Abstract
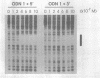
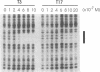
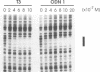
The binding of guanosine/thymidine-rich oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing various deletions, extensions, and point mutations to polypurine DNA targets was investigated by DNase I footprinting. Intermolecular purine-purine-pyrimidine triple-helical DNA formation was best achieved using oligonucleotides 12 nucleotides in length. Longer oligonucleotides were slightly weaker in binding affinity, whereas shorter oligonucleotides were considerably weaker. Oligonucleotide extensions had a slight effect on triplex formation, while single point mutations located near the oligonucleotide ends had a greater effect. In the cases of extensions and point mutations, changes to the 3' end of the oligonucleotide had a consistently greater effect on triplex formation than changes to the 5' end. Such differences in triplex-forming ability were not caused by an intrinsic property of these oligonucleotides, since the same point mutated oligonucleotides could bind with high affinity to duplex DNAs containing complementary sites. Taken together, our data suggest that there may be an asymmetry involved in the process of purine-motif triplex formation, with interactions between the 3' end of the oligonucleotide and complementary sequences on the target duplex DNA being dominant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOLTON E. T., McCARTHY B. J. A general method for the isolation of RNA complementary to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1390–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. The influence of single base triplet changes on the stability of a pur.pur.pyr triple helix determined by affinity cleaving. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2773–2776. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng A. J., Van Dyke M. W. Monovalent cation effects on intermolecular purine-purine-pyrimidine triple-helix formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 11;21(24):5630–5635. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.24.5630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz G., Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Hogan M. E. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.3293213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig M. E., Crothers D. M., Doty P. Relaxation kinetics of dimer formation by self complementary oligonucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):383–401. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durland R. H., Kessler D. J., Gunnell S., Duvic M., Pettitt B. M., Hogan M. E. Binding of triple helix forming oligonucleotides to sites in gene promoters. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9246–9255. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbinghaus S. W., Gee J. E., Rodu B., Mayfield C. A., Sanders G., Miller D. M. Triplex formation inhibits HER-2/neu transcription in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2433–2439. doi: 10.1172/JCI116850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing N. H., Beekman J. M., Kessler D. J., Murphy M., Jayaraman K., Zendegui J. G., Hogan M. E., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. In vivo transcription of a progesterone-responsive gene is specifically inhibited by a triplex-forming oligonucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2789–2796. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson B. L., Dervan P. B. Adenine specific DNA chemical sequencing reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7823–7830. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. J., Pettitt B. M., Cheng Y. K., Smith S. R., Jayaraman K., Vu H. M., Hogan M. E. Triple helix formation at distant sites: hybrid oligonucleotides containing a polymeric linker. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Oct 11;21(20):4810–4815. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.20.4810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd DNA triple-helix formation: an approach to artificial gene repressors? Bioessays. 1992 Dec;14(12):807–815. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McShan W. M., Rossen R. D., Laughter A. H., Trial J., Kessler D. J., Zendegui J. G., Hogan M. E., Orson F. M. Inhibition of transcription of HIV-1 in infected human cells by oligodeoxynucleotides designed to form DNA triple helices. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5712–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergny J. L., Duval-Valentin G., Nguyen C. H., Perrouault L., Faucon B., Rougée M., Montenay-Garestier T., Bisagni E., Hélène C. Triple helix-specific ligands. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1681–1684. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Krawczyk S. H., Wadwani S., Matteucci M. D. An anti-parallel triple helix motif with oligodeoxynucleotides containing 2'-deoxyguanosine and 7-deaza-2'-deoxyxanthosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):327–333. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orson F. M., Thomas D. W., McShan W. M., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Oligonucleotide inhibition of IL2R alpha mRNA transcription by promoter region collinear triplex formation in lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3435–3441. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pochon F., Michelson A. M. Polynucleotides. VI. Interaction between polyguanylic acid and polycytidylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1425–1430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Evidence that a triplex-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotide binds to the c-myc promoter in HeLa cells, thereby reducing c-myc mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pörschke D., Eigen M. Co-operative non-enzymic base recognition. 3. Kinetics of the helix-coil transition of the oligoribouridylic--oligoriboadenylic acid system and of oligoriboadenylic acid alone at acidic pH. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):361–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougée M., Faucon B., Mergny J. L., Barcelo F., Giovannangeli C., Garestier T., Hélène C. Kinetics and thermodynamics of triple-helix formation: effects of ionic strength and mismatches. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 29;31(38):9269–9278. doi: 10.1021/bi00153a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. Inhibition of gene transcription by purine rich triplex forming oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2845–2852. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W. A rapid method for the purification of deprotected oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):674–674. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Torigoe H., Sarai A. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of DNA triplex formation of an oligohomopyrimidine and a matched duplex by filter binding assay. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 31;32(34):8963–8969. doi: 10.1021/bi00085a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., François J. C., Montenay-Garestier T., Saison-Behmoaras T., Roig V., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific intercalating agents: intercalation at specific sequences on duplex DNA via major groove recognition by oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9198–9202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung C. H., Breslauer K. J., Stein S. Polyamine-linked oligonucleotides for DNA triple helix formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 25;21(23):5489–5494. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.23.5489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]