Abstract
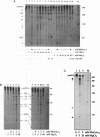
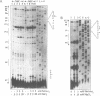
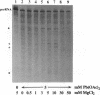
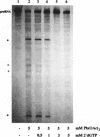
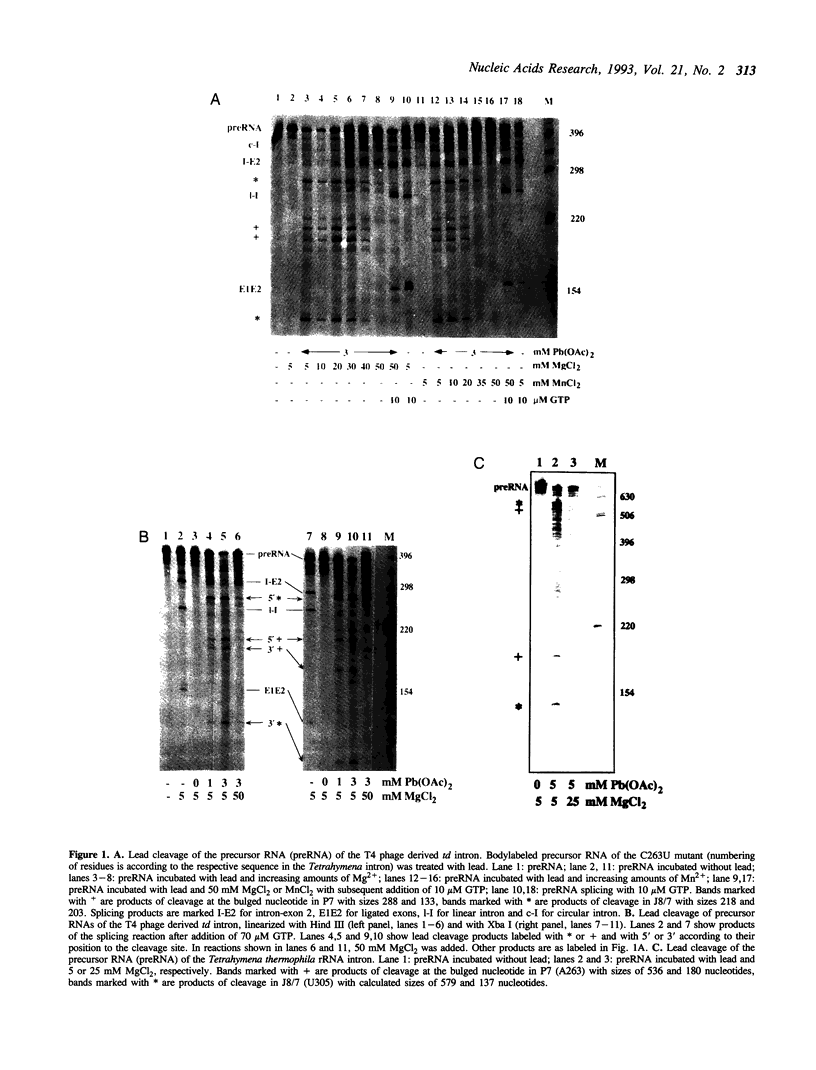
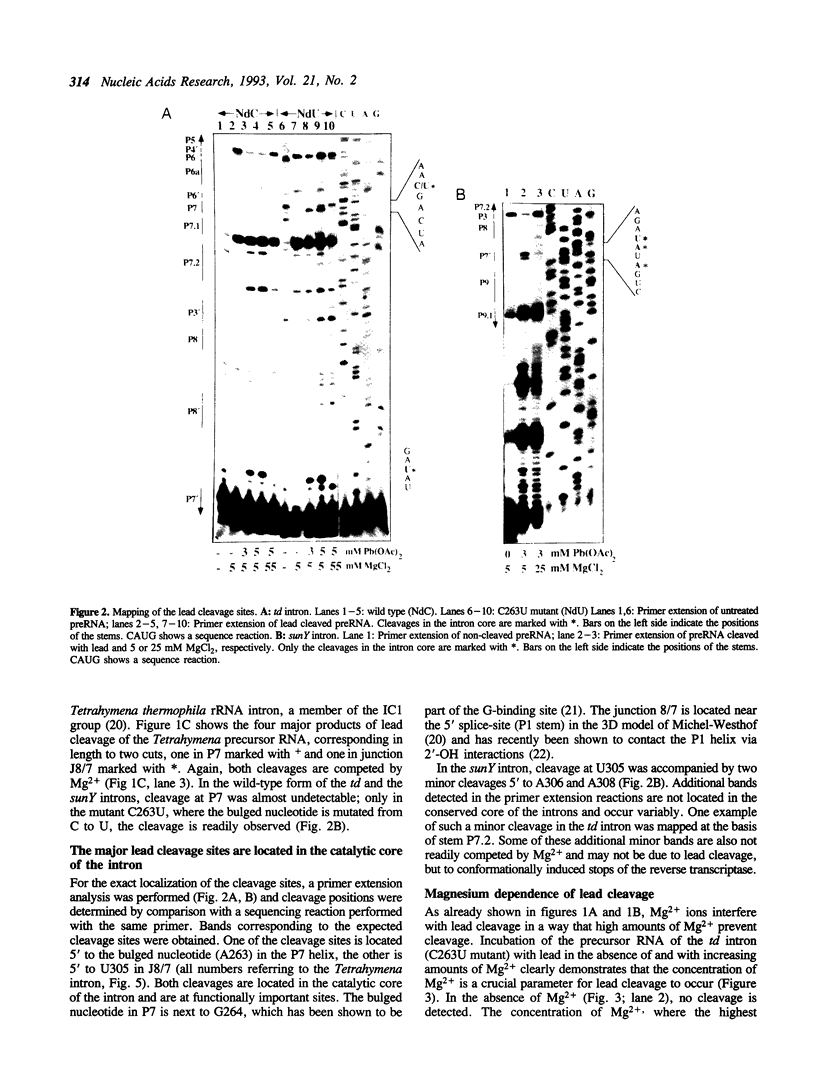
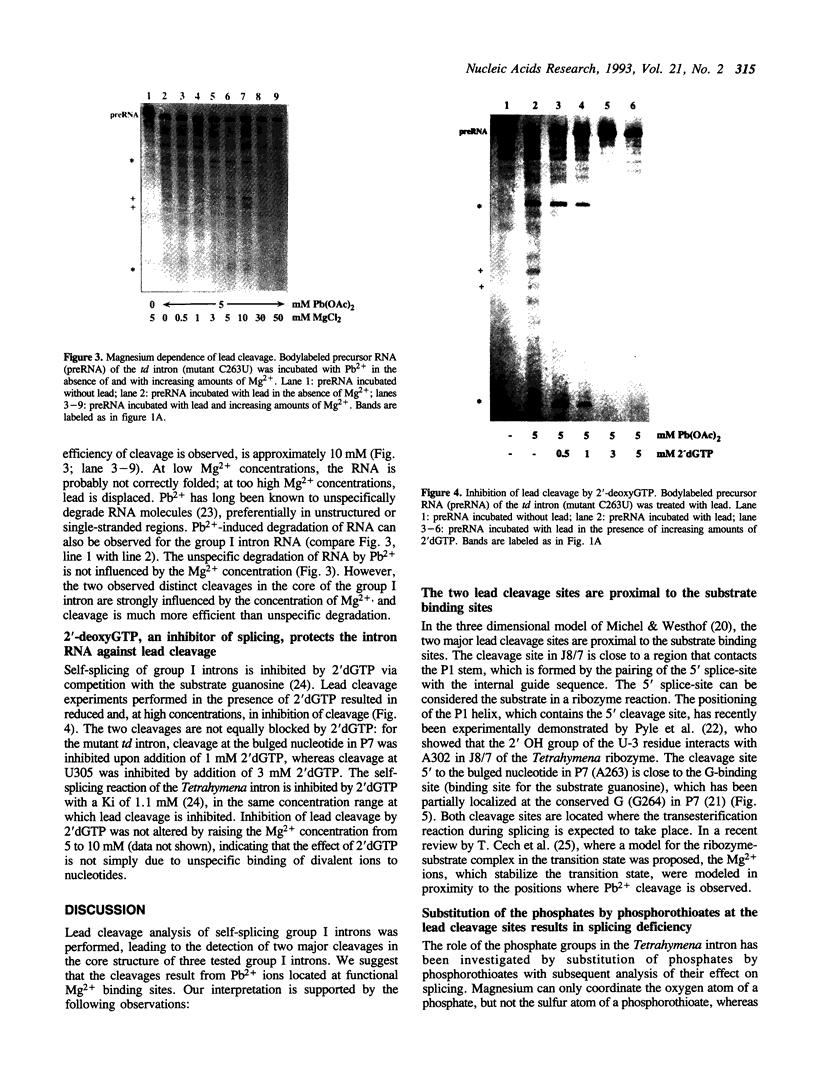
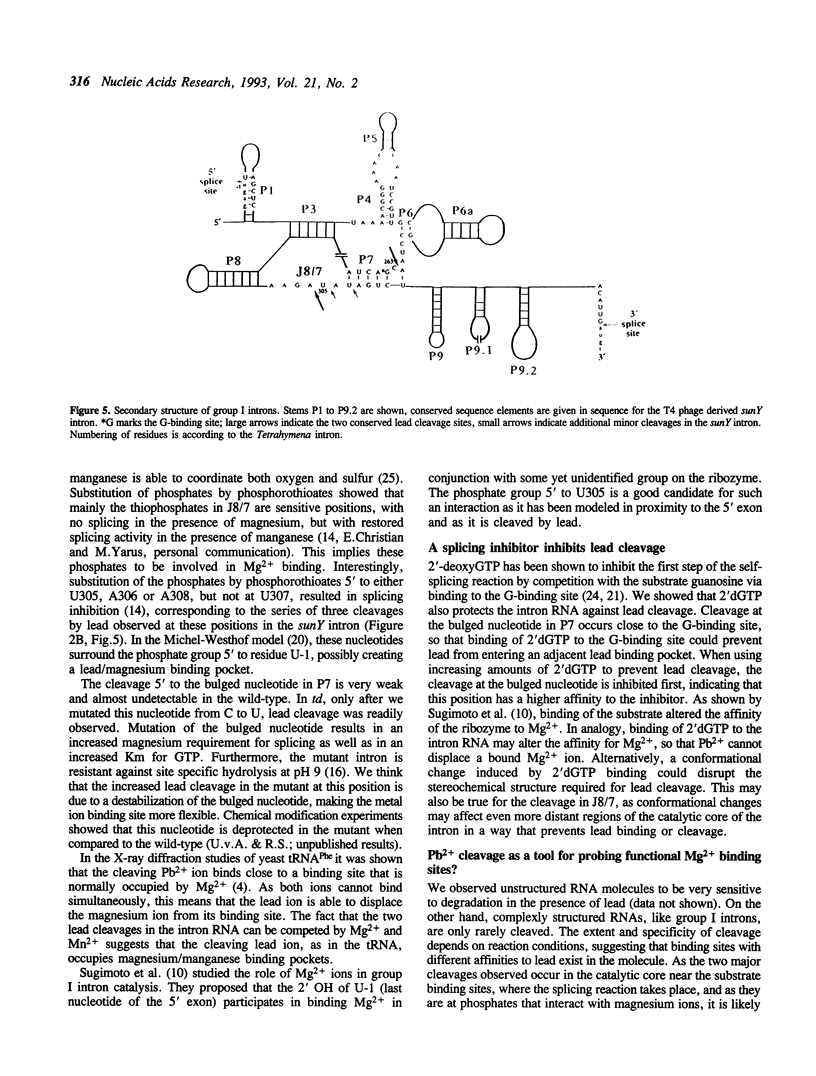
Self-splicing of group I introns requires divalent metal ions to promote catalysis as well as for the correct folding of the RNA. Lead cleavage has been used to probe the intron RNA for divalent metal ion binding sites. In the conserved core of the intron, only two sites of Pb2+ cleavage have been detected, which are located close to the substrate binding sites in the junction J8/7 and at the bulged nucleotide in the P7 stem. Both lead cleavages can be inhibited by high concentrations of Mg2+ and Mn2+ ions, suggesting that they displace Pb2+ ions from the binding sites. The RNA is protected from lead cleavage by 2'-deoxyGTP, a competitive inhibitor of splicing. The two major lead induced cleavages are both located in the conserved core of the intron and at phosphates, which had independently been demonstrated to interact with magnesium ions and to be essential for splicing. Thus, we suggest that the conditions required for lead cleavage occur mainly at those sites, where divalent ions bind that are functionally involved in catalysis. We propose lead cleavage analysis of functional RNA to be a useful tool for mapping functional magnesium ion binding sites.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass B. L., Cech T. R. Ribozyme inhibitors: deoxyguanosine and dideoxyguanosine are competitive inhibitors of self-splicing of the Tetrahymena ribosomal ribonucleic acid precursor. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4473–4477. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlen L. S., Sampson J. R., DiRenzo A. B., Uhlenbeck O. C. Lead-catalyzed cleavage of yeast tRNAPhe mutants. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2515–2523. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Dewan J. C., Klug A. Crystallographic and biochemical investigation of the lead(II)-catalyzed hydrolysis of yeast phenylalanine tRNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4785–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Hingerty B. E., Dewan J. C., Klug A. Pb(II)-catalysed cleavage of the sugar-phosphate backbone of yeast tRNAPhe--implications for lead toxicity and self-splicing RNA. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):543–546. doi: 10.1038/303543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Herschlag D., Piccirilli J. A., Pyle A. M. RNA catalysis by a group I ribozyme. Developing a model for transition state stabilization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17479–17482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H. Y., Termini J. Catalytic RNA reactions of yeast tRNA(Phe) fragments. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10518–10528. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas W. R. Depolymerization of ribonucleic acid by plumbous ion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway Salvo J. L., Coetzee T., Belfort M. Deletion-tolerance and trans-splicing of the bacteriophage T4 td intron. Analysis of the P6-L6a region. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 5;211(3):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90264-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gornicki P., Baudin F., Romby P., Wiewiorowski M., Kryzosiak W., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Use of lead(II) to probe the structure of large RNA's. Conformation of the 3' terminal domain of E. coli 16S rRNA and its involvement in building the tRNA binding sites. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Apr;6(5):971–984. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10506525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosshans C. A., Cech T. R. Metal ion requirements for sequence-specific endoribonuclease activity of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 22;28(17):6888–6894. doi: 10.1021/bi00443a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Ladner J. E., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Klug A. A crystallographic study of metal-binding to yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 15;111(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSwiggen J. A., Cech T. R. Stereochemistry of RNA cleavage by the Tetrahymena ribozyme and evidence that the chemical step is not rate-limiting. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):679–683. doi: 10.1126/science.2470150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Hanna M., Green R., Bartel D. P., Szostak J. W. The guanosine binding site of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):391–395. doi: 10.1038/342391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90386-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. A small metalloribozyme with a two-step mechanism. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):560–563. doi: 10.1038/358560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. In vitro selection of RNAs that undergo autolytic cleavage with Pb2+. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):3887–3895. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle A. M., Murphy F. L., Cech T. R. RNA substrate binding site in the catalytic core of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):123–128. doi: 10.1038/358123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rordorf B. F., Kearns D. R. Effects of europium (III) on the thermal denaturation and cleavage of transfer ribonucleic acids. Biopolymers. 1976 Aug;15(8):1491–1504. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., Sullivan F. X., Behlen L. S., DiRenzo A. B., Uhlenbeck O. C. Characterization of two RNA-catalyzed RNA cleavage reactions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:267–275. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder R., von Ahsen U., Belfort M. Effects of mutations of the bulged nucleotide in the conserved P7 pairing element of the phage T4 td intron on ribozyme function. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3295–3303. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto N., Tomka M., Kierzek R., Bevilacqua P. C., Turner D. H. Effects of substrate structure on the kinetics of circle opening reactions of the self-splicing intervening sequence from Tetrahymena thermophila: evidence for substrate and Mg2+ binding interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):355–371. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan F. X., Cech T. R. Reversibility of cyclization of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: implication for the mechanism of splice site choice. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):639–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walstrum S. A., Uhlenbeck O. C. The self-splicing RNA of Tetrahymena is trapped in a less active conformation by gel purification. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 20;29(46):10573–10576. doi: 10.1021/bi00498a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B. Identification of phosphate groups important to self-splicing of the Tetrahymena rRNA intron as determined by phosphorothioate substitution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10281–10293. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner C., Krebs B., Keith G., Dirheimer G. Specific cleavages of pure tRNAs by plumbous ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 3;432(2):161–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Kent J. R., Cech T. R. Reactions of the intervening sequence of the Tetrahymena ribosomal ribonucleic acid precursor: pH dependence of cyclization and site-specific hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6211–6218. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Ahsen U., Davies J., Schroeder R. Non-competitive inhibition of group I intron RNA self-splicing by aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):935–941. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91043-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]