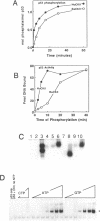
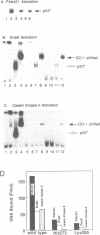
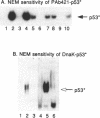
Abstract
Wild type p53 assembles into a latent multiprotein complex which can be activated for sequence-specific DNA binding in vitro by proteins targeting the carboxy-terminal domain. Using an optimized system coupling the post-translational modification of wild type p53 to activation of sequence specific DNA binding, we examined the affects of common mutations on the cryptic DNA binding function of p53. Two mutant forms of p53 were shown to be efficiently converted from the latent state by PAb421 and DnaK, but were defective in activation by casein kinase II, indicating that mutant p53 may not be receptive to allosteric regulation by casein kinase II phosphorylation. A reactive sulfhydryl group is absolutely required for DNA binding by wild type and mutant forms of p53 once converted to the activated state. Together, these data show that some mutant forms of p53 harbour the wild-type machinery required to engage in sequence-specific DNA binding and define a signalling pathway whose inactivation may directly result in a loss of p53 function.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Y., Juven T., Haffner R., Oren M. mdm2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):461–468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Delphin C., Grunwald D., Khochbin S., Lawrence J. J. Characterization of the tumor suppressor protein p53 as a protein kinase C substrate and a S100b-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11627–11631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Casso D., Beach D. Human p53 inhibits growth in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1405–1411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borellini F., Glazer R. I. Induction of Sp1-p53 DNA-binding heterocomplexes during granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-dependent proliferation in human erythroleukemia cell line TF-1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7923–7928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Santoro N., Marshak D. R. Regulating cell growth: casein-kinase-II-dependent phosphorylation of nuclear oncoproteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):91–95. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. F., Cheng K., Frey A. B., Stein R., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. Purification of complexes of nuclear oncogene p53 with rat and Escherichia coli heat shock proteins: in vitro dissociation of hsc70 and dnaK from murine p53 by ATP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1206–1215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Harvey M., Slagle B. L., McArthur M. J., Montgomery C. A., Jr, Butel J. S., Bradley A. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but susceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):215–221. doi: 10.1038/356215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer G., Bargonetti J., Zhu H., Friedman P., Prywes R., Prives C. Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):83–86. doi: 10.1038/358083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. N., Chen X., Bargonetti J., Prives C. The p53 protein is an unusually shaped tetramer that binds directly to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Milner J. Interaction of heat-shock protein 70 with p53 translated in vitro: evidence for interaction with dimeric p53 and for a role in the regulation of p53 conformation. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3513–3520. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., McKee P. H., Menage H. D., Dover R., Lane D. P. High levels of p53 protein in UV-irradiated normal human skin. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang D. S., Crooke E., Kornberg A. Aggregated dnaA protein is dissociated and activated for DNA replication by phospholipase or dnaK protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19244–19248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandror K. V., Benumov A. O., Stepanov A. S. Casein kinase II from Rana temporaria oocytes. Intracellular localization and activity during progesterone-induced maturation. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Baker S. J., Nigro J. M., Rotter V., Levine A. J., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Mutant p53 proteins bind DNA abnormally in vitro. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraiss S., Quaiser A., Oren M., Montenarh M. Oligomerization of oncoprotein p53. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4737–4744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4737-4744.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb P., Crawford L. Characterization of the human p53 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1379–1385. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Benchimol S. p53: oncogene or anti-oncogene? Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):1–8. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees-Miller S. P., Chen Y. R., Anderson C. W. Human cells contain a DNA-activated protein kinase that phosphorylates simian virus 40 T antigen, mouse p53, and the human Ku autoantigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6472–6481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone L. R., White A., Sprouse J., Livanos E., Jacks T., Tlsty T. D. Altered cell cycle arrest and gene amplification potential accompany loss of wild-type p53. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):923–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Park S. H., Thompson T. C., Lane D. P. Ras-induced hyperplasia occurs with mutation of p53, but activated ras and myc together can induce carcinoma without p53 mutation. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90541-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macilwain C. OTA panel opens inquiry into patenting of genes. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):386–386. doi: 10.1038/362386b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Li F. P., Strong L. C., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Nelson C. E., Kim D. H., Kassel J., Gryka M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Tainsky M. A. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltzman W., Czyzyk L. UV irradiation stimulates levels of p53 cellular tumor antigen in nontransformed mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1689–1694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Klausner R. D., Howley P. M. Conserved cysteine residue in the DNA-binding domain of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 protein confers redox regulation of the DNA-binding activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7531–7535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Simon S., Kikkawa U., Eckhart W. The p53 tumour suppressor protein is phosphorylated at serine 389 by casein kinase II. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3253–3260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisner H., Czech M. P. Phosphorylation of transcriptional factors and cell-cycle-dependent proteins by casein kinase II. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):474–483. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90076-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne D. M., Palmer R. H., Campbell D. G., Meek D. W. Phosphorylation of the p53 tumour-suppressor protein at three N-terminal sites by a novel casein kinase I-like enzyme. Oncogene. 1992 Jul;7(7):1361–1369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne D. M., Palmer R. H., Meek D. W. Mutation of the casein kinase II phosphorylation site abolishes the anti-proliferative activity of p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5565–5570. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulner-Lorillon O., Cormier P., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Poulhe R., Osborne H., Bellé R. M-phase-specific cdc2 protein kinase phosphorylates the beta subunit of casein kinase II and increases casein kinase II activity. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 24;193(2):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A. Casein kinase 2: an 'eminence grise' in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schärer E., Iggo R. Mammalian p53 can function as a transcription factor in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1539–1545. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Usheva A., Zambetti G. P., Momand J., Horikoshi N., Weinmann R., Levine A. J., Shenk T. Wild-type p53 binds to the TATA-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12028–12032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulian E., Zauberman A., Ginsberg D., Oren M. Identification of a minimal transforming domain of p53: negative dominance through abrogation of sequence-specific DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5581–5592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Bovey R., Tardy S., Sahli R., Sordat B., Costa J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., May P. Structural aspects of the p53 protein in relation to gene evolution. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):945–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Evans A., Jenkins J. R. Precise epitope mapping of the murine transformation-associated protein, p53. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):699–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Curran T. Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):653–665. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Y., Tainsky M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Strong L. C., Wahl G. M. Wild-type p53 restores cell cycle control and inhibits gene amplification in cells with mutant p53 alleles. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Grunwald D., Wilder S., Kimchi A., May E., Lawrence J. J., May P., Oren M. p53-mediated cell death: relationship to cell cycle control. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1415–1423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]