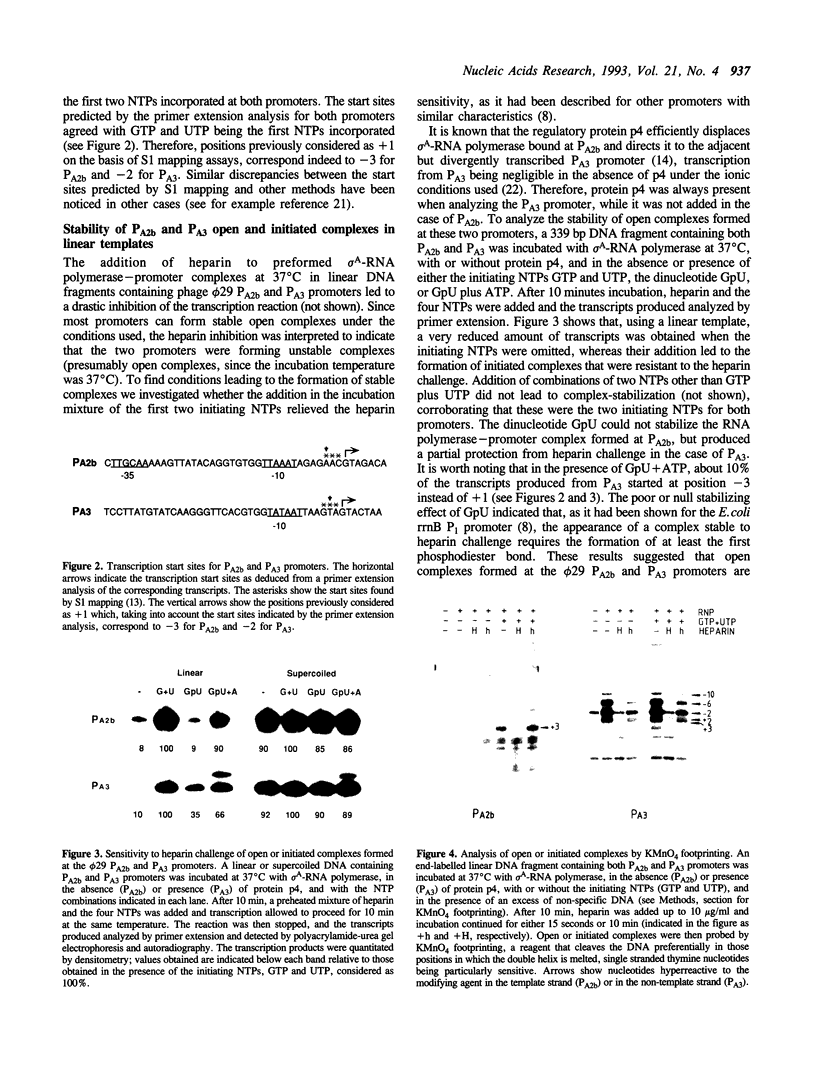
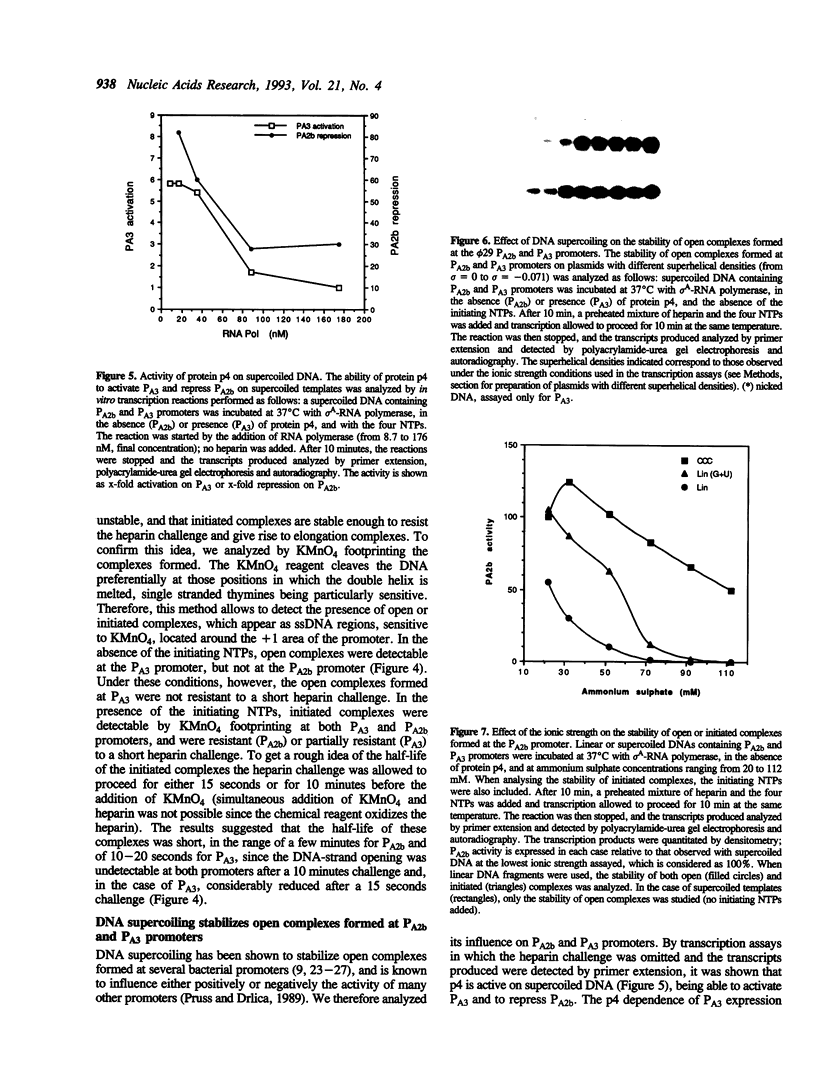
Abstract
Most Escherichia coli promoters studied so far form stable open complexes with sigma 70-RNA polymerase which have relatively long half-lives and, therefore, are resistant to a competitor challenge. A few exceptions are nevertheless known. The analysis of a number of promoters in Bacillus subtilis has suggested that the instability of open complexes formed by the vegetative sigma A-RNA polymerase may be a more general phenomenon than in Escherichia coli. We show that the main early and late promoters from the Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 form unstable open complexes that are stabilized either by the formation of the first phosphodiester bond between the initiating nucleoside triphosphates or by DNA supercoiling. The functional characteristics of these two strong promoters suggest that they are not optimized for a tight and stable RNA polymerase binding. Their high activity is probably the consequence of the efficiency of further steps leading to the formation of an elongation complex.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthelemy I., Lázaro J. M., Méndez E., Mellado R. P., Salas M. Purification in an active form of the phage phi 29 protein p4 that controls the viral late transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7781–7793. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthelemy I., Salas M. Characterization of a new prokaryotic transcriptional activator and its DNA recognition site. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 20;208(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Gralla J. D. High-resolution analysis of lac transcription complexes inside cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5051–5057. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Gralla J. D. Supercoiling response of the lac ps promoter in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):587–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahms J. G., Dargouge O., Brahms S., Ohara Y., Vagner V. Activation and inhibition of transcription by supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 20;181(4):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90419-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner M., Bujard H. Promoter recognition and promoter strength in the Escherichia coli system. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3139–3144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02624.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buc H., McClure W. R. Kinetics of open complex formation between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and the lac UV5 promoter. Evidence for a sequential mechanism involving three steps. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2712–2723. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Kammerer W., Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters of Escherichia coli: a hierarchy of in vivo strength indicates alternate structures. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2987–2994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobinson K. F., Spiegelman G. B. Effect of the delta subunit of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase on initiation of RNA synthesis at two bacteriophage phi 29 promoters. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8206–8213. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L. Visualization and quantitative analysis of complex formation between E. coli RNA polymerase and an rRNA promoter in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9789–9809. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann H., Ricchetti M., Werel W. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli induces bending or an increased flexibility of DNA by specific complex formation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4379–4381. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus R., Bujard H. PL of coliphage lambda: an alternative solution for an efficient promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2919–2923. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnke G., Theres C., Fritz H. J., Ehring R. RNA polymerase and gal repressor bind simultaneously and with DNA bending to the control region of the Escherichia coli galactose operon. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langert W., Meuthen M., Mueller K. Functional characteristics of the rrnD promoters of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21608–21615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzer M., Bujard H. Promoters largely determine the efficiency of repressor action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8973–8977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leirmo S., Gourse R. L. Factor-independent activation of Escherichia coli rRNA transcription. I. Kinetic analysis of the roles of the upstream activator region and supercoiling on transcription of the rrnB P1 promoter in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):555–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90100-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiklejohn A. L., Gralla J. D. Activation of the lac promoter and its variants. Synergistic effects of catabolite activator protein and supercoiling in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):661–673. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Barthelemy I., Salas M. In vivo transcription of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA early and late promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90256-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuez B., Rojo F., Barthelemy I., Salas M. Identification of the sequences recognized by phage phi 29 transcriptional activator: possible interaction between the activator and the RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2337–2342. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuez B., Rojo F., Salas M. Phage phi 29 regulatory protein p4 stabilizes the binding of the RNA polymerase to the late promoter in a process involving direct protein-protein contacts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11401–11405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsen K. L., Gralla J. D. DNA melting within stable closed complexes at the Escherichia coli rrnB P1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19813–19818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D., Keener J., Kustu S. Purification of the alternative sigma factor, sigma 54, from Salmonella typhimurium and characterization of sigma 54-holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19510–19518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling and prokaryotic transcription. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Salas M. A DNA curvature can substitute phage phi 29 regulatory protein p4 when acting as a transcriptional repressor. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3429–3438. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Salas M., Hermoso J. M. A novel nucleoprotein complex at a replication origin. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1012–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.2111580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Inciarte M. R., Corral J., Viñuela E., Salas M. RNA polymerase binding sites and transcription map of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):411–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Crothers D. M. A stressed intermediate in the formation of stably initiated RNA chains at the Escherichia coli lac UV5 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Peck L. J., Becherer K. DNA supercoiling and its effects on DNA structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):85–91. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias W., Jaworski A., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. The B- to Z-DNA equilibrium in vivo is perturbed by biological processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7069–7073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





