Abstract
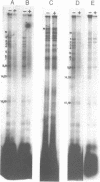
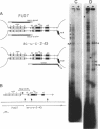
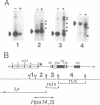
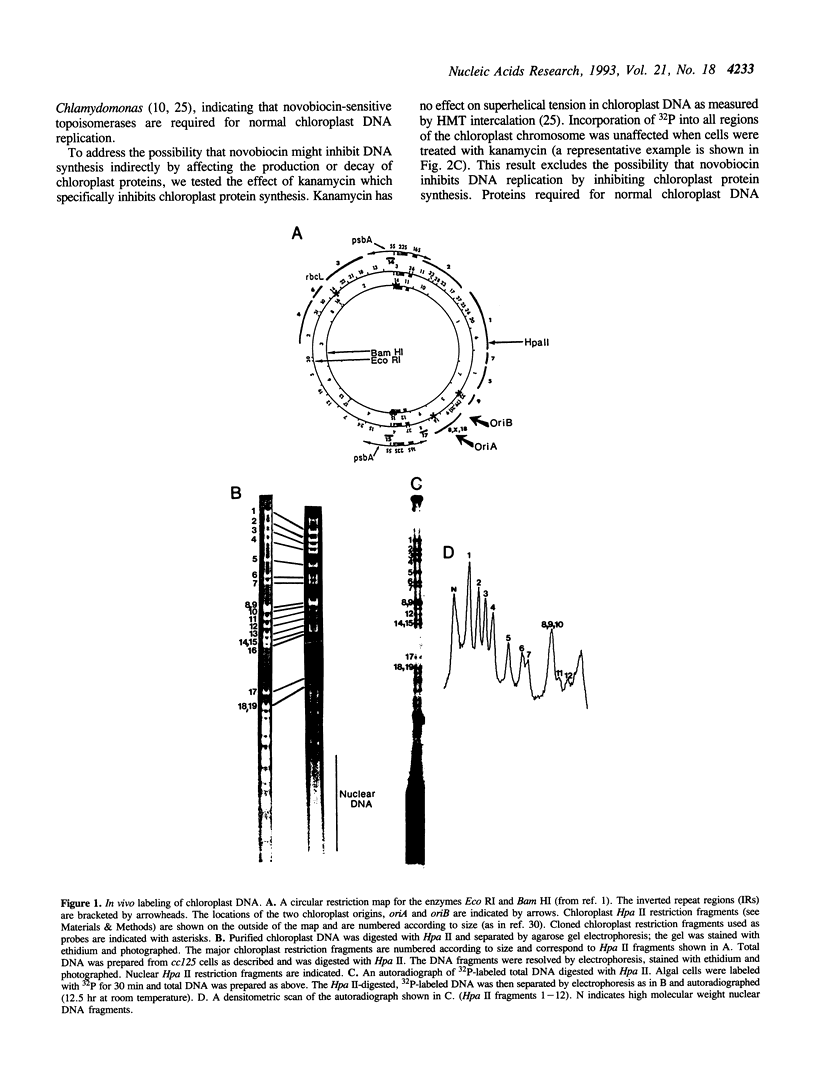
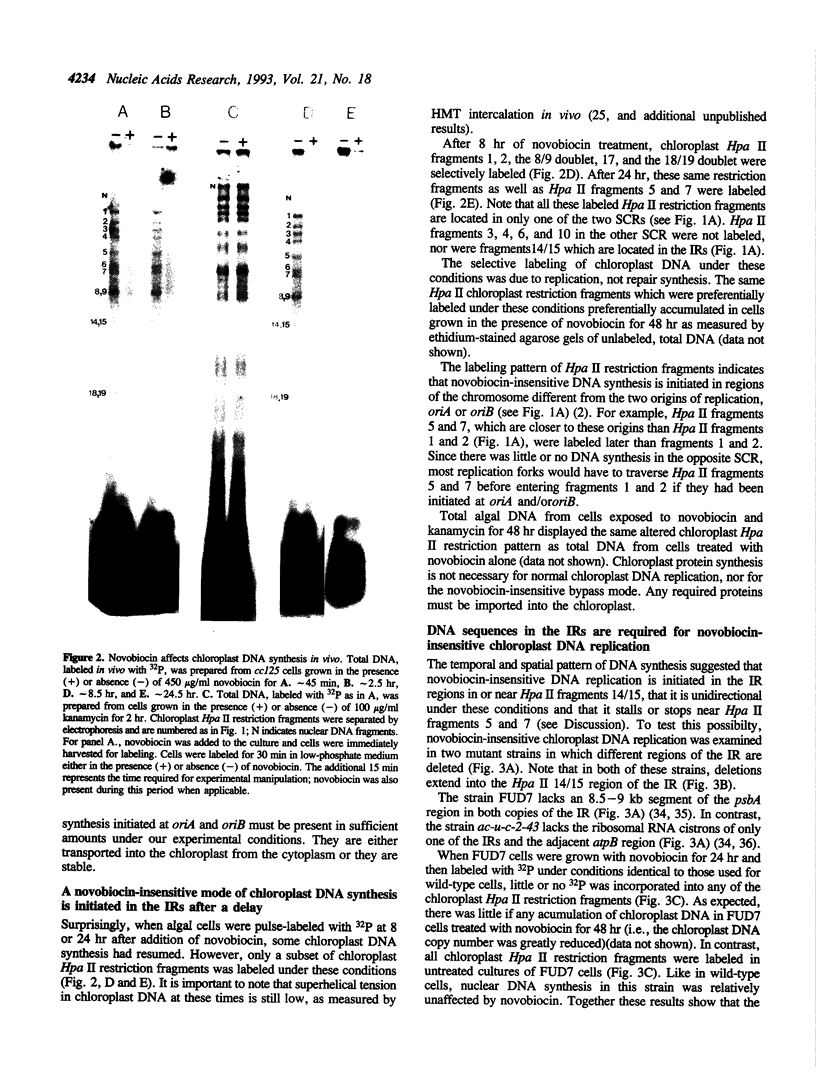
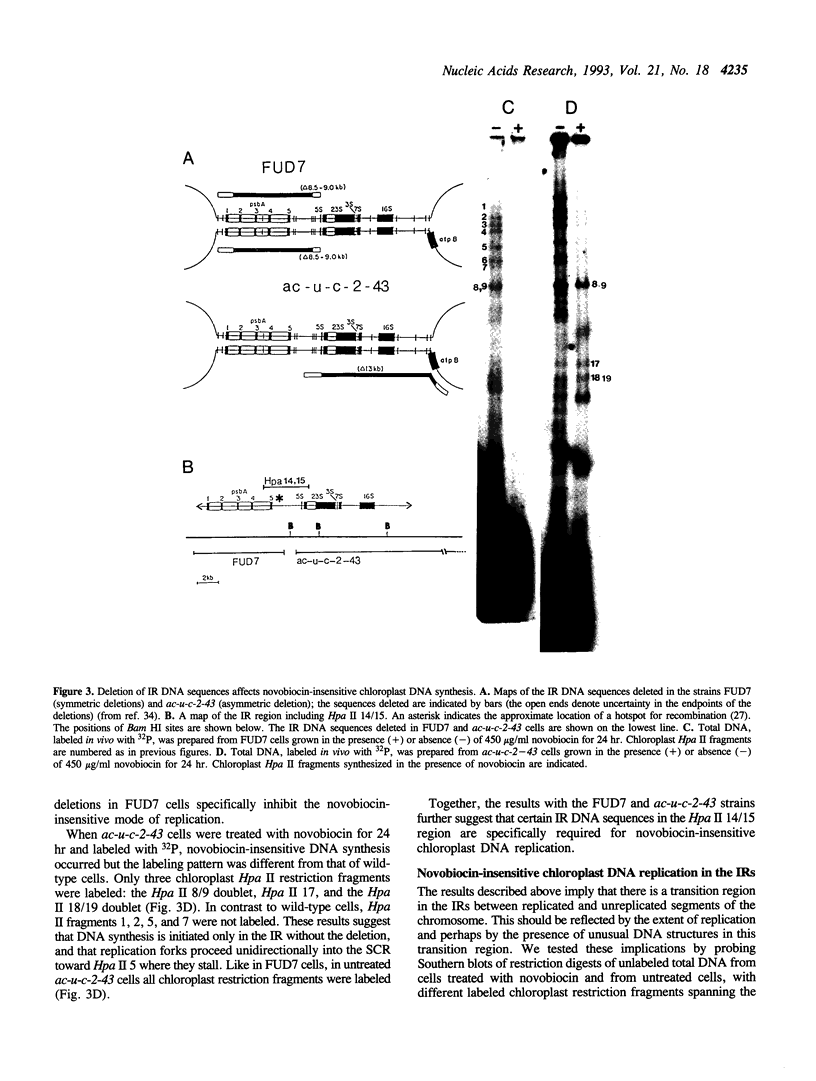
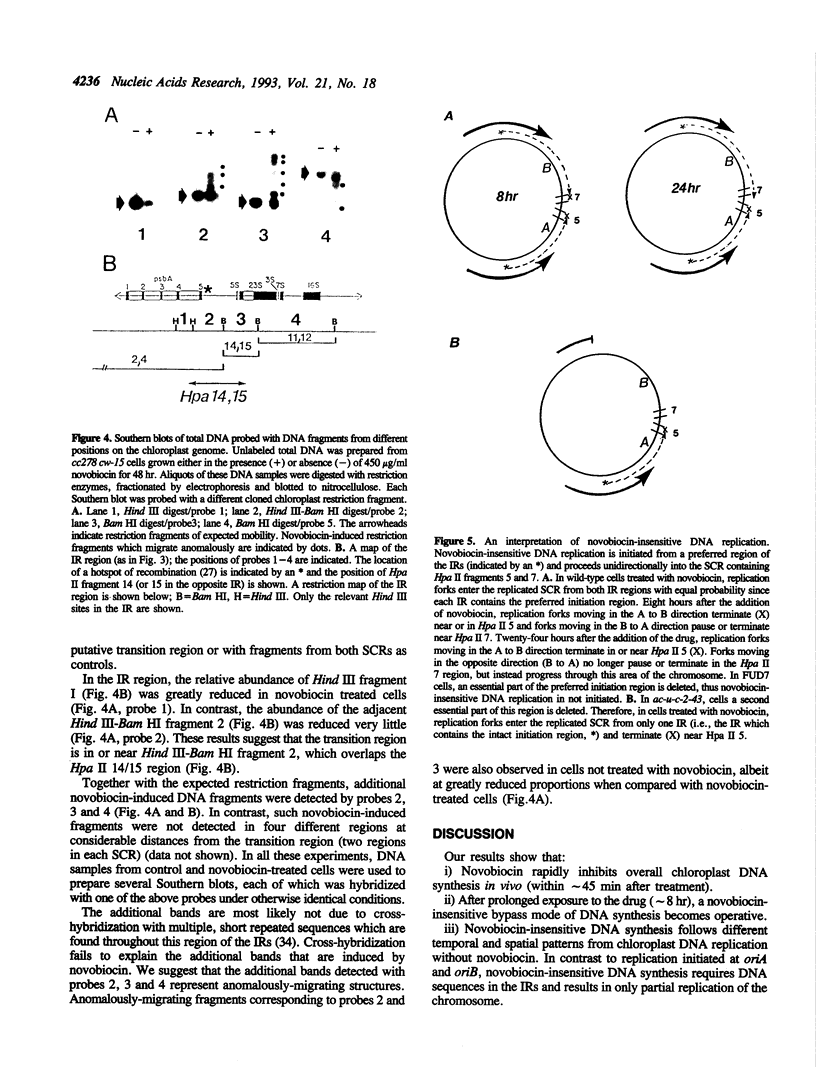
We have examined DNA replication in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplasts in vivo when chloroplast type II topoisomerases are inactivated with sublethal doses of novobiocin. DNA replication is at first inhibited under these conditions. However, after a delay of several hours, chloroplast chromosomes initiate a novobiocin-insensitive mode of DNA replication. This replication starts preferentially near a hotspot of recombination in the large inverted repeats, instead of from the normal chloroplast origins, oriA and oriB. It replicates one, but not the other single-copy region of the chloroplast chromosome. We speculate that novobiocin-insensitive DNA replication in chloroplasts requires recombination in this preferred initiation region.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. E., Shekhtman E. M., Zechiedrich E. L., Schmid M. B., Cozzarelli N. R. The role of topoisomerase IV in partitioning bacterial replicons and the structure of catenated intermediates in DNA replication. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90356-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. P., Thompson R. J., Mosig G. Intercalation of psoralen into DNA of plastid chromosomes decreases late during barley chloroplast development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5219–5225. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. M., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Inheritance of chloroplast DNA in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6067–6071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. H., Wu M., Yang J. M. The sequence-directed bent DNA detected in the replication origin of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast DNA is important for the replication function. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):25–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00282638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Nishimura Y., Imamura R., Niki H., Hiraga S., Suzuki H. New topoisomerase essential for chromosome segregation in E. coli. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90172-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Nishimura Y., Yamada M., Suzuki H., Hirota Y. Gene organization in the region containing a new gene involved in chromosome partition in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3967–3977. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3967-3977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Suzuki H., Ikeda H. Purification and characterization of DNA topoisomerase IV in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25676–25684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Richards K. L., Stern D. B. Engineering the chloroplast genome: techniques and capabilities for chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1721–1725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogoma T., Lark K. G. Characterization of the replication of Escherichia coli DNA in the absence of protein synthesis: stable DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):243–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogoma T., Lark K. G. DNA replication in Escherihia coli: replication in absence of protein synthesis after replication inhibition. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 14;52(2):143–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. Inverted repeats in chloroplast DNA from higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Escherichia coli mutants thermosensitive for deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase subunit A: effects on deoxyribonucleic acid replication, transcription, and bacteriophage growth. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):424–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.424-435.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luder A., Mosig G. Two alternative mechanisms for initiation of DNA replication forks in bacteriophage T4: priming by RNA polymerase and by recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1101–1105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee T. R., Asai T., Malka D., Kogoma T. DNA damage-inducible origins of DNA replication in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4219–4225. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee T. R., Kogoma T. Requirement of RecBC enzyme and an elevated level of activated RecA for induced stable DNA replication in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1834–1839. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1834-1839.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeker R., Nielsen B., Tewari K. K. Localization of replication origins in pea chloroplast DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1216–1223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosig G., Luder A., Ernst A., Canan N. Bypass of a primase requirement for bacteriophage T4 DNA replication in vivo by a recombination enzyme, endonuclease VII. New Biol. 1991 Dec;3(12):1195–1205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. M., Harris E. H., Johnson A. M., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Nonrandom distribution of chloroplast recombination events in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: evidence for a hotspot and an adjacent cold region. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):413–429. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nie Z Q, Chang D Y, Wu M. Protein-DNA interaction within one cloned chloroplast DNA replication origin of Chlamydomonas. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):265–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00329652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann T., Hong T. H., Surzycki S. J. Chloroplast and nuclear genomes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii share homology with Escherichia coli genes for DNA replication, repair and transcription. Curr Genet. 1989 Jan;15(1):39–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00445750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. The repair of double-strand breaks in DNA; a model involving recombination. J Theor Biol. 1976 Jun;59(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(76)80025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. B. A locus affecting nucleoid segregation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5416–5424. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5416-5424.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. The intrinsic ATPase of DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6299–6306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. Energy coupling in DNA gyrase and the mechanism of action of novobiocin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Mosig G. An ATP-dependent supercoiling topoisomerase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii affects accumulation of specific chloroplast transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):873–891. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Mosig G. Light affects the structure of Chlamydomonas chloroplast chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2625–2631. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Mosig G. Light and Genetic Determinants in the Control of Specific Chloroplast Transcripts in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):1–6. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Mosig G. Stimulation of a Chlamydomonas chloroplast promoter by novobiocin in situ and in E. coli implies regulation by torsional stress in the chloroplast DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90431-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell J., Wang X. M., Wu M. Electron microscopic localization of the chloroplast DNA replicative origins in Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3843–3856. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. F., Yang J., Nie Z. Q., Wu M. Purification and characterization of a gamma-like DNA polymerase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):1127–1131. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Kong X. F., Kung S. D. Prokaryotic promoters in the chloroplast DNA replication origin of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr Genet. 1986;10(11):819–822. doi: 10.1007/BF00418528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Lou J. K., Chang D. Y., Chang C. H., Nie Z. Q. Structure and function of a chloroplast DNA replication origin of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6761–6765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Nie Z. Q., Yang J. The 18-kD protein that binds to the chloroplast DNA replicative origin is an iron-sulfur protein related to a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase. Plant Cell. 1989 May;1(5):551–557. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.5.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurtz E. A., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Perturbation of chloroplast DNA amounts and chloroplast gene transmission in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by 5-fluorodeoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4552–4556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]