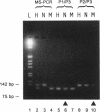
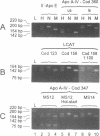
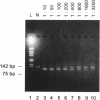
Abstract
With increasing knowledge about the causal role of genetic defects in clinical diseases the necessity is apparent to have procedures for rapid diagnosis of point mutations. We developed a PCR-based technique, whereby both normal and mutant alleles can be amplified in the same reaction tube, using different length allele-specific primers. Furthermore the allele-specific primers introduce additional deliberate differences into the allelic PCR-products that drastically reduce crossreactions in subsequent cycles. This mutagenesis separates the amplification reactions of the alleles performed in the same tube. Subsequent identification of the PCR-products is done by gel electrophoresis and shows at least one of the two allelic products. Therefore, in addition to simple handling, MS-PCR provides a within-assay quality control for the exclusion of false negative results. The feasibility of this technique has been tested using six different mutations. The high sensitivity of MS-PCR also allows screening for mutation carriers in pooled DNA samples.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barany F. Genetic disease detection and DNA amplification using cloned thermostable ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):189–193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Yang C. Y., Chen P. F., Setzer D., Tanimura M., Li W. H., Gotto A. M., Jr, Chan L. The complete cDNA and amino acid sequence of human apolipoprotein B-100. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):12918–12921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Q., Russell M., Birch D. E., Raymond J., Bloch W. Prevention of pre-PCR mis-priming and primer dimerization improves low-copy-number amplifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1717–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlen T., Dubeau L. Detection of ras point mutations by polymerase chain reaction using mutation-specific, inosine-containing oligonucleotide primers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Walker D. W., Paik Y. K., Boguski M. S., Freeman M., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Structure and expression of the human apolipoprotein A-IV gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7973–7981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrie R. M., Schwarz M. J., Robertson N. H., Vaudin S., Super M., Malone G., Little S. Development, multiplexing, and application of ARMS tests for common mutations in the CFTR gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):251–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funke H., von Eckardstein A., Pritchard P. H., Hornby A. E., Wiebusch H., Motti C., Hayden M. R., Dachet C., Jacotot B., Gerdes U. Genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) deficiency. Six newly identified defective alleles further contribute to the structural heterogeneity in this disease. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):677–683. doi: 10.1172/JCI116248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Nguyen P. N., Caskey C. T. Detection of single DNA base differences by competitive oligonucleotide priming. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2437–2448. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guatelli J. C., Whitfield K. M., Kwoh D. Y., Barringer K. J., Richman D. D., Gingeras T. R. Isothermal, in vitro amplification of nucleic acids by a multienzyme reaction modeled after retroviral replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1874–1878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Bersot T. P., Krauss R. M., Vega G. L., Grundy S. M., Friedl W., Davignon J., McCarthy B. J. Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100: a mutation of apolipoprotein B that causes hypercholesterolemia. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1337–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Weisgraber K. H., Arnold K. S., Mahley R. W., Krauss R. M., Vega G. L., Grundy S. M. Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100: low density lipoproteins with abnormal receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6919–6923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Barbacid M. Oncogene detection at the single cell level. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):647–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Kellogg D. E., McKinney N., Spasic D., Goda L., Levenson C., Sninsky J. J. Effects of primer-template mismatches on the polymerase chain reaction: human immunodeficiency virus type 1 model studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):999–1005. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1155–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.2479983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J., Wion K., Drayna D., Fielding C., Lawn R. Human lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase gene: complete gene sequence and sites of expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9397–9406. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motti C., Funke H., Rust S., Dergunov A., Assmann G. Using mutagenic polymerase chain reaction primers to detect carriers of familial defective apolipoprotein B-100. Clin Chem. 1991 Oct;37(10 Pt 1):1762–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. R., Graham A., Heptinstall L. E., Powell S. J., Summers C., Kalsheker N., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2503–2516. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik Y. K., Chang D. J., Reardon C. A., Davies G. E., Mahley R. W., Taylor J. M. Nucleotide sequence and structure of the human apolipoprotein E gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster H., Rauh G., Kormann B., Hepp T., Humphries S., Keller C., Wolfram G., Zöllner N. Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100. Comparison with familial hypercholesterolemia in 18 cases detected in Munich. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Jul-Aug;10(4):577–581. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.4.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria L. F., Ludwig E. H., Clarke H. R., Vega G. L., Grundy S. M., McCarthy B. J. Association between a specific apolipoprotein B mutation and familial defective apolipoprotein B-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):587–591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J., Wentworth D., Neaton J. D. Is relationship between serum cholesterol and risk of premature death from coronary heart disease continuous and graded? Findings in 356,222 primary screenees of the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT). JAMA. 1986 Nov 28;256(20):2823–2828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tybjaerg-Hansen A., Gallagher J., Vincent J., Houlston R., Talmud P., Dunning A. M., Seed M., Hamsten A., Humphries S. E., Myant N. B. Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100: detection in the United Kingdom and Scandinavia, and clinical characteristics of ten cases. Atherosclerosis. 1990 Jan;80(3):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(90)90031-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eckardstein A., Funke H., Schulte M., Erren M., Schulte H., Assmann G. Nonsynonymous polymorphic sites in the apolipoprotein (apo) A-IV gene are associated with changes in the concentration of apo B- and apo A-I-containing lipoproteins in a normal population. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):1115–1128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]