Abstract
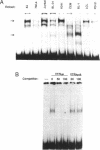
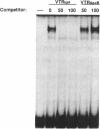
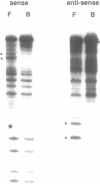
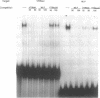
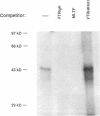
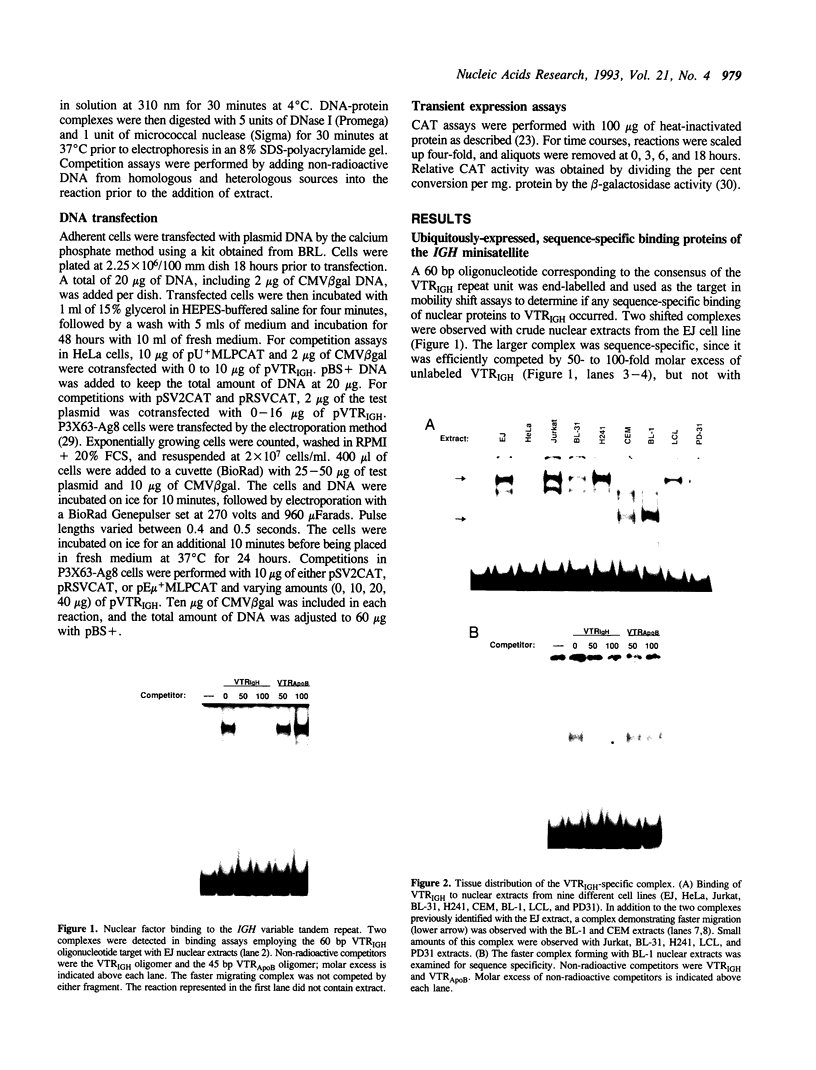
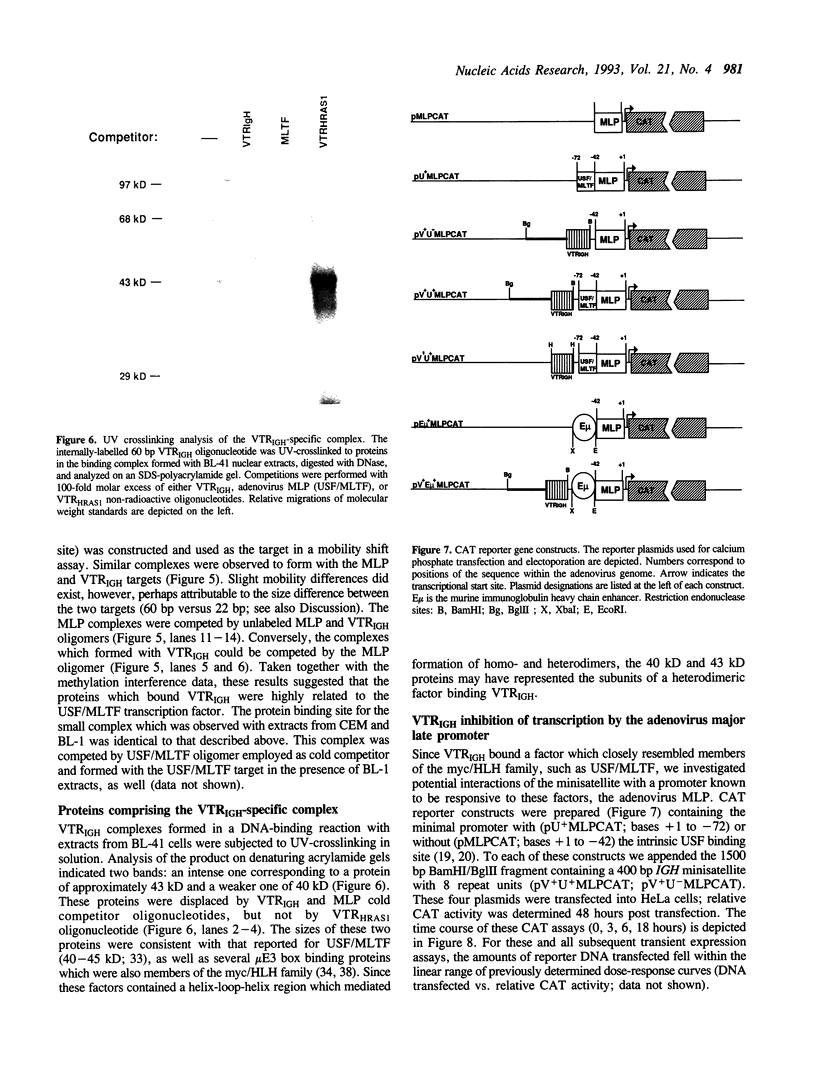
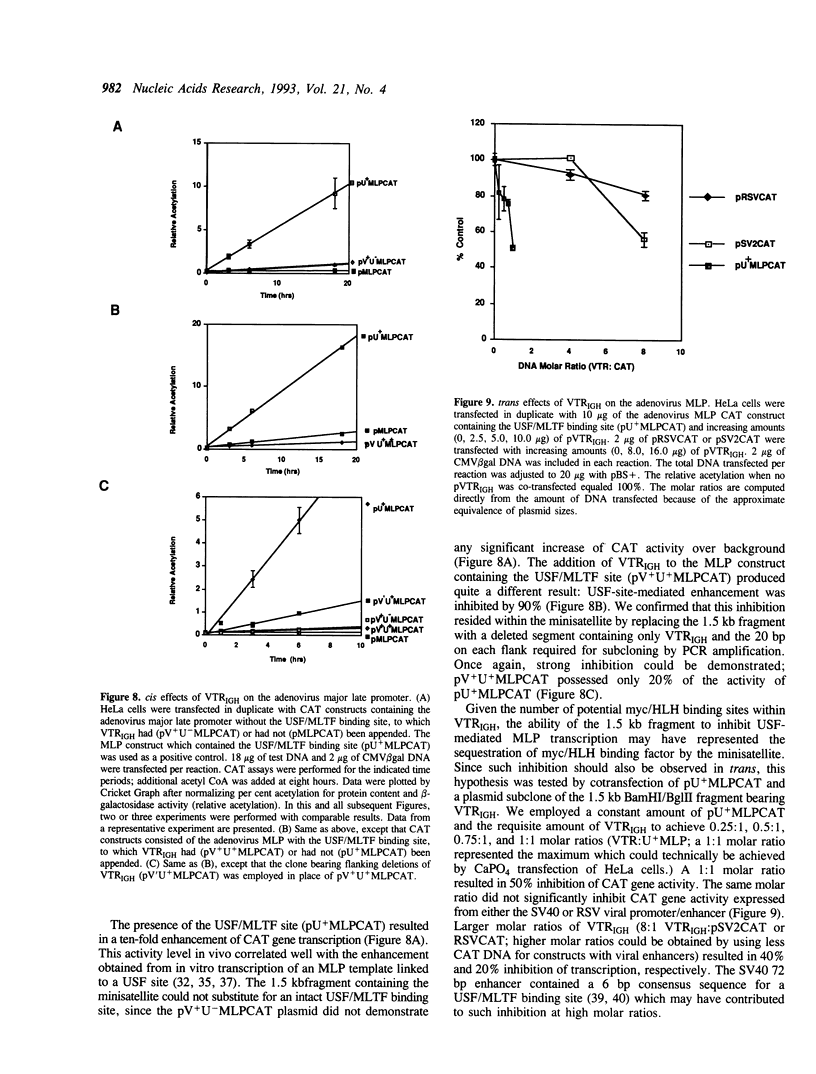
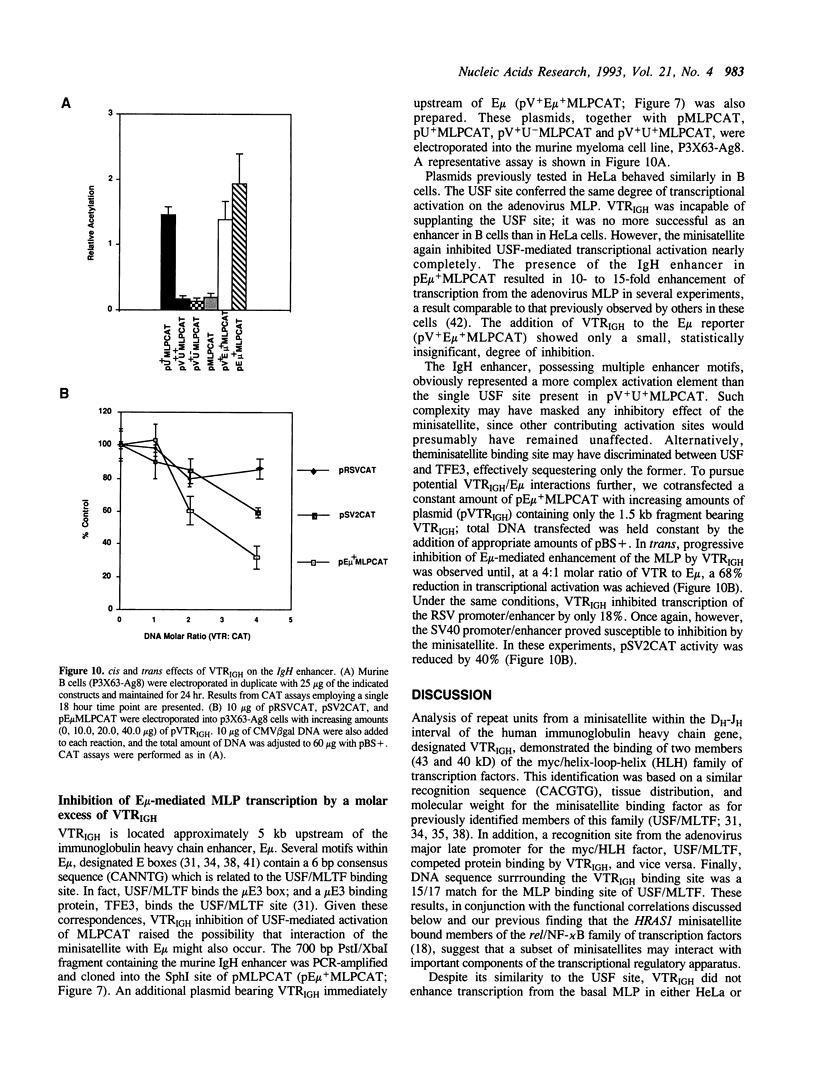
The 50bp repeat unit of the minisatellite within the DH-JH interval of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain locus binds a nuclear factor present in a wide variety of cell types. The binding site contains the myc/HLH motif, CACGTG, and represents a 15 of 17 base match for the USF/MLTF binding site adjacent to the adenovirus major late promoter (MLP). Unlike the USF/MLTF site, the IGH minisatellite possesses no enhancer activity. However, it can significantly suppress, in cis and in trans, USF-site-mediated transcriptional activation of the MLP. In murine myeloma cells, the IGH minisatellite can suppress, in trans, MLP activation by the murine heavy chain gene enhancer, E mu. These activities potentially represent a DNA-based form of squelching.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Kadesch T. The leucine zipper of TFE3 dictates helix-loop-helix dimerization specificity. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1057–1066. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):721–724. doi: 10.1038/334721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Calame K. Proteins binding to site C2 (muE3) in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer exist in multiple oligomeric forms. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):776–786. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Cohn L., Calame K. A dominant negative form of transcription activator mTFE3 created by differential splicing. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):94–97. doi: 10.1126/science.1840705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Wang X. F., Peterson C. L., Calame K. In vivo functional analysis of in vitro protein binding sites in the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3239–3253. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1817–1825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]