Abstract
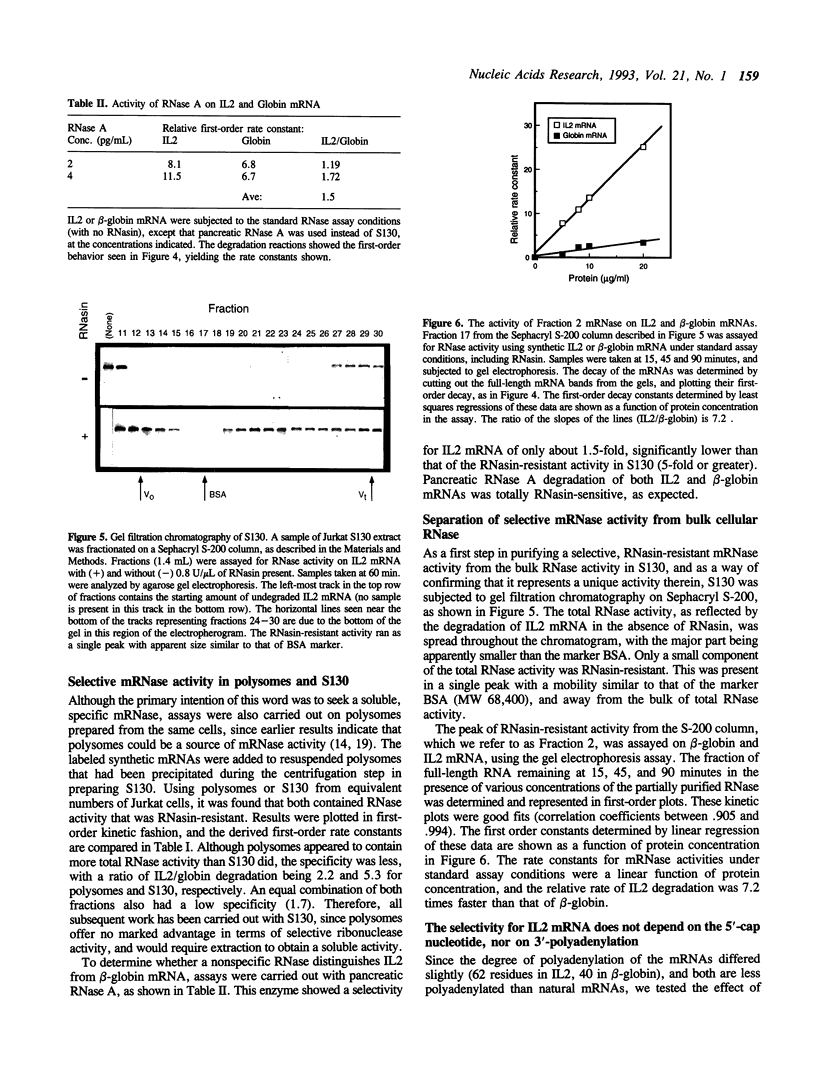
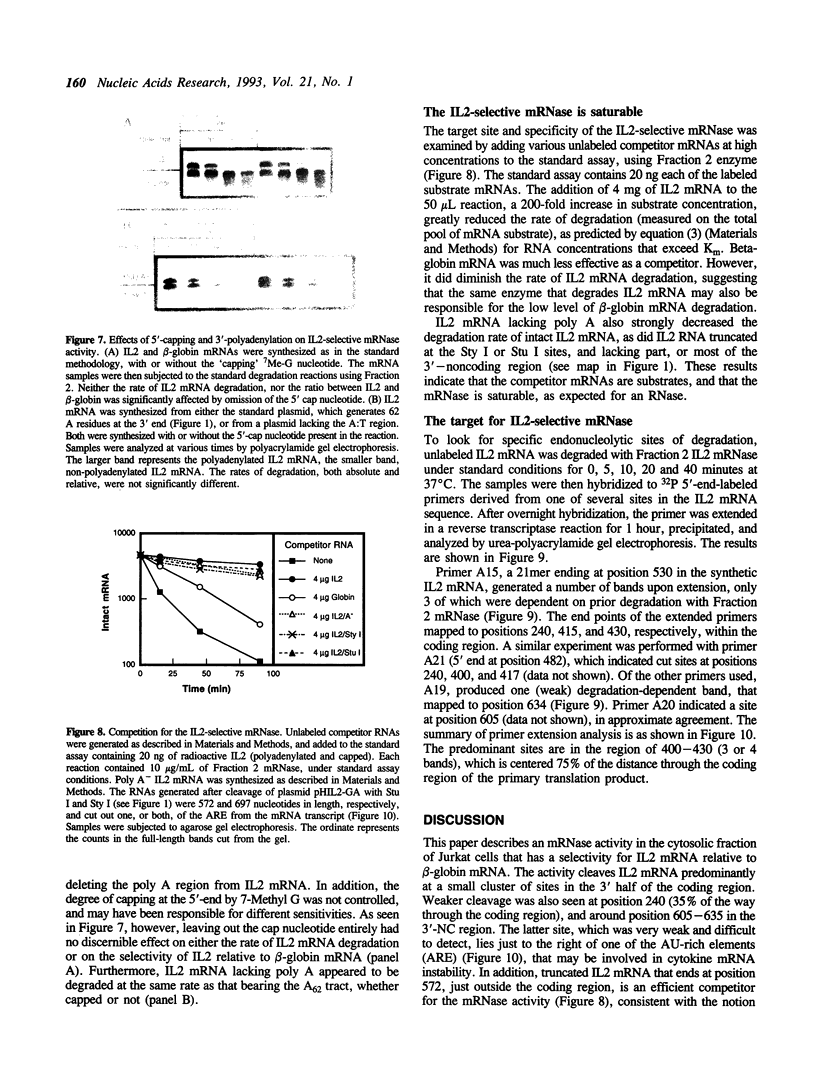
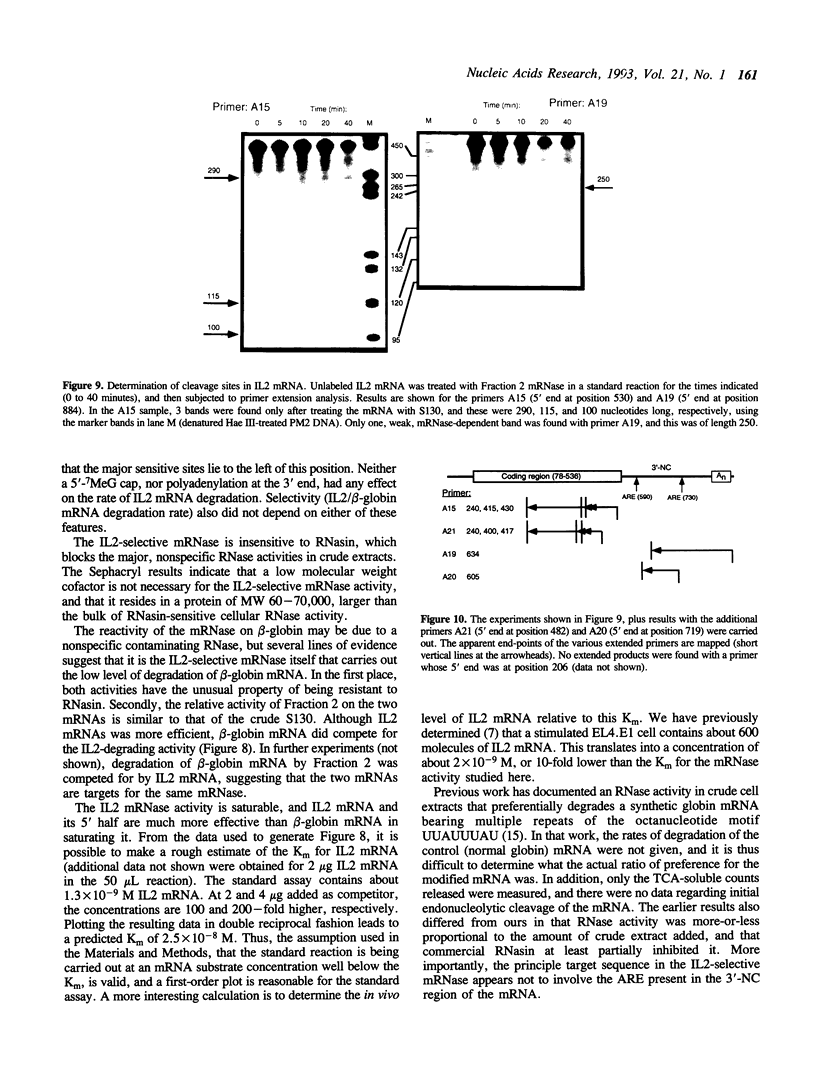
Interleukin 2 (IL2) mRNA has a short half-life in the cytoplasm of T lymphocytes, relative to most mRNA. We have discovered a candidate ribonuclease to account for the rapid turnover of IL2 mRNA in the cytosol of the human T lymphocyte cell line Jurkat. In partially purified form, this RNase is about 7 times as active on IL2 as on beta-globin mRNA. Pancreatic RNase, by contrast, does not show a significant preference for IL2 mRNA. Neither 5' capping, nor polyadenylation of the substrate mRNAs affects their degradation by the IL2-selective mRNase, whose activity is optimal in 0.5 mM Mg++ and 100 mM potassium acetate. The mRNase behaves like a protein of molecular weight 60-70,000 on gel chromatography, and is unusual in that it is insensitive to placental RNase inhibitor (RNasin). The mRNase cleaves IL2 mRNA at a small number of sites in the coding region, and IL2 mRNA containing only the coding region and 36 nucleotides of the 3'-noncoding region competes efficiently with full-length IL2 mRNA for the mRNase, whereas beta-globin mRNA does not.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akahane K., Cohen R. B., Bickel M., Pluznik D. H. IL-1 alpha induces granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene expression in murine B lymphocyte cell lines via mRNA stabilization. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4190–4196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein P., Peltz S. W., Ross J. The poly(A)-poly(A)-binding protein complex is a major determinant of mRNA stability in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):659–670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Thompson P., Keyes J., Hagerty K., Crawford D. Assay of a ribonuclease that preferentially hydrolyses mRNAs containing cytokine-derived UA-rich instability sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):973–980. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickel M., Cohen R. B., Pluznik D. H. Post-transcriptional regulation of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor synthesis in murine T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):840–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Relation of ribonuclease and ribonuclease inhibitor to the isolation of polysomes from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1283–1288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T. An inducible cytoplasmic factor (AU-B) binds selectively to AUUUA multimers in the 3' untranslated region of lymphokine mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3288–3295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. An A + U-rich element RNA-binding factor regulates c-myc mRNA stability in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2460–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Regulation of c-myc mRNA stability in vitro by a labile destabilizer with an essential nucleic acid component. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1996–2006. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Mechti N., Piechaczyk M., Lebleu B., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Increased rate of degradation of c-myc mRNA in interferon-treated Daudi cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4896–4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. High stability of messenger RNA in growing cultured cells. Nature. 1972 Nov 10;240(5376):102–104. doi: 10.1038/240102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrove J. L., Schmidt F. H. The role of mRNA and protein stability in gene expression. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2360–2370. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpold M. M., Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Chinese hamster polyadenylated messenger ribonucleic acid: relationship to non-polyadenylated sequences and relative conservation during messenger ribonucleic acid processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):188–198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B. Evidence for the involvement of three distinct signals in the induction of IL-2 gene expression in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Linsley P. S., Thompson C. B. Role of the CD28 receptor in T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1990 Jun;11(6):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90085-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., Spritz R. A. In vitro splicing pathways of pre-mRNAs containing multiple intervening sequences? Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3428–3437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Imboden J. B., Schieven G. L., Grosmaire L. S., Rabinovitch P. S., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B., June C. H. CD28 ligation in T-cell activation: evidence for two signal transduction pathways. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1531–1539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstein T., June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Stella G., Thompson C. B. Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T cell activation pathway. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):339–343. doi: 10.1126/science.2540528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei R., Calame K. Differential stability of c-myc mRNAS in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2860–2868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers J. R., Johnson M. L., Rosen J. M. Measurement of mRNA concentration and mRNA half-life as a function of hormonal treatment. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:572–592. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G., Brewer G., Peltz S. W. Properties of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9374–9381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J., Meerovitch K., Bleackley R. C., Paetkau V. Mechanisms regulating the level of IL-2 mRNA in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2243–2248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J., Meerovitch K., Elliott J. F., Bleackley R. C., Paetkau V. Induction, suppression and superinduction of lymphokine mRNA in T lymphocytes. Mol Immunol. 1987 May;24(5):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volloch V., Housman D. Stability of globin mRNA in terminally differentiating murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wager R. E., Assoian R. K. A phorbol ester-regulated ribonuclease system controlling transforming growth factor beta 1 gene expression in hematopoietic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5983–5990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]