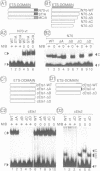
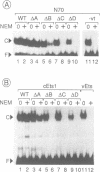
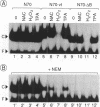
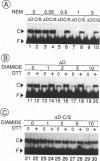
Abstract
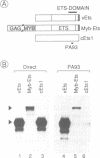
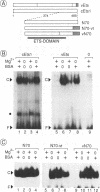
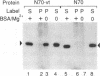
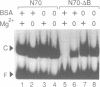
The avian acute leukemia virus E26 encodes a fusion protein between viral Gag and the cellular transcription factors cMyb and cEts1(p68). vEts on its own transforms more mature erythroid cells. We have compared the properties of vEts and cEts1(p68). vEts interacts preferentially with an antibody that recognizes the active conformation of the DNA-binding domain. The DNA-binding activity of vEts is particularly sensitive to incubation conditions for band-shift assays, phosphorylation and modification by sulphydryl-specific reagents. Increased sensitivity is due to loss of a protective function of cEts1 C-terminal sequences. cEts2 has a related C-terminal sequence with a similar role. These results suggest that the vEts DNA-binding domain is more accessible to protein-protein interactions and to regulatory mechanisms. Indeed, vEts DNA binding is preferentially inactivated by oxidizing conditions in-vivo. We suggest that the 'open' conformation of the vEts DNA-binding domain favours interactions with other proteins or DNA and facilitates transformation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D., Curran T. Crossed signals: oncogenic transcription factors. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Feb;2(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., LaMontagne K., Whittaker L., Stohr S., Lipsick J. S. A highly conserved cysteine in the v-Myb DNA-binding domain is essential for transformation and transcriptional trans-activation. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):1005–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guehmann S., Vorbrueggen G., Kalkbrenner F., Moelling K. Reduction of a conserved Cys is essential for Myb DNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20(9):2279–2286. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.9.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Rabson A. B., Gélinas C. The RxxRxRxxC motif conserved in all Rel/kappa B proteins is essential for the DNA-binding activity and redox regulation of the v-Rel oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3094–3106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M. Transcriptional regulation during T-cell development: the alpha TCR gene as a molecular model. Immunol Today. 1992 Jan;13(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90200-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Crepieux P., Stehelin D. c-ets-1 DNA binding to the PEA3 motif is differentially inhibited by all the mutations found in v-ets. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Gegonne A., Coll J., de Taisne C., Schneeberger A., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):395–397. doi: 10.1038/306395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Oncogenic conversion by regulatory changes in transcription factors. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90640-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim F., Kraut N., Framptom J., Graf T. DNA binding by c-Ets-1, but not v-Ets, is repressed by an intramolecular mechanism. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):643–652. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod K., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The ets gene family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jul;17(7):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90404-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger D., Losson R., Bornert J. M., Lemoine Y., Chambon P. Promoter specificity of the two transcriptional activation functions of the human oestrogen receptor in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2813–2817. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. Kappa B-specific DNA binding proteins are differentially inhibited by enhancer mutations and biological oxidation. New Biol. 1991 Oct;3(10):987–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. S., Rao V. N. erg, an ets-related gene, codes for sequence-specific transcriptional activators. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2285–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Ascione R., Fisher R. J., Mavrothalassitis G. J., Bhat N. K., Papas T. S. The ets gene family. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 May;3(5):327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Kerckaert J. P., Wasylyk B. A novel modulator domain of Ets transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):965–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Oncogenic conversion alters the transcriptional properties of ets. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Sep;3(9):617–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]