Abstract
We have isolated the cDNA encoding a binding protein to the sequence motif of the immunoglobulin S mu region by the southwestern method. The binding protein designated S mu bp-2 specifically binds to 5'-phosphorylated single-stranded DNA containing 5'-G and GGGG stretches. The amino acid sequence deduced from the cDNA sequence showed that the S mu bp-2 belongs to the putative helicase superfamily which is involved in replication, recombination and repair. Expression of S mu bp-2 mRNA is ubiquitous and augmented in spleen cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and interleukin 4 which also induce class switching. The S mu bp-2 gene is conserved among vertebrates. Possible involvement of S mu bp-2 in class switching is discussed.
Full text
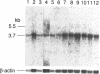
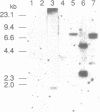
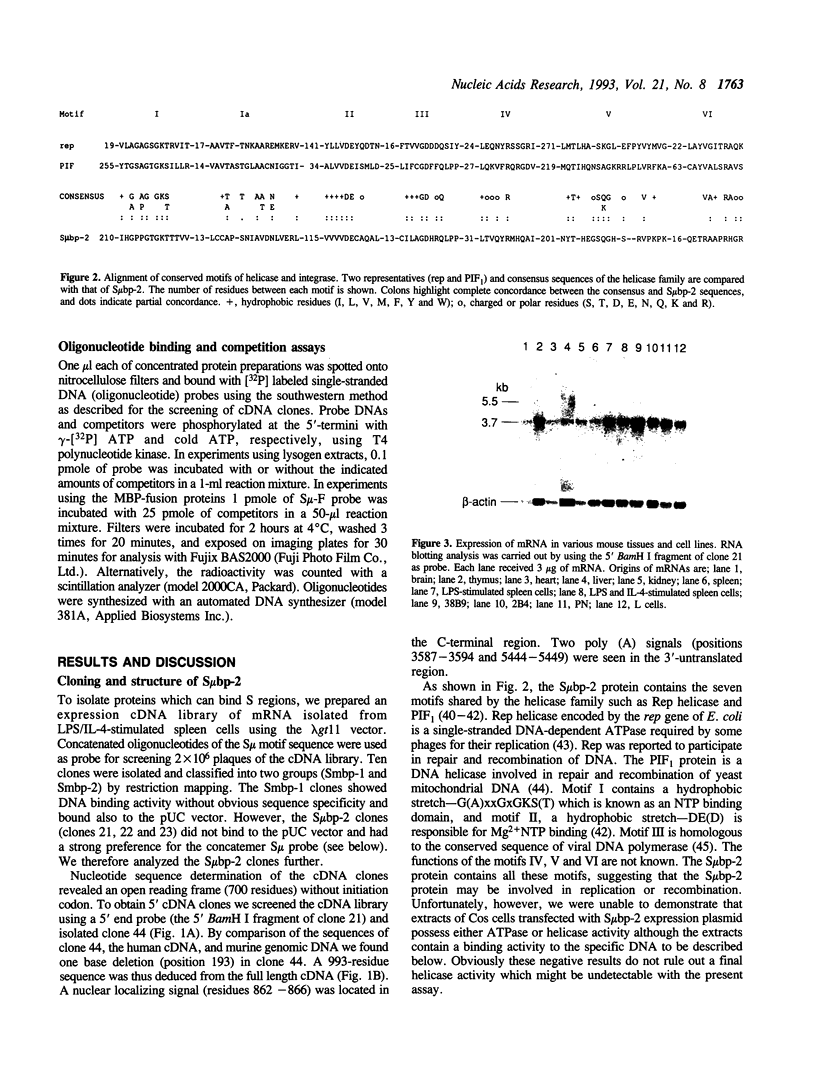
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chase J. W., Williams K. R. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins required for DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:103–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Lebman D. A., Shrader B. Transforming growth factor beta specifically enhances IgA production by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):1039–1044. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collick A., Dunn M. G., Jeffreys A. J. Minisatellite binding protein Msbp-1 is a sequence-specific single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6399–6404. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collick A., Jeffreys A. J. Detection of a novel minisatellite-specific DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):625–629. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Jackson J., Adams J. M. Deletions in the constant region locus can account for switches in immunoglobulin heavy chain expression. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):450–456. doi: 10.1038/285450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L. The mechanism of conservative site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:77–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler D., Potter H. Molecular mechanisms in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:727–761. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foury F., Lahaye A. Cloning and sequencing of the PIF gene involved in repair and recombination of yeast mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1441–1449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist C. A., Denhardt D. T. Escherichia coli rep gene: sequence of the gene, the encoded helicase, and its homology with uvrD. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):465–475. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han H., Okamoto M., Honjo T., Shimizu A. Regulated expression of immunoglobulin trans-mRNA consisting of the variable region of a transgenic mu chain and constant regions of endogenous isotypes. Int Immunol. 1991 Dec;3(12):1197–1206. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.12.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. A new superfamily of replicative proteins. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–23. doi: 10.1038/333022b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. An amino acid sequence motif linking viral DNA polymerases and plant virus proteins involved in RNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6769–6769. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Kataoka T. Organization of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes and allelic deletion model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J. L., Coleclough C., Cebra J. J. CH gene rearrangements in IgM-bearing B cells and in the normal splenic DNA component of hybridomas making different isotypes of antibody. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasato T., Arakawa H., Shimizu A., Honjo T., Yamagishi H. Biased distribution of recombination sites within S regions upon immunoglobulin class switch recombination induced by transforming growth factor beta and lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1539–1546. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasato T., Shimizu A., Honjo T., Yamagishi H. Circular DNA is excised by immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90248-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Honjo T. Rearrangement of immunoglobulin gamma 1-chain gene and mechanism for heavy-chain class switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):919–923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Miyata T., Honjo T. Repetitive sequences in class-switch recombination regions of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D., Khalili K. A recombinant cDNA derived from human brain encodes a DNA binding protein that stimulates transcription of the human neurotropic virus JCV. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15876–15881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita K., Shimizu A., Honjo T. The membrane exons of the pseudo-gamma-chain gene of the human immunoglobulin are apparently functional and highly homologous to those of the gamma 1 gene. Immunol Lett. 1991 Feb;27(2):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(91)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yokota T., Otsuka T., Meyerson P., Villaret D., Coffman R., Mosmann T., Rennick D., Roehm N., Smith C. Isolation and characterization of a mouse interleukin cDNA clone that expresses B-cell stimulatory factor 1 activities and T-cell- and mast-cell-stimulating activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2061–2065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Yoshida K., Maeda T., Usuda S., Sakano H. Switch circular DNA formed in cytokine-treated mouse splenocytes: evidence for intramolecular DNA deletion in immunoglobulin class switching. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90247-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Brooker J. S., Camerini-Otero R. D. Sequences of human immunoglobulin switch regions: implications for recombination and transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7305–7316. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P. The role of recombinational hotspots in genome instability in mammalian cells. Bioessays. 1990 Dec;12(12):577–581. doi: 10.1002/bies.950121204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Nakai S., Honjo T. Switch region of immunoglobulin Cmu gene is composed of simple tandem repetitive sequences. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):845–848. doi: 10.1038/292845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequences of switch regions of immunoglobulin C epsilon and C gamma genes and their comparison. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7322–7329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma Y., Sideras P., Naito T., Bergstedt-Lindquist S., Azuma C., Severinson E., Tanabe T., Kinashi T., Matsuda F., Yaoita Y. Cloning of cDNA encoding the murine IgG1 induction factor by a novel strategy using SP6 promoter. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):640–646. doi: 10.1038/319640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Sablitzky F. Deletion of Cmu genes in mouse B lymphocytes upon stimulation with LPS. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1929–1935. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Honjo T. Immunoglobulin class switching. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):801–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Chi hotspots of generalized recombination. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):709–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90525-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Finkelman F. D., Paul W. E. Differential regulation of IgG1 and IgE synthesis by interleukin 4. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):183–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Taniguchi H., Yoda K., Shimizu M., Sakiyama S. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for mouse cytoskeletal beta-actin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2829–2829. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahls W. P., Swenson G., Moore P. D. Two hypervariable minisatellite DNA binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3269–3274. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahls W. P., Wallace L. J., Moore P. D. Hypervariable minisatellite DNA is a hotspot for homologous recombination in human cells. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90719-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Maizels N. LR1, a lipopolysaccharide-responsive factor with binding sites in the immunoglobulin switch regions and heavy-chain enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2353–2361. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuerffel R. A., Nathan A. T., Kenter A. L. Detection of an immunoglobulin switch region-specific DNA-binding protein in mitogen-stimulated mouse splenic B cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1714–1718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Deletion of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes from expressed allelic chromosome. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):850–853. doi: 10.1038/286850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Matsuoka M., Usuda S., Mori A., Ishizaka K., Sakano H. Immunoglobulin switch circular DNA in the mouse infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: evidence for successive class switching from mu to epsilon via gamma 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7829–7833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Schwedler U., Jäck H. M., Wabl M. Circular DNA is a product of the immunoglobulin class switch rearrangement. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):452–456. doi: 10.1038/345452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]