Abstract
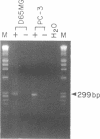
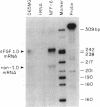
We have previously isolated two different aFGF cDNA clones from kidney and brain. The two corresponding mRNA, designated aFGF 1.A and 1.B, are the predominant species in kidney and brain, respectively. During the characterization of aFGF mRNA in glioblastoma cells, we demonstrated that aFGF mRNA in U1242MG and D65MG glioblastoma cells contain 5'-untranslated sequences different from those of 1.A and 1.B. Through a strategy combining chromosome walking, identification and sequencing of evolutionarily conserved DNA regions, and a reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)-based assay for RNA expression, we have isolated two novel aFGF cDNA clones. The cDNA clone representing aFGF mRNA 1.C was isolated from U1242MG cells; another aFGF cDNA, designated 1.D, was isolated from D65MG cells. Promoter 1C has extensive sequence homology to the hamster aFGF gene promoter that was shown to respond to testosterone stimulation by chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene assays. Using RT-PCR, we showed that normal, benign and cancerous prostate tissues do not express aFGF 1.C mRNA. In contrast, a prostate carcinoma cell line (PC-3) expresses 1.C mRNA. RT-PCR using 1.D-specific primers showed that kidney, brain and prostate do not express 1.D mRNA even though kidney and brain are the most abundant source for aFGF protein. RNase protection analysis further showed that 1.D mRNA is the predominant aFGF transcript in D65MG glioblastoma cells and in NFF-6 neonatal foreskin fibroblast cells. The genomic DNA corresponding to these two cDNA clones and the 5'-flanking regions were also isolated and their sequences determined. These DNA clones will provide important reagents for studying the regulatory elements of aFGF gene expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A. Growth factors and cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1146–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.1659742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alterio J., Courtois Y., Robelin J., Bechet D., Martelly I. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor mRNAs are expressed by skeletal muscle satellite cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 14;166(3):1205–1212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90994-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunnag P., Waddell K. S., Varban M. L., Chiu I. M. Transformed phenotype conferred to NIH/3T3 cells by ectopic expression of heparin-binding growth factor 1/acidic fibroblast growth factor. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1991 Jan;27(1):89–96. doi: 10.1007/BF02630899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Shaheen A. M., Ravera M., Jaye M., Donohue P. J., Winkles J. A. Possible dissociation of the heparin-binding and mitogenic activities of heparin-binding (acidic fibroblast) growth factor-1 from its receptor-binding activities by site-directed mutagenesis of a single lysine residue. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2129–2138. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion-Arnaud P., Ronsin C., Gilbert E., Gesnel M. C., Houssaint E., Breathnach R. Multiple mRNAs code for proteins related to the BEK fibroblast growth factor receptor. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):979–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu I. M., Wang W. P., Lehtoma K. Alternative splicing generates two forms of mRNA coding for human heparin-binding growth factor 1. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):755–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. W., Coffey R. J., Jr, Magun B. E., Pittelkow M. R., Shipley G. D. Expression and regulation of mRNA coding for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha in cells derived from human skin. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1377–1385. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb J. W., Armes L. G., Carr S. A., Johnson C. M., Roberts G. D., Bordoli R. S., McKeehan W. L. Complete primary structure of prostatropin, a prostate epithelial cell growth factor. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):4988–4993. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne C. A., Crumley G., Bellot F., Kaplow J. M., Searfoss G., Ruta M., Burgess W. H., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of two distinct high-affinity receptors cross-reacting with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2685–2692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Schon E., Gora-Maslak G., Patterson J., Efstratiadis A. S1-hypersensitive sites in eukaryotic promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8043–8058. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Cho K. R., Nigro J. M., Kern S. E., Simons J. W., Ruppert J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Thomas G., Kinzler K. W. Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):49–56. doi: 10.1126/science.2294591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and characterization of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1987;147:106–119. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)47102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. A., Harris M. A., Malark M., Mansson P. E., Zhou H., Harris S. E. Characterization of the hamster DDT-1 cell aFGF/HGBF-I gene and cDNA and its modulation by steroids. J Cell Biochem. 1990 May;43(1):17–26. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240430103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halley C., Courtois Y., Laurent M. Nucleotide sequence of bovine acidic fibroblast growth factor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10913–10913. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wells R. D. Intramolecular DNA triplexes in supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6292–6296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori Y., Odagiri H., Nakatani H., Miyagawa K., Naito K., Sakamoto H., Katoh O., Yoshida T., Sugimura T., Terada M. K-sam, an amplified gene in stomach cancer, is a member of the heparin-binding growth factor receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5983–5987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. Z., Kan M. K., McKeehan K., McBride G., Adams P., McKeehan W. L. Fibroblast growth factor receptors from liver vary in three structural domains. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):665–668. doi: 10.1126/science.1846977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Lyall R. M., Mudd R., Schlessinger J., Sarver N. Expression of acidic fibroblast growth factor cDNA confers growth advantage and tumorigenesis to Swiss 3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):963–969. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H. The S1-sensitive form of d(C-T)n.d(A-G)n: chemical evidence for a three-stranded structure in plasmids. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1800–1804. doi: 10.1126/science.2845572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh M., Hattori Y., Sasaki H., Tanaka M., Sugano K., Yazaki Y., Sugimura T., Terada M. K-sam gene encodes secreted as well as transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2960–2964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T., Hayman M. J. Isolation of an additional member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, FGFR-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Woodsworth M. L., Latimer L. J., Morgan A. R. Poly(pyrimidine) . poly(purine) synthetic DNAs containing 5-methylcytosine form stable triplexes at neutral pH. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6603–6614. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. L., Johnson D. E., Cousens L. S., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. Purification and complementary DNA cloning of a receptor for basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):57–60. doi: 10.1126/science.2544996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):667–669. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace H. A., Pelham H. R., Travers A. A. Association of an S1 nuclease-sensitive structure with short direct repeats 5' of Drosophila heat shock genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):555–557. doi: 10.1038/304555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Cerundolo J., Ilsley S., Kelley P. R., Forand R. An endothelial cell growth factor from bovine hypothalamus: identification and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansukhani A., Dell'Era P., Moscatelli D., Kornbluth S., Hanafusa H., Basilico C. Characterization of the murine BEK fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor: activation by three members of the FGF family and requirement for heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3305–3309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., Drumm M., Saulino A., Collins F. S. Construction of T-vectors, a rapid and general system for direct cloning of unmodified PCR products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1154–1154. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. A common ancestor DNA motif for invertebrate and vertebrate hormone response elements. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):263–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Smith C. L., Burgess W. H., Chan A. M., Aaronson S. A. Determination of ligand-binding specificity by alternative splicing: two distinct growth factor receptors encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):246–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of the KGF receptor by creation of a transforming autocrine loop. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.1846048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Mäkelä T. P., Eerola E., Korhonen J., Hirvonen H., Claesson-Welsh L., Alitalo K. FGFR-4, a novel acidic fibroblast growth factor receptor with a distinct expression pattern. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Osada H., Finch P. W., Taylor W. G., Rudikoff S., Aaronson S. A. Purification and characterization of a newly identified growth factor specific for epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):802–806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K. Superhelicity induces hypersensitivity of a human polypyrimidine . polypurine DNA sequence in the human alpha 2-alpha 1 globin intergenic region to S1 nuclease digestion--high resolution mapping of the clustered cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7899–7910. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. P., Lehtoma K., Varban M. L., Krishnan I., Chiu I. M. Cloning of the gene coding for human class 1 heparin-binding growth factor and its expression in fetal tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2387–2395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. P., Myers R. L., Chiu I. M. Single primer-mediated polymerase chain reaction: application in cloning of two different 5'-untranslated sequences of acidic fibroblast growth factor mRNA. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;10(10):771–777. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. P., Quick D., Balcerzak S. P., Needleman S. W., Chiu I. M. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human acidic fibroblast growth factor gene and its preservation in leukemia patients. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1521–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkles J. A., Gay C. G. Serum, phorbol ester, and polypeptide mitogens increase class 1 and 2 heparin-binding (acidic and basic fibroblast) growth factor gene expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Nov;2(11):531–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]