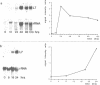
Abstract
By subtractive screening of a library made from mRNA of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated mouse B lymphocytes we isolated cDNA-clones encoding the ribosomal protein L7. Human L7 mRNA was cloned from activated T-lymphocytes. Although no specific function of L7 in the translation apparatus is known as yet, it should be a critical one as indicated by its high degree of structural conservation during evolution and its regulated expression in lymphoid cells. Human and rodent L7 proteins carry sequences similar to the basic-region-leucine-zipper(BZIP)-motif of DNA-binding eucaryotic transcription factors. We show here that the region of L7 carrying the latter motif mediates L7-dimerization and stable binding to DNA and RNA. A preferential binding to RNA-structures is demonstrated.
Full text
PDF


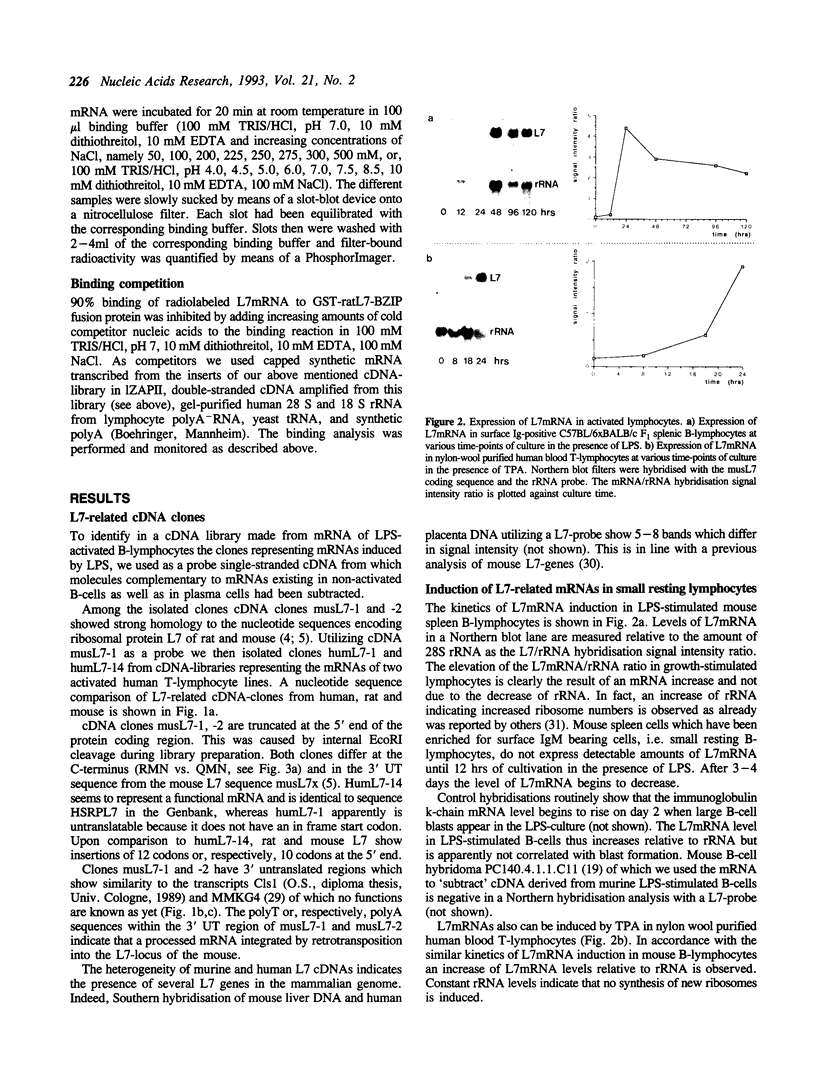


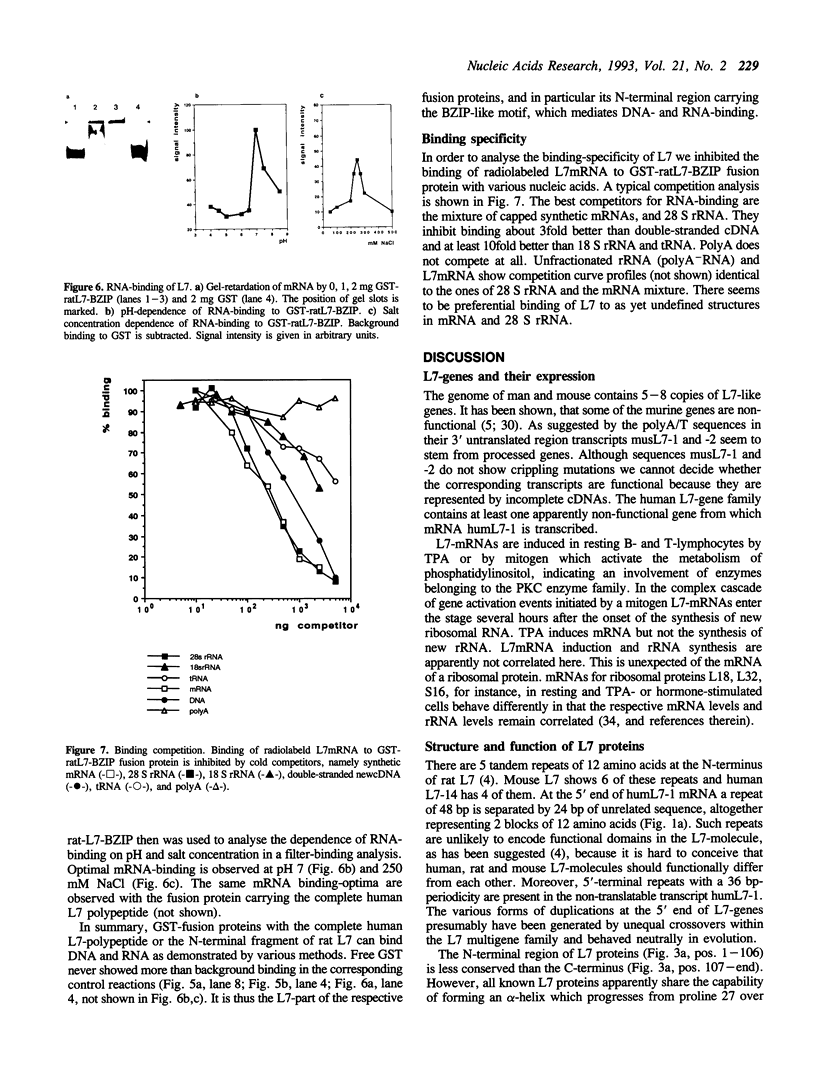


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdella P. M., Smith P. K., Royer G. P. A new cleavable reagent for cross-linking and reversible immobilization of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):734–742. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Absi M., La Vergne J. P., Marzouki A., Giraud F., Rigal D., Reboud A. M., Reboud J. P., Monier J. C. Heterogeneity of ribosomal autoantibodies from human, murine and canine connective tissue diseases. Immunol Lett. 1989 Nov;23(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch S. J., Sassone-Corsi P. Dimers, leucine zippers and DNA-binding domains. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90071-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Ransom J. T. Molecular mechanisms of transmembrane signaling in B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:175–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. Analysis of dimerization and DNA binding functions in Fos and Jun by domain-swapping: involvement of residues outside the leucine zipper/basic region. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):929–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. L., Braverman R. Free fibosomes and growth stimulation in human peripheral lymphocytes: activation of free ribisomes as an essential event in growth induction. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Nov;93(2):213–225. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040930207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Cohen D. I., Nielsen E. A., Steinmetz M., Paul W. E., Hood L. Cell-type-specific cDNA probes and the murine I region: the localization and orientation of Ad alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2194–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Swanson M. S., Piñol-Roma S. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and the pathway of mRNA formation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Mar;13(3):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser C., Radbruch A. Rapid induction of transcription of unrearranged S gamma 1 switch regions in activated murine B cells by interleukin 4. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):483–488. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filion M., Lussier M., Royal A., Gervais C., Suh M. Identification of a proliferation-related transcript with an elevated expression in the mid-gestation mouse embryo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 7;950(3):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Meyuhas O. A multigene family of intron lacking and containing genes, encoding for mouse ribosomal protein L7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3763–3776. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Zoebelein R. Rapid synthesis of cDNA for cloning into lambda vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1913–1913. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Chan Y. L., McNally J., Peleg D., Meyuhas O., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L7. The presence near the amino terminus of L7 of five tandem repeats of a sequence of 12 amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12665–12671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. Localization of surface peptide from ribosomal protein L7 on 80 S ribosome by biotinylation. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Klein A. The mouse ribosomal protein L7 gene. Its primary structure and functional analysis of the promoter region. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11465–11473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta K., Hashimoto T., Otaka E. Yeast ribosomal proteins: XIII. Saccharomyces cerevisiae YL8A gene, interrupted with two introns, encodes a homolog of mammalian L7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1011–1016. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Watts F. Z. Isolation of a Schizosaccharomyces pombe homologue to the rat ribosomal protein, L7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4590–4590. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paluh J. L., Orbach M. J., Legerton T. L., Yanofsky C. The cross-pathway control gene of Neurospora crassa, cpc-1, encodes a protein similar to GCN4 of yeast and the DNA-binding domain of the oncogene v-jun-encoded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3728–3732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapp M., Knippers R., Richter A. DNA binding properties of a 110 kDa nucleolar protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6803–6820. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymkowski D. E., Kelly B., Deering R. A. A Dictyostelium discoideum cDNA coding for a protein with homology to the rat ribosomal protein L7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5393–5393. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thammana P., Scharff M. D. Immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch from IgM to IgG in a hybridoma. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Aug;13(8):614–619. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropsha A., Bowen J. P., Brown F. K., Kizer J. S. Do interhelical side chain-backbone hydrogen bonds participate in formation of leucine zipper coiled coils? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9488–9492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Mitsui K. Bilateral hydrophobic zipper as a hypothetical structure which binds acidic ribosomal protein family together on ribosomes in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1318–1323. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91566-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Davidson D. Src-related protein tyrosine kinases and T-cell receptor signalling. Trends Genet. 1992 Feb;8(2):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G. The structure and function of eukaryotic ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:719–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Chan A., Chin B., Minden M., Mak T. W. Analysis of cDNA clones specific for human T cells and the alpha and beta chains of the T-cell receptor heterodimer from a human T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3430–3434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]