Abstract
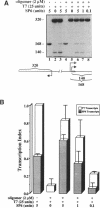
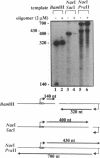
We have characterized triple-helix-mediated inhibition of an artificial bacteriophage promoter with respect to relief of inhibition by incoming RNA polymerases that initiate upstream or downstream from the operator sequence. Whereas oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation inhibits the test promoter, promoter activity is restored when the triple-helical complexes are disrupted by transcription of either strand of the homopurine operator sequence. The degree of relief from inhibition is related to the frequency of operator transcription. These observations demonstrate that this artificial repressor-operator complex is subject to antagonism by cis elements (other promoters) acting at a distance. Such antagonism might also arise between certain natural transcriptional control regions. Our results suggest that the efficiency of artificial repressors based on triple-helix formation may be limited by transcriptional activity in the gene control region.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen W., Tabor S., Struhl K. Distinguishing between mechanisms of eukaryotic transcriptional activation with bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1047–1055. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. lac Repressor blocks transcribing RNA polymerase and terminates transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4134–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Hipskind R. A., Bujard H. RNA polymerase II transcription blocked by Escherichia coli lac repressor. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):480–483. doi: 10.1126/science.2158670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. Position and density effects on repression by stationary and mobile DNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):185–197. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano T. J., Deuschle U., Bujard H., McAllister W. T. Regulation of coliphage T3 and T7 RNA polymerases by the lac repressor-operator system. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90494-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Goldfarb A. lac repressor acts by modifying the initial transcribing complex so that it cannot leave the promoter. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):793–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90122-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. J. Kinetic analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation on DNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8820–8826. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd Inhibition of T7 RNA polymerase initiation by triple-helical DNA complexes: a model for artificial gene repression. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7587–7594. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavco P. A., Steege D. A. Characterization of elongating T7 and SP6 RNA polymerases and their response to a roadblock generated by a site-specific DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4639–4646. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellitti M. A., Pavco P. A., Steege D. A. lac repressor blocks in vivo transcription of lac control region DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3199–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Krawczyk S. H., Matteucci M. D., Toole J. J. Triple helix formation inhibits transcription elongation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10023–10026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]