Abstract
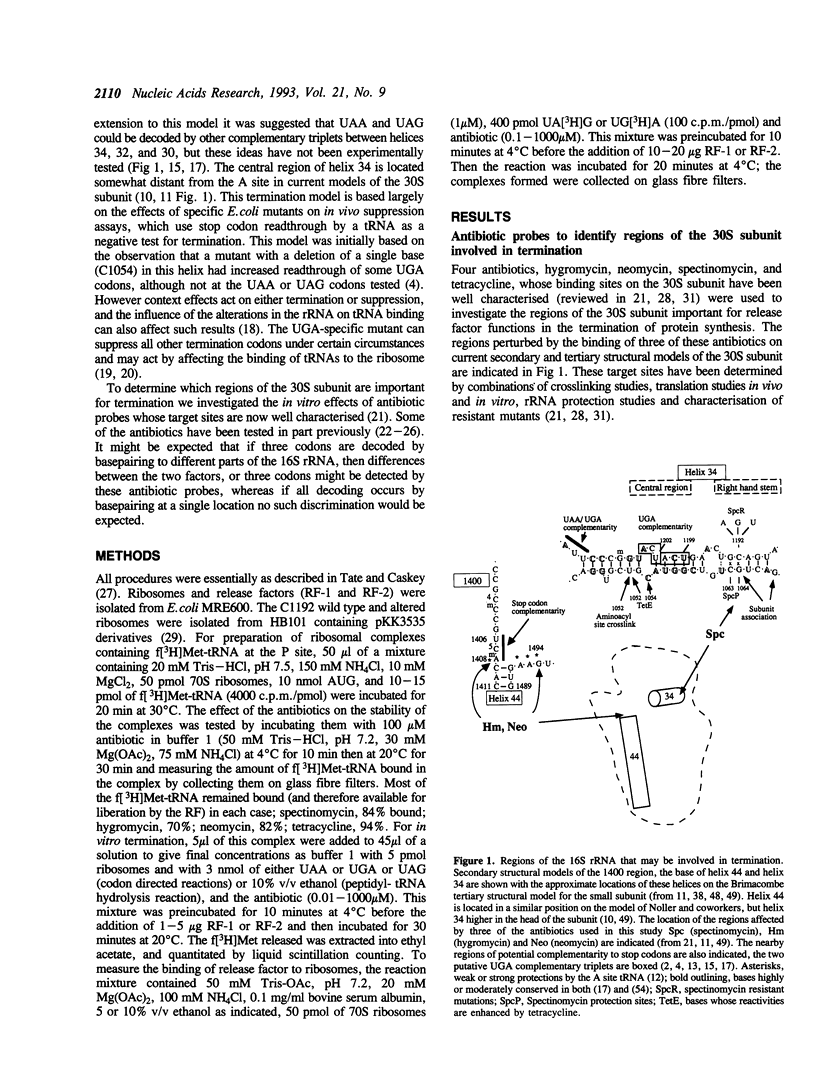
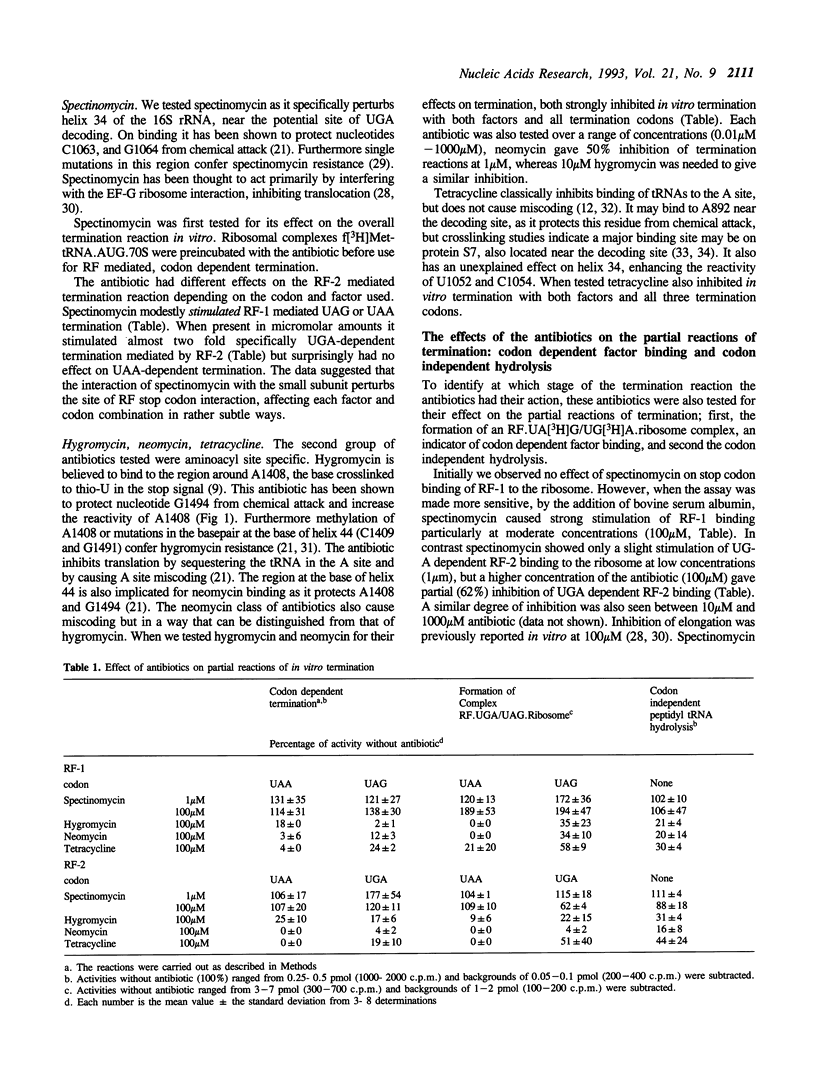
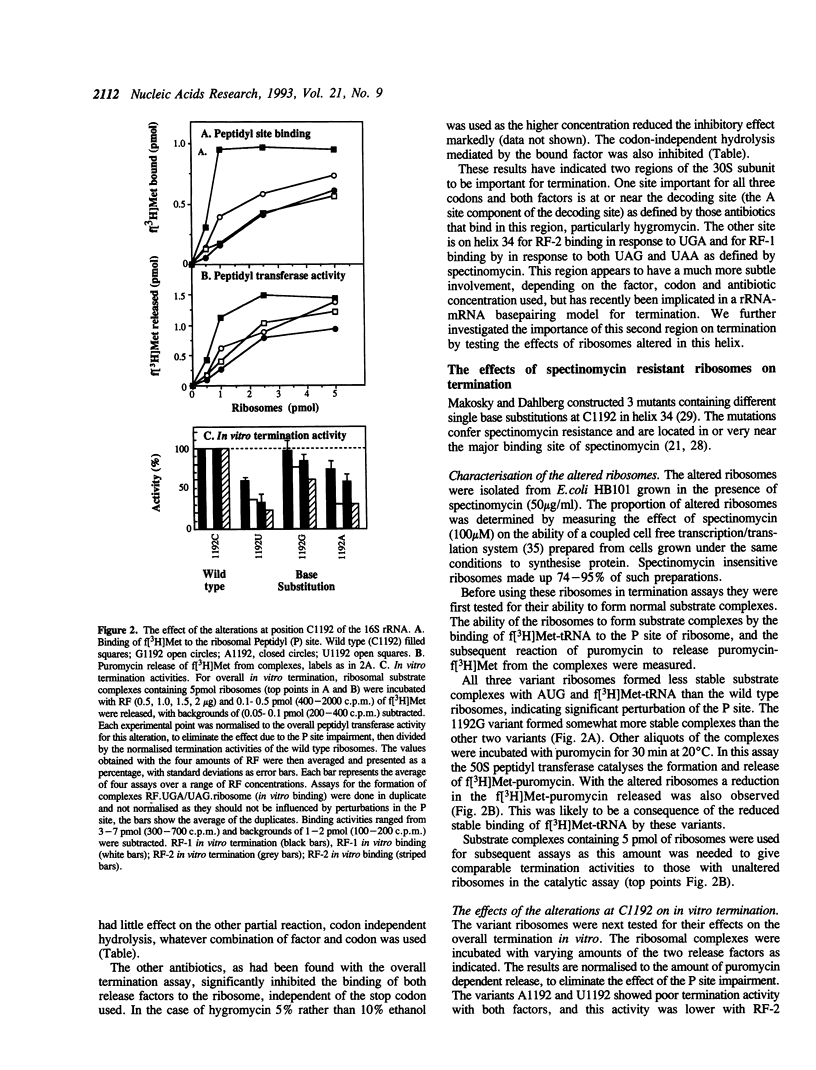
Two regions of the 16S rRNA, helix 34, and the aminoacyl site component of the decoding site at the base of helix 44, have been implicated in decoding of translational stop signals during the termination of protein synthesis. Antibiotics specific for these regions have been tested to see how they discriminate the decoding of UAA, UAG, and UGA by the two polypeptide chain release factors (RF-1 and RF-2). Spectinomycin, which interacts with helix 34, stimulated RF-1 dependent binding to the ribosome and termination. It also stimulated UGA dependent RF-2 termination at micromolar concentrations but inhibited UGA dependent RF-2 binding at higher concentrations. Alterations at position C1192 of helix 34, known to confer spectinomycin resistance, reduced the binding of f[3H]Met-tRNA to the peptidyl-tRNA site. They also impaired termination in vitro, with both factors and all three stop codons, although the effect was greater with RF-2 mediated reactions. These alterations had previously been shown to inhibit EF-G mediated translocation. As perturbations in helix 34 effect both termination and elongation reactions, these results indicate that helix 34 is close to the decoding site on the bacterial ribosome. Several antibiotics, hygromycin, neomycin and tetracycline, specific for the aminoacyl site, were shown to inhibit the binding and function of both RFs in termination with all three stop codons in vitro. These studies indicate that decoding of all stop signals is likely to occur at a similar site on the ribosome to the decoding of sense codons, the aminoacyl site, and are consistent with a location for helix 34 near this site.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Davies J., Davis B. D. Effect of spectinomycin on polypeptide synthesis in extracts of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudin F., Ehresmann C., Romby P., Mougel M., Colin J., Lempereur L., Bachellerie J. P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Higher-order structure of domain III in Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA, 30S subunit and 70S ribosome. Biochimie. 1987 Oct;69(10):1081–1096. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudin F., Mougel M., Romby P., Eyermann F., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Probing the phosphates of the Escherichia coli ribosomal 16S RNA in its naked form, in the 30S subunit, and in the 70S ribosome. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5847–5855. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhangu R., Wollenzien P. The mRNA binding track in the Escherichia coli ribosome for mRNAs of different sequences. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 30;31(25):5937–5944. doi: 10.1021/bi00140a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin N., Richter A. A., Ehrenberg M., Dahlberg A. E., Kurland C. G. Ribosomal RNA and protein mutants resistant to spectinomycin. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):735–739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Gornicki P., Greuer B., Mitchell P., Osswald M., Rinke-Appel J., Schüler D., Stade K. The three-dimensional structure and function of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA, as studied by cross-linking techniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):8–13. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90133-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Mitchell P., Osswald M., Stade K., Bochkariov D. Clustering of modified nucleotides at the functional center of bacterial ribosomal RNA. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):161–167. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R. Structure-function correlations (and discrepancies) in the 16S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1992 Apr;74(4):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90109-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R. The emerging three-dimensional structure and function of 16S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4207–4214. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M. A., Cooperman B. S. Single protein omission reconstitution studies of tetracycline binding to the 30S subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5374–5379. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham K., Chung D. G., Neilson T., Ganoza M. C. Recognition of translational termination signals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 14;909(2):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham R. H. Codon context. Experientia. 1990 Dec 1;46(11-12):1126–1133. doi: 10.1007/BF01936922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigen W. J., Lee C. C., Caskey C. T. Recent advances in peptide chain termination. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):861–865. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E. The functional role of ribosomal RNA in protein synthesis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Stasio E. A., Moazed D., Noller H. F., Dahlberg A. E. Mutations in 16S ribosomal RNA disrupt antibiotic--RNA interactions. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1213–1216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dontsova O., Dokudovskaya S., Kopylov A., Bogdanov A., Rinke-Appel J., Jünke N., Brimacombe R. Three widely separated positions in the 16S RNA lie in or close to the ribosomal decoding region; a site-directed cross-linking study with mRNA analogues. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3105–3116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dontsova O., Kopylov A., Brimacombe R. The location of mRNA in the ribosomal 30S initiation complex; site-directed cross-linking of mRNA analogues carrying several photo-reactive labels simultaneously on either side of the AUG start codon. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2613–2620. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07803.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Schiltz E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XXVII. Localization of the amino acid exchanges in protein S5 from two Escherichia coli mutants resistant to spectinomycin. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):106–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00332781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Buckingham K., Hader P., Neilson T. Effect of base sequence on in vitro protein-chain termination. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14101–14104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geigenmüller U., Nierhaus K. H. Tetracycline can inhibit tRNA binding to the ribosomal P site as well as to the A site. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):723–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göringer H. U., Hijazi K. A., Murgola E. J., Dahlberg A. E. Mutations in 16S rRNA that affect UGA (stop codon)-directed translation termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6603–6607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göringer H. U., Hijazi K. A., Murgola E. J., Dahlberg A. E. Mutations in 16S rRNA that affect UGA (stop codon)-directed translation termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6603–6607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Chapman N. M., Noller H. F. Mechanism of ribosomal subunit association: discrimination of specific sites in 16 S RNA essential for association activity. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 5;130(4):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A. S., Eaton D. H., de Boer H. A. Mutagenesis at the mRNA decoding site in the 16S ribosomal RNA using the specialized ribosome system in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4383–4388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03337.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänfler A., Kleuvers B., Göringer H. U. The involvement of base 1054 in 16S rRNA for UGA stop codon dependent translational termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5625–5632. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makosky P. C., Dahlberg A. E. Spectinomycin resistance at site 1192 in 16S ribosomal RNA of E. coli: an analysis of three mutants. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):885–889. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Binding of tRNA to the ribosomal A and P sites protects two distinct sets of nucleotides in 16 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90016-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Stern S., Noller H. F. Rapid chemical probing of conformation in 16 S ribosomal RNA and 30 S ribosomal subunits using primer extension. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):399–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat J. G., Timms K. M., Trotman C. N., Tate W. P. Interaction of the release factors with the Escherichia coli ribosome: structurally and functionally-important domains. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):1113–1120. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90154-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgola E. J., Hijazi K. A., Göringer H. U., Dahlberg A. E. Mutant 16S ribosomal RNA: a codon-specific translational suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4162–4165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., De Rijk P., Goris A., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):1987–2015. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Overbeek R., Larsen N., Marsh T. L., McCaughey M. J., Maciukenas M. A., Kuan W. M., Macke T. J., Xing Y., Woese C. R. The Ribosomal Database Project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2199–2200. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrullo L. A., Gallagher P. J., Elseviers D. The role of 2-methylthio-N6-isopentenyladenosine in readthrough and suppression of nonsense codons in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):289–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00330653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott C. D., Kleuvers B., Göringer H. U. A rRNA-mRNA base pairing model for UGA-dependent termination. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):1121–1129. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90155-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott C. D., Kornau H. C. Mutations in E.coli 16s rRNA that enhance and decrease the activity of a suppressor tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1567–1571. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott C., Krabben L., Nierhaus K. Ribosomes containing the C1054-deletion mutation in E. coli 16S rRNA act as suppressors at all three nonsense codons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5281–5283. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., White S. W. The structure of ribosomal protein S5 reveals sites of interaction with 16S rRNA. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):768–771. doi: 10.1038/358768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stade K., Rinke-Appel J., Brimacombe R. Site-directed cross-linking of mRNA analogues to the Escherichia coli ribosome; identification of 30S ribosomal components that can be cross-linked to the mRNA at various points 5' with respect to the decoding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9889–9908. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Weiser B., Noller H. F. Model for the three-dimensional folding of 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):447–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90588-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W. P., Brown C. M. Translational termination: "stop" for protein synthesis or "pause" for regulation of gene expression. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2443–2450. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W. P., Hornig H., Lührmann R. Recognition of termination codon by release factor in the presence of a tRNA-occupied A site. Evidence for flexibility in accommodation of the release factor on the ribosome. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10360–10365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W. P., McCaughan K. K., Kastner B., Trotman C. N., Stoffler-Meilicke M., Stoffler G. Interaction of the release factor with the Escherichia coli ribosome: inhibition of the 30S subunit domain by specific antibodies. Biochem Int. 1988 Jul;17(1):179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W., Greuer B., Brimacombe R. Codon recognition in polypeptide chain termination: site directed crosslinking of termination codon to Escherichia coli release factor 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6537–6544. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins R. K., Scolnick E. M., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination. VII. The ribosomal and release factor requirements for peptide release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):702–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara Y., Hori M., Umezawa H. Specific inhibition of the termination process of protein synthesis by negamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 18;442(2):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


