Abstract
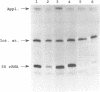
Six human 5S rRNA genes and gene variants and one pseudogene have been sequenced. The six genes/variants were transcribed in a HeLa cell extract with about equal efficiency. Three genes contain the Sp1 binding sequence GGGCGG in position -43 to -38 and three genes contain the Sp1 like sequence GGGCCG in this position. The six genes contain furthermore one Sp1 binding site in a position about -245 and one ATF recognition site in a position about -202. A 12 bp sequence (GGCTCTTGGGGC) found in position -32 to -21 strongly influenced the transcriptional efficiency in vitro. This 12-mer, designated the D box, has also been found upstream a 5S rRNA gene from hamster and mouse. Removal of the Sp1 binding sites had no effect on the transcription in vitro whereas the transcriptional efficiency decreased to 10% if the D box was removed from the human 5S rRNA gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold G. J., Kahnt B., Herrenknecht K., Gross H. J. A variant gene and a pseudogene for human 5S RNA are transcriptionally active in vitro. Gene. 1987;60(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Brown W. L., Groudine M. Accurate, TATA box-dependent polymerase III transcription from promoters of the c-myc gene in injected Xenopus oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1179–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredow S., Kleinert H., Benecke B. J. Sequence and factor requirements for faithful in vitro transcription of human 7SL DNA. Gene. 1990 Feb 14;86(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90282-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredow S., Sürig D., Müller J., Kleinert H., Benecke B. J. Activating-transcription-factor (ATF) regulates human 7S L RNA transcription by RNA polymerase III in vivo and in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6779–6784. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sussman D. J., Zeller R., Leder P. The c-myc gene encodes superimposed RNA polymerase II and III promoters. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90586-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Tanese N., Tjian R. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):965–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90039-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran J. L., Bingle W. H., Roy K. L. The nucleotide sequences of two human 5S rRNA pseudogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6297–6297. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Roeder R. G. Isolation and genomic arrangement of active and inactive forms of mammalian 5 S RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7916–7925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Chubb A., Maroney P. A., Hannon G., Altman S., Nilsen T. W. Multiple cis-acting elements are required for RNA polymerase III transcription of the gene encoding H1 RNA, the RNA component of human RNase P. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22796–22799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., Folk W. R. Structure and organization of a mammalian 5 S gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11706–11711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heery D. M., Gannon F., Powell R. A simple method for subcloning DNA fragments from gel slices. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):173–173. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Shu M. D. Epstein-Barr virus small RNA (EBER) genes: unique transcription units that combine RNA polymerase II and III promoter elements. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90797-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelekar A., Keene J. D. Downregulation of RNA polymerase III transcription of the hY3 gene in vitro. Mol Biol Rep. 1990;14(2-3):173–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00360463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J. Transcription of Xenopus 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):101–105. doi: 10.1038/295101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R. RNA polymerase III transcription of genes that lack internal control regions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leah R., Frederiksen S., Engberg J., Sørensen P. D. Nucleotide sequence of a mouse 5S rRNA variant gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7441–7441. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little R. D., Braaten D. C. Genomic organization of human 5 S rDNA and sequence of one tandem repeat. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):376–383. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90345-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Tanaka M., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. A TBP complex essential for transcription from TATA-less but not TATA-containing RNA polymerase III promoters is part of the TFIIIB fraction. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90397-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oei S. L., Pieler T. A transcription stimulatory factor binds to the upstream region of Xenopus 5 S RNA and tRNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7485–7491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Folk W. R. Unraveling the complexities of transcription by RNA polymerase III. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):300–304. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Rothblum L., Busch H. Some gene variants for 5 S RNA are dispersed in the rat genome. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10618–10623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifart K. H., Wang L., Waldschmidt R., Jahn D., Wingender E. Purification of human transcription factor IIIA and its interaction with a chemically synthesized gene encoding human 5 S rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1702–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S. J., Garcia A. D. Transcription of the Drosophila melanogaster 5S RNA gene requires an upstream promoter and four intragenic sequence elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1266–1274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Bernués J., Lewis J. D., Mattaj I. W. Cofractionation of the TATA-binding protein with the RNA polymerase III transcription factor TFIIIB. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):5889–5898. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman D. J., Chung J., Leder P. In vitro and in vivo analysis of the c-myc RNA polymerase III promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):5045–5052. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.5045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen P. D., Frederiksen S. Characterization of human 5S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4147–4151. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen P. D., Simonsen H., Frederiksen S. Nucleotide sequence of a human 5S rRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3060–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart A. K., Fisher T. S., Pugh B. F. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are components of pol III transcription factor TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1015–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90396-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiedge H., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Weinstock P. H., Arancio O., Brosius J. Dendritic location of neural BC1 RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2093–2097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. M. Transcription of Neurospora crassa 5 S rRNA genes requires a TATA box and three internal elements. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):801–811. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90406-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P. Mechanism of TATA-binding protein recruitment to a TATA-less class III promoter. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1041–1053. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90398-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P., Rigby P. W. A role for the TATA-box-binding protein component of the transcription factor IID complex as a general RNA polymerase III transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1949–1953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E., Frank R., Blöcker H., Wang L. R., Jahn D., Seifart K. H. Complete synthesis and transcription in vitro of a gene coding for human ribosomal 5S RNA. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90482-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Bogenhagen D. F., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A quantitative assay for Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):809–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Reddy R. 5' flanking sequences of human MRP/7-2 RNA gene are required and sufficient for the transcription by RNA polymerase III. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 2;1089(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90081-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Reddy R. Genes for human U3 small nucleolar RNA contain highly conserved flanking sequences. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 1;1008(1):14–22. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]