Abstract
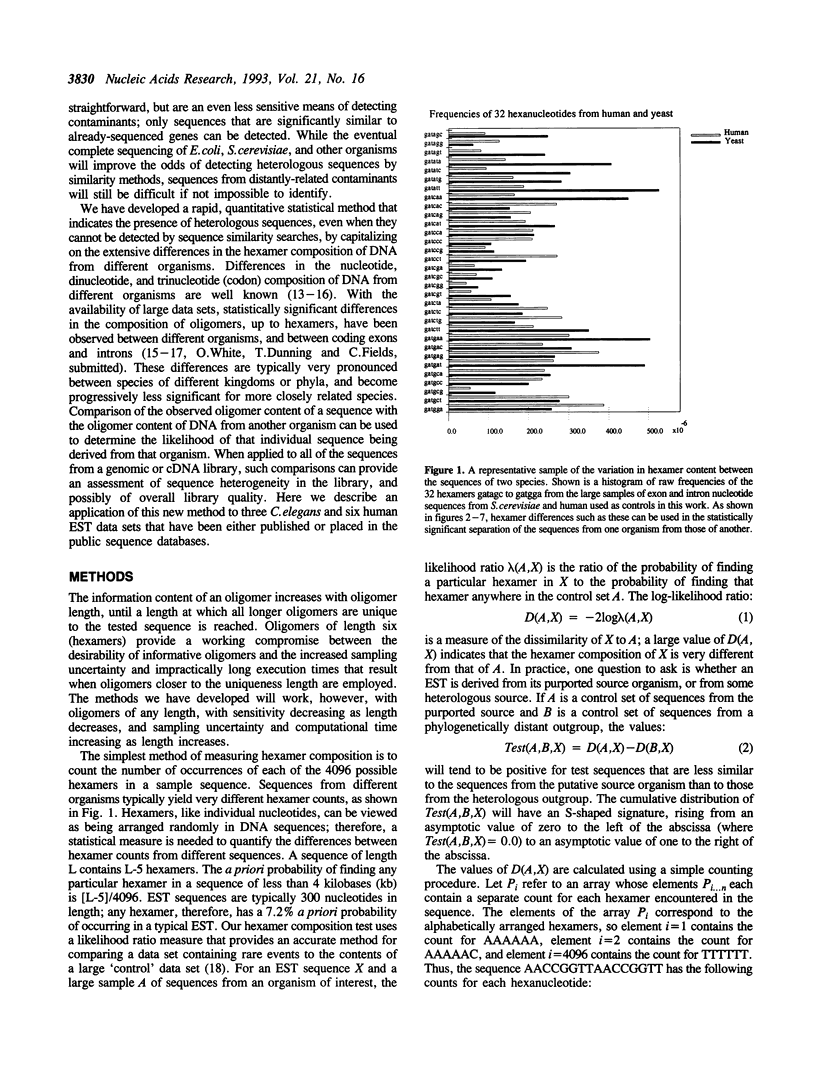
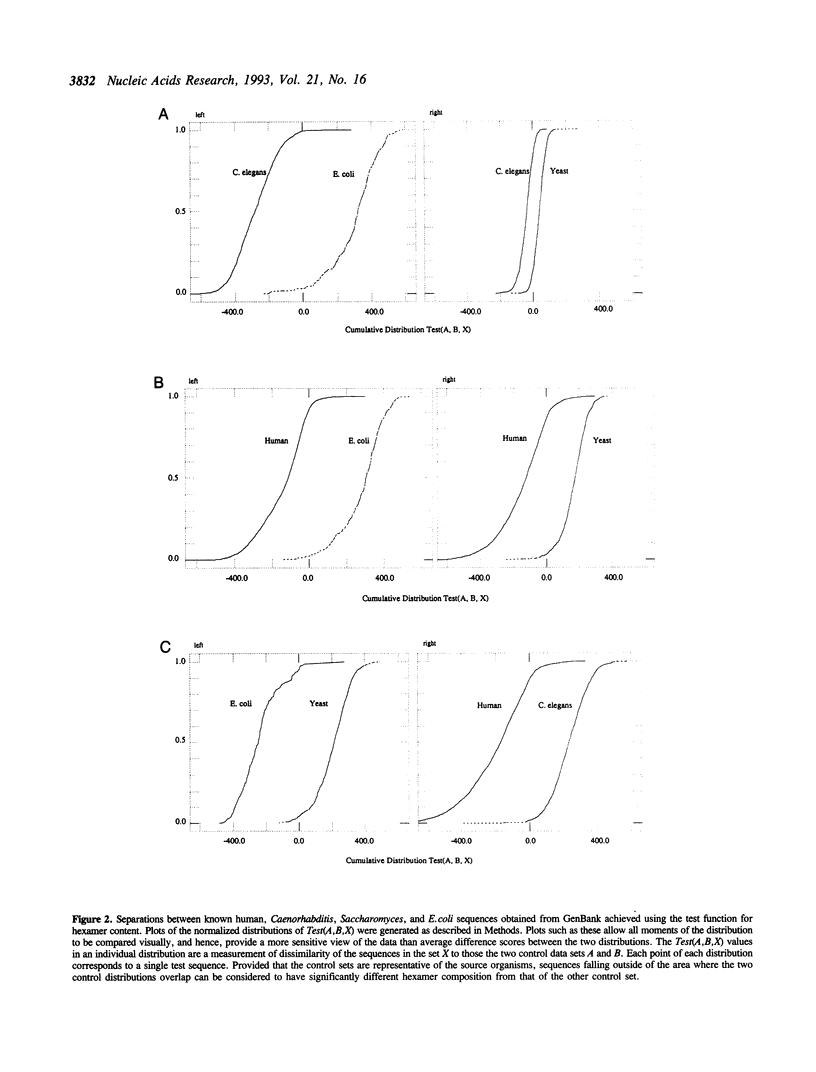
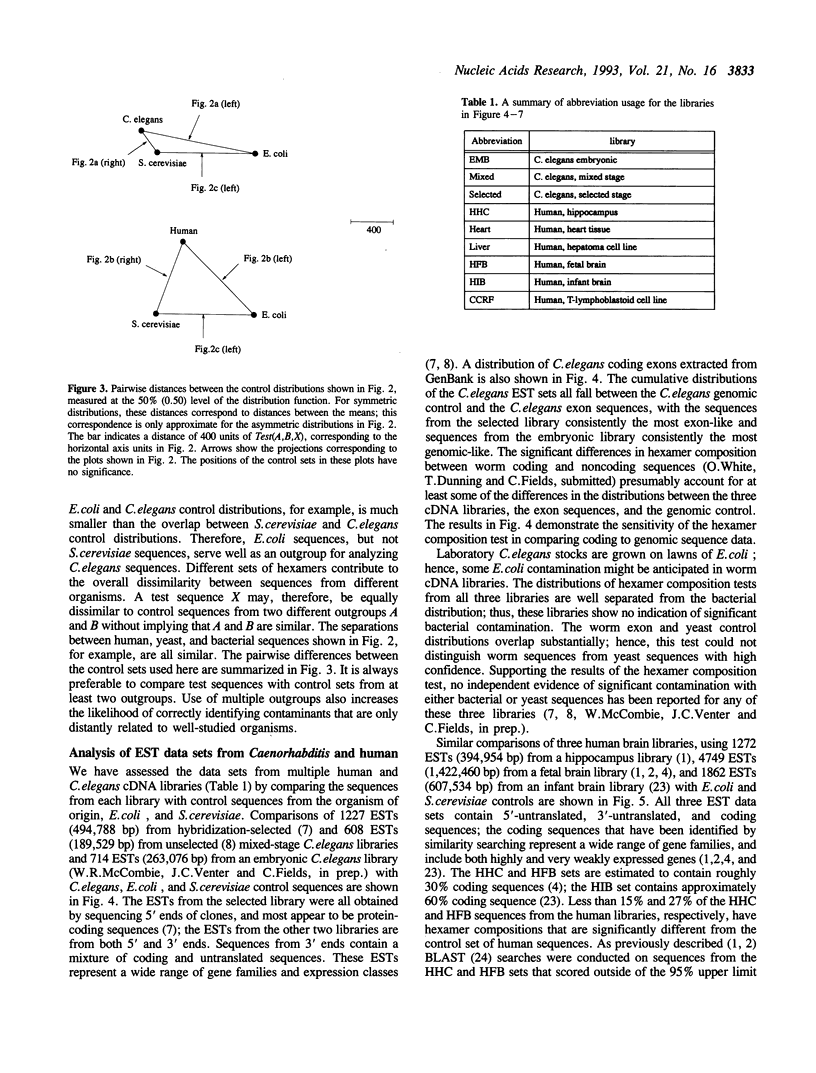
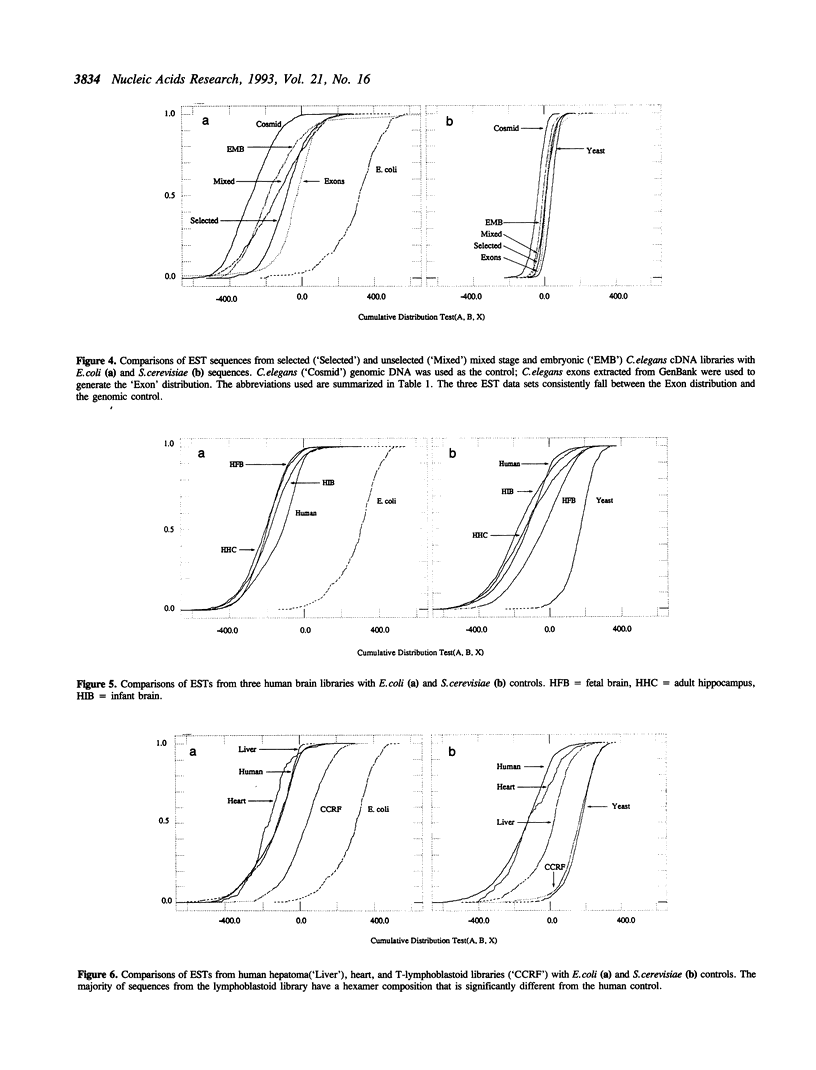
Heterologous DNA sequences from rearrangements with the genomes of host cells, genomic fragments from hybrid cells, or impure tissue sources can threaten the purity of libraries that are derived from RNA or DNA. Hybridization methods can only detect contaminants from known or suspected heterologous sources, and whole library screening is technically very difficult. Detection of contaminating heterologous clones by sequence alignment is only possible when related sequences are present in a known database. We have developed a statistical test to identify heterologous sequences that is based on the differences in hexamer composition of DNA from different organisms. This test does not require that sequences similar to potential heterologous contaminants are present in the database, and can in principle detect contamination by previously unknown organisms. We have applied this test to the major public expressed sequence tag (EST) data sets to evaluate its utility as a quality control measure and a peer evaluation tool. There is detectable heterogeneity in most human and C.elegans EST data sets but it is not apparently associated with cross-species contamination. However, there is direct evidence for both yeast and bacterial sequence contamination in some public database sequences annotated as human. Results obtained with the hexamer test have been confirmed with similarity searches using sequences from the relevant data sets.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Moreno R., Kelley J. M., Utterback T. R., Nagle J. W., Fields C., Venter J. C. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):632–634. doi: 10.1038/355632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams M. D., Kelley J. M., Gocayne J. D., Dubnick M., Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Merril C. R., Wu A., Olde B., Moreno R. F. Complementary DNA sequencing: expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1651–1656. doi: 10.1126/science.2047873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benian G. M., Kiff J. E., Neckelmann N., Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegans. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):45–50. doi: 10.1038/342045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge C., Campbell A. M., Karlin S. Over- and under-representation of short oligonucleotides in DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1358–1362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., Barnes T. M. Introns in sequence tags. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):367–368. doi: 10.1038/357367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., Barnes T. M. Introns in sequence tags. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):367–368. doi: 10.1038/357367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen R., Ratto A., Baroin A., Perasso R., Grell K. G., Adoutte A. An analysis of the origin of metazoans, using comparisons of partial sequences of the 28S RNA, reveals an early emergence of triploblasts. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):499–503. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07975.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M., Sauvaget I., Bougueleret L. K-tuple frequency analysis: from intron/exon discrimination to T-cell epitope mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:237–252. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D. L., Plunkett G., 3rd, Burland V., Blattner F. R. Analysis of the Escherichia coli genome: DNA sequence of the region from 84.5 to 86.5 minutes. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):771–778. doi: 10.1126/science.1379743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög C. Isolation of a large number of novel mammalian genes by a differential cDNA library screening strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6123–6127. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Wilcox A. S., Polymeropoulos M. H., Hopkins J. A., Stevens T. J., Robinson M., Orpana A. K., Sikela J. M. Single pass sequencing and physical and genetic mapping of human brain cDNAs. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):180–185. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombie W. R., Adams M. D., Kelley J. M., FitzGerald M. G., Utterback T. R., Khan M., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Venter J. C., Fields C. Caenorhabditis elegans expressed sequence tags identify gene families and potential disease gene homologues. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):124–131. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. Compositional variations in DNA sequences. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Jul;7(3):287–293. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.3.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo K., Hori N., Matoba R., Niiyama T., Fukushima A., Kojima Y., Matsubara K. Large scale cDNA sequencing for analysis of quantitative and qualitative aspects of gene expression. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):173–179. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., van der Aart Q. J., Agostoni-Carbone M. L., Aigle M., Alberghina L., Alexandraki D., Antoine G., Anwar R., Ballesta J. P., Benit P. The complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome III. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):38–46. doi: 10.1038/357038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrokovski S., Hirshon J., Trifonov E. N. Linguistic measure of taxonomic and functional relatedness of nucleotide sequences. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Jun;7(6):1251–1268. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10508563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savakis C., Doelz R. Contamination of cDNA sequences in databases. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1677–1678. doi: 10.1126/science.8456288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volinia S., Gambari R., Bernardi F., Barrai I. The frequency of oligonucleotides in mammalian genic regions. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Feb;5(1):33–40. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterston R., Martin C., Craxton M., Huynh C., Coulson A., Hillier L., Durbin R., Green P., Shownkeen R., Halloran N. A survey of expressed genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):114–123. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


