Abstract
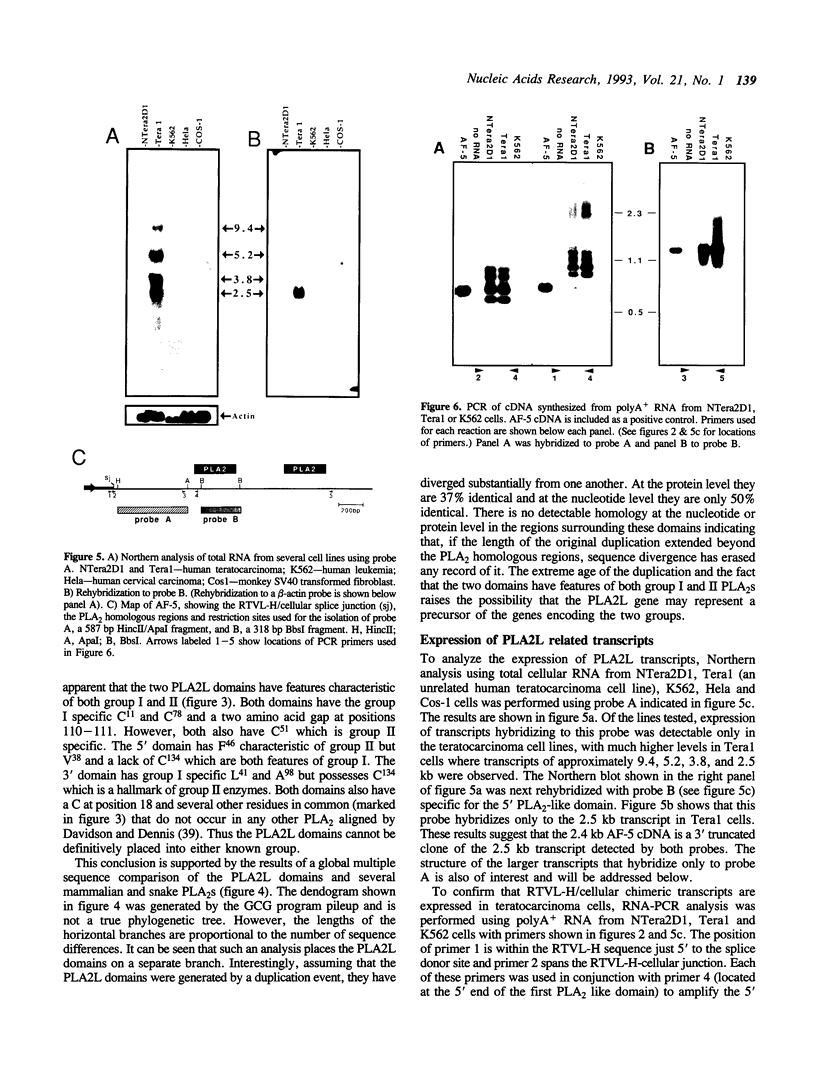
As part of an investigation into the effects of endogenous retroviruses on adjacent genes, we have isolated a cDNA clone derived from the human teratocarcinoma cell line NTera2D1 representing a chimeric transcript in which an endogenous retrovirus-like element, RTVL-H, has been spliced to downstream cellular sequences. The 5' terminus of this clone, termed AF-5, occurs one bp downstream of the predicted transcriptional start site in the RTVL-H long terminal repeat (LTR). AF-5 contains an open reading frame of 689 amino acids beginning within RTVL-H sequences that has two domains of homology with phospholipase A2 (PLA2). These domains, of approximately 120 amino acids each, are 30-38% identical to secreted PLA2s and contain sequence features of both group I and II enzymes. The corresponding AF-5 transcript is 2.5 kb and is derived from a single copy novel gene termed PLA2L. Southern analysis indicates that the RTVL-H element is normally present in human DNA upstream of the PLA2L gene. RTVL-H/PLA2L chimeric transcripts were detected in two independent teratocarcinoma cell lines but not in several other cell lines or primary human tissues. Characterization of additional cDNA clones and PCR analysis indicates that multiple RTVL-H/PLA2L alternatively spliced transcripts are expressed. No evidence has been found for transcription from a non-LTR promoter. These findings strongly suggest that the endogenous LTR promotes expression of the human PLA2L gene in teratocarcinoma cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. W., Damjanov I., Simon D., Banting G. S., Carlin C., Dracopoli N. C., Føgh J. Pluripotent embryonal carcinoma clones derived from the human teratocarcinoma cell line Tera-2. Differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Lab Invest. 1984 Feb;50(2):147–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C. A., Tam A. W., Nelson P. A., Engleman E. G., Suzuki N., Fry K. E., Larrick J. W. Message amplification phenotyping (MAPPing): a technique to simultaneously measure multiple mRNAs from small numbers of cells. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1096–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang-Yeh A., Mold D. E., Huang R. C. Identification of a novel murine IAP-promoted placenta-expressed gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3667–3672. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Dennis E. A. Evolutionary relationships and implications for the regulation of phospholipase A2 from snake venom to human secreted forms. J Mol Evol. 1990 Sep;31(3):228–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02109500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G. Drosophila retrotransposons: interactions with genome. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:33–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuchter A. E., Freeman J. D., Mager D. L. Strategy for detecting cellular transcripts promoted by human endogenous long terminal repeats: identification of a novel gene (CDC4L) with homology to yeast CDC4. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1237–1246. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90041-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuchter A., Mager D. Functional heterogeneity of a large family of human LTR-like promoters and enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1261–1270. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C., Humphries R. K., Mager D. L. Chromosomal distribution of the RTVL-H family of human endogenous retrovirus-like sequences. Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):280–287. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein C., Kawai M., Franz M. J., Beck-Engeser G., Daniel C. P., Ostertag W., Stocking C. Retrotransposons as mutagens in the induction of growth autonomy in hematopoietic cells. Oncogene. 1990 Dec;5(12):1799–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Krueger E. T., Keim P. S. Amino acid sequence of phospholipase A2-alpha from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus. A new classification of phospholipases A2 based upon structural determinants. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4913–4921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T., Holm T., Bjørklid E. Members of the RTVL-H family of human endogenous retrovirus-like elements are expressed in placenta. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda A., Ono T., Yoshida N., Tojo H., Okamoto M. The primary structure of a membrane-associated phospholipase A2 from human spleen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):42–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Larsson E., Cohen M. Absence of expression of a human endogenous retrovirus is correlated with choriocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988 Mar 15;41(3):380–385. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Kato M., Larsson E., Rydnert J., Ohlsson R., Cohen M. Tissue-specific expression of human provirus ERV3 mRNA in human placenta: two of the three ERV3 mRNAs contain human cellular sequences. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2182–2191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2182-2191.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Shimotohno K., VanLeeuwen D., Cohen M. Human proviral mRNAs down regulated in choriocarcinoma encode a zinc finger protein related to Krüppel. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4401–4405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Schiff R., Itin A. Mouse retrotransposons: a cellular reservoir of long terminal repeat (LTR) elements with diverse transcriptional specificities. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:215–251. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komada M., Kudo I., Mizushima H., Kitamura N., Inoue K. Structure of cDNA coding for rat platelet phospholipase A2. J Biochem. 1989 Oct;106(4):545–547. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Gmachl M., Sippl M. J., Kreil G. Analysis of the cDNA for phospholipase A2 from honeybee venom glands. The deduced amino acid sequence reveals homology to the corresponding vertebrate enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Sep 1;184(1):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K. The intracisternal A-particle gene family: structure and functional aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:183–276. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusunoki C., Satoh S., Kobayashi M., Niwa M. Structure of genomic DNA for rat platelet phospholipase A2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 10;1087(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90127-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E., Kato N., Cohen M. Human endogenous proviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;148:115–132. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74700-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib-Mösch C., Brack-Werner R., Werner T., Bachmann M., Faff O., Erfle V., Hehlmann R. Endogenous retroviral elements in human DNA. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17 Suppl):5636S–5642S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Abraham B. A. Subtractive cloning of a hybrid human endogenous retrovirus and calbindin gene in the prostate cell line PC3. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4107–4110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Freeman J. D. Human endogenous retroviruslike genome with type C pol sequences and gag sequences related to human T-cell lymphotropic viruses. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4060–4066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4060-4066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Henthorn P. S. Identification of a retrovirus-like repetitive element in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7510–7514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L. Polyadenylation function and sequence variability of the long terminal repeats of the human endogenous retrovirus-like family RTVL-H. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):591–599. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90570-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Tamaki M., Nakamura E., Tsuruta Y., Fujii Y., Shin M., Teraoka H., Okamoto M. Dog and rat pancreatic phospholipases A2: complete amino acid sequences deduced from complementary DNAs. J Biochem. 1986 Mar;99(3):733–739. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Matera A. G., Deka N., Schmid C. W. Transcription of a human transposon-like sequence is usually directed by other promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5199–5215. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Vadas P. Phospholipase A2--a mediator between proximal and distal effectors of inflammation. Immunol Today. 1991 May;12(5):143–146. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph A., Heinrikson R. L. Crotalus atrox phospholipase A2. Amino acid sequence and studies on the function of the NH2-terminal region. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2155–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Plant S., Miller J. A., Kloss J., Johnson L. K. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5335–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Randall T. L., Yamanaka M., Johnson L. K. Pancreatic phospholipase A2: isolation of the human gene and cDNAs from porcine pancreas and human lung. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):519–527. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. Unit-length line-1 transcripts in human teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1385–1397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavenhagen J. B., Robins D. M. An ancient provirus has imposed androgen regulation on the adjacent mouse sex-limited protein gene. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Klocke R., Ortland C., Gronemeier M., Jockusch H., Gründer S., Jentsch T. J. Inactivation of muscle chloride channel by transposon insertion in myotonic mice. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):304–308. doi: 10.1038/354304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki C., Kuramochi H., Shimazu T., Tamiya N. Correction of amino acid sequence of phospholipase A2 I from the venom of Laticauda semifasciata (Erabu sea snake). Toxicon. 1988;26(8):747–749. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Function of the retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90367-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting C. N., Rosenberg M. P., Snow C. M., Samuelson L. C., Meisler M. H. Endogenous retroviral sequences are required for tissue-specific expression of a human salivary amylase gene. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1457–1465. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai I. H., Wu S. H., Lo T. B. Complete amino acid sequence of a phospholipase A2 from the venom of Naja naja atra (Taiwan cobra). Toxicon. 1981;19(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(81)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij H. M., Westerman J., Sternby B., De Haas G. H. The complete primary structure of phospholipase A2 from human pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 14;747(1-2):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljoen C. C., Botes D. P., Kruger H. Isolation and amino acid sequence of caudoxin, a presynaptic acting toxic phospholipase A2 from the venom of the horned puff adder (Bitis caudalis). Toxicon. 1982;20(4):715–737. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke C. M., Adams J. Fitness effects of Ty transposition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1992 May;131(1):31–42. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. A., Freeman J. D., Goodchild N. L., Kelleher C. A., Mager D. L. Autonomous expression of RTVL-H endogenous retroviruslike elements in human cells. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2157–2167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2157-2167.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Tucker W. Q., Sanderson C. J., Hapel A. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Constitutive synthesis of interleukin-3 by leukaemia cell line WEHI-3B is due to retroviral insertion near the gene. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):255–258. doi: 10.1038/317255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bergh C. J., Slotboom A. J., Verheij H. M., de Haas G. H. The role of Asp-49 and other conserved amino acids in phospholipases A2 and their importance for enzymatic activity. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Apr;39(4):379–390. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]