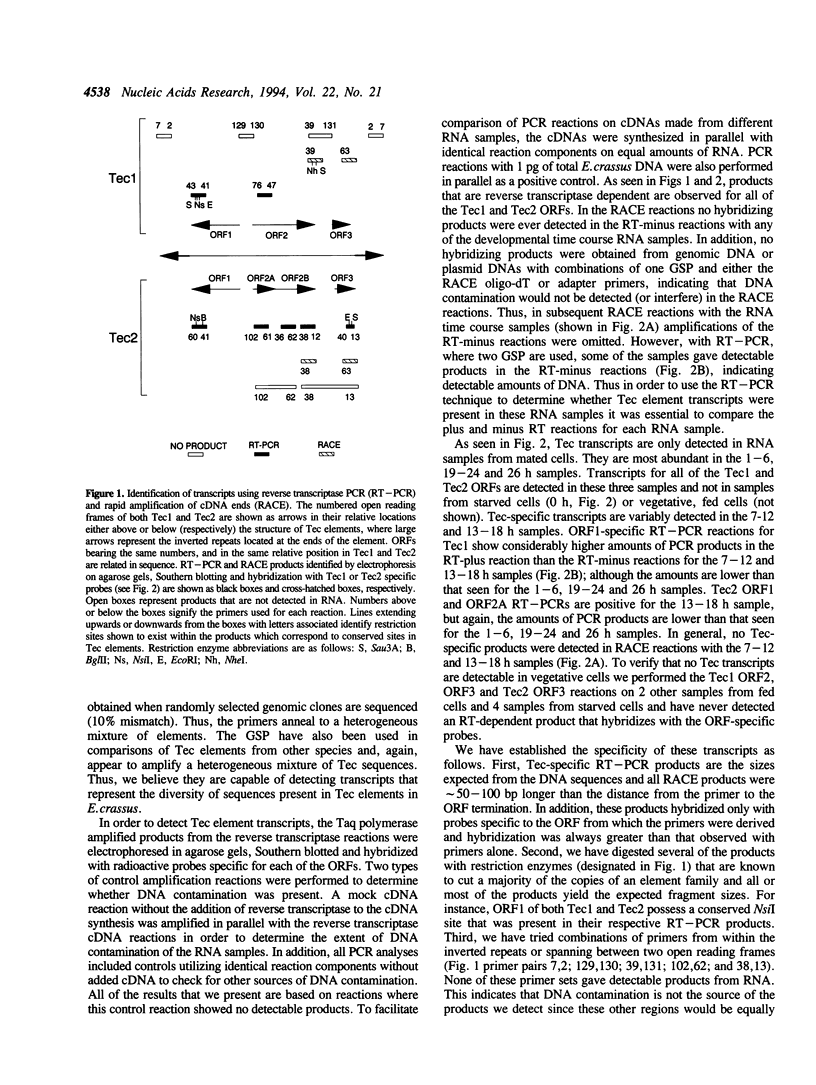
- Jahn C. L., Doktor S. Z., Frels J. S., Jaraczewski J. W., Krikau M. F. Structures of the Euplotes crassus Tec1 and Tec2 elements: identification of putative transposase coding regions. Gene. 1993 Oct 29;133(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90226-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L., Krikau M. F., Shyman S. Developmentally coordinated en masse excision of a highly repetitive element in E. crassus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L., Nilles L. A., Krikau M. F. Organization of the Euplotes crassus micronuclear genome. J Protozool. 1988 Nov;35(4):590–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1988.tb04157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L. The nuclear genomes of hypotrichous ciliates: maintaining the maximum and the minimum of information. J Protozool. 1991 May-Jun;38(3):252–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1991.tb04438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
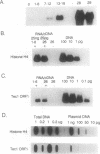
- Jaraczewski J. W., Jahn C. L. Elimination of Tec elements involves a novel excision process. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):95–105. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Jahn C. L. Developmentally controlled genomic rearrangements in ciliated protozoa. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Oct;1(3):397–403. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80306-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Turner L. R., LaPlante J. Circular forms of developmentally excised DNA in Euplotes crassus have a heteroduplex junction. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):84–94. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikau M. F., Jahn C. L. Tec2, a second transposon-like element demonstrating developmentally programmed excision in Euplotes crassus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4751–4759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Rio D. C., Rubin G. M. Tissue specificity of Drosophila P element transposition is regulated at the level of mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):7–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Kleckner N. Mismatch repair mutations of Escherichia coli K12 enhance transposon excision. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):3–19. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Taylor A. F., Smith G. R., Kleckner N. Unusual alleles of recB and recC stimulate excision of inverted repeat transposons Tn10 and Tn5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):824–828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martindale D. W., Allis C. D., Bruns P. J. RNA and protein synthesis during meiotic prophase in Tetrahymena thermophila. J Protozool. 1985 Nov;32(4):644–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K. Transpositional recombination: mechanistic insights from studies of mu and other elements. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1011–1051. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monstein H. J., Geijer T., Bakalkin G. Y. BLOTTO-MF, an inexpensive and reliable hybridization solution in northern blot analysis using complementary RNA probes. Biotechniques. 1992 Dec;13(6):842–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Kleckner N. Tn10 transposition and circle formation in vitro. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Kleckner N. Transposase promotes double strand breaks and single strand joints at Tn10 termini in vivo. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polard P., Prère M. F., Fayet O., Chandler M. Transposase-induced excision and circularization of the bacterial insertion sequence IS911. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5079–5090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Adams A. K., Vermeesch J. R. Accumulation of telomerase RNA and telomere protein transcripts during telomere synthesis in Euplotes. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1994 May-Jun;41(3):267–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1994.tb01507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Kleckner N. Quantitation of insertion sequence IS10 transposase gene expression by a method generally applicable to any rarely expressed gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1787–1791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Wang A., Mark D., Werb Z. Novel method for studying mRNA phenotypes in single or small numbers of cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jan;39(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. M., Snutch T. P. Isolation of the closed circular form of the transposable element Tc1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):485–486. doi: 10.1038/311485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Lin M., Prescott D. M. Large scale synchronous mating and the study of macronuclear development in Euplotes crassus. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):79–84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan K., Emmons S. W. Extrachromosomal copies of transposon Tc1 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4018–4022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stargell L. A., Bowen J., Dadd C. A., Dedon P. C., Davis M., Cook R. G., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Temporal and spatial association of histone H2A variant hv1 with transcriptionally competent chromatin during nuclear development in Tetrahymena thermophila. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2641–2651. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stargell L. A., Gorovsky M. A. TATA-binding protein and nuclear differentiation in Tetrahymena thermophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):723–734. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugai T., Hiwatashi K. Cytologic and autoradiographic studies of the micronucleus at meiotic prophase in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Protozool. 1974 Oct;21(4):542–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan V., Freeling M. An extrachromosomal form of the Mu transposons of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4924–4928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tausta S. L., Klobutcher L. A. Detection of circular forms of eliminated DNA during macronuclear development in E. crassus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tausta S. L., Turner L. R., Buckley L. K., Klobutcher L. A. High fidelity developmental excision of Tec1 transposons and internal eliminated sequences in Euplotes crassus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3229–3236. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenkert D., Allis C. D. Timing of the appearance of macronuclear-specific histone variant hv1 and gene expression in developing new macronuclei of Tetrahymena thermophila. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2107–2117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K., Doak T. G., Herrick G. Developmental precise excision of Oxytricha trifallax telomere-bearing elements and formation of circles closed by a copy of the flanking target duplication. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4593–4601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]