Abstract
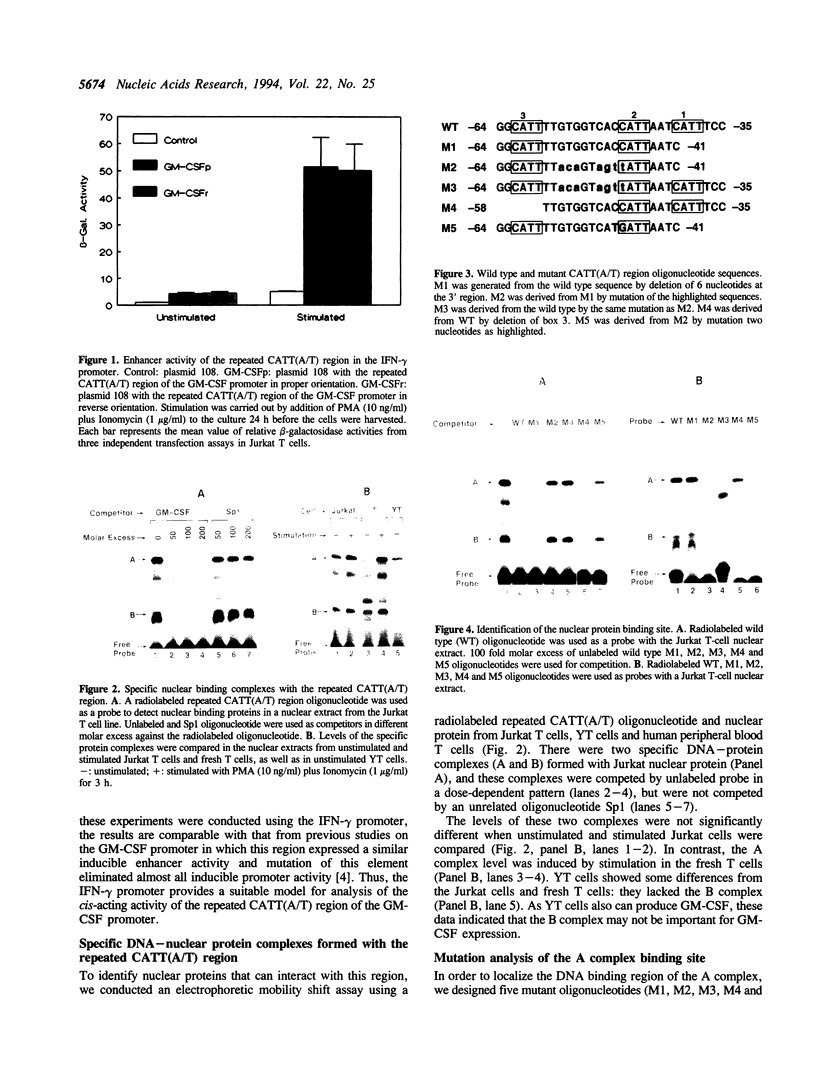
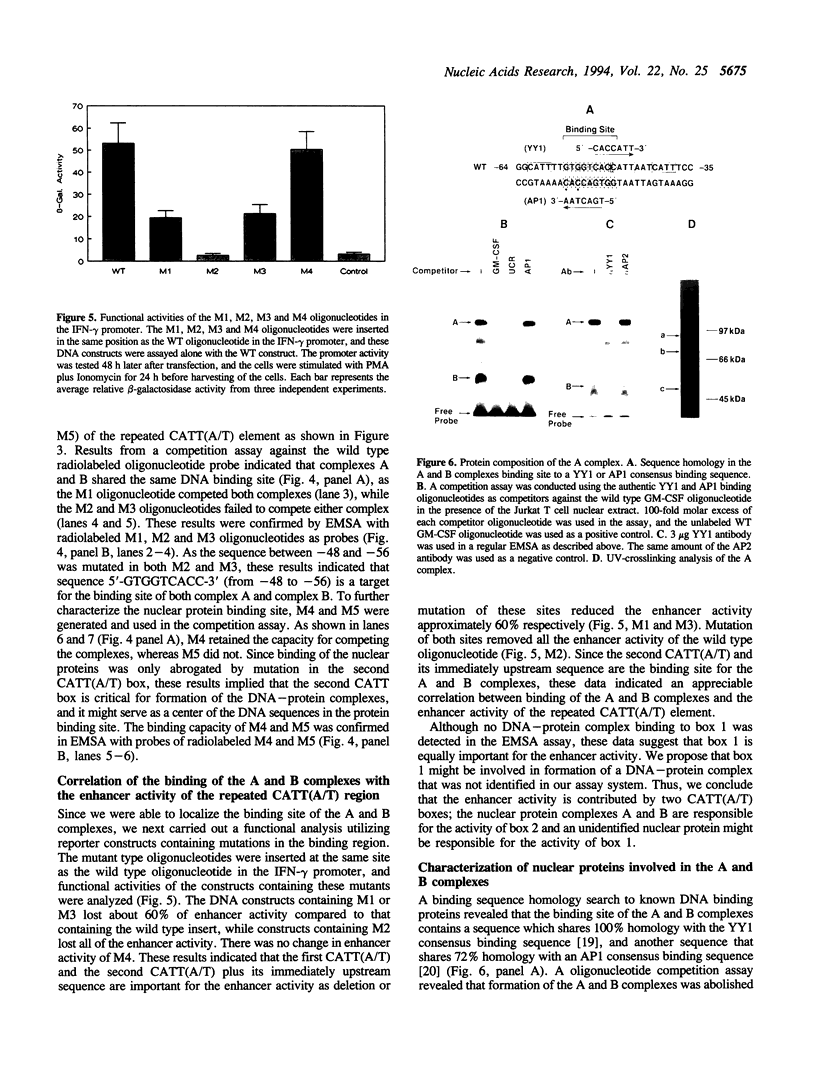
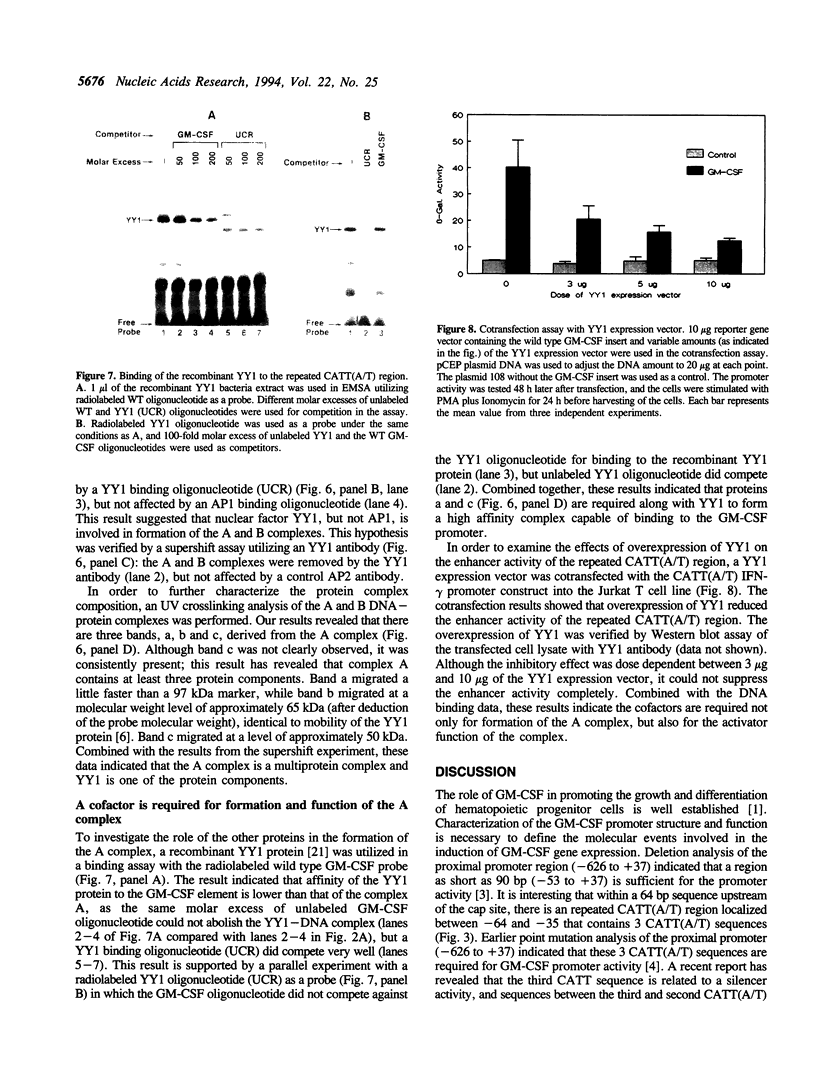
It has been well documented that the repeated CATT(A/T) sequence, localized between -64 and -35 in the human GM-CSF promoter, is required for the promoter activity, and this region likely serves as a core recognition sequence for a cellular transcription factor. However, the transcription factor that interacts with this site was not identified. Here, we report that this element contains a binding site for the nuclear factor YY1, which has not been reported to play a role in the regulation of cytokine gene transcription. Results from transient transfection assays of the Jurkat T cell line revealed that this repeated CATT(A/T) element exhibited enhancer activity when linked to both the human IFN-gamma promoter and the TK promoter. Mutation of the YY1 binding site eliminated about 60% of the enhancer activity of the element. We have found that the YY1 binding site could form two specific DNA-protein complexes, A and B, with Jurkat nuclear proteins in the electrophoretic mobility shift assay and that the binding of these complexes correlates with the enhancer activity. UV cross-linking analysis revealed that the A complex is a multi-protein complex and in addition to YY1, other proteins are required for formation of the protein complex. Cotransfection assays with a YY1 expression vector revealed that overexpression of YY1 resulted in an inhibitory effect on the repeated CATT(A/T) element, indicating that in addition to YY1, cofactors also are required for the activator function of the A complex.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu A., Park K., Atchison M. L., Carter R. S., Avadhani N. G. Identification of a transcriptional initiator element in the cytochrome c oxidase subunit Vb promoter which binds to transcription factors NF-E1 (YY-1, delta) and Sp1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4188–4196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K. L., Schwartz R. J. A combination of closely associated positive and negative cis-acting promoter elements regulates transcription of the skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):528–538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. R., Boam D. S., Docherty K. A new series of CAT expression vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10130–10130. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Shannon M. F., Bert A. G., Ryan G. R., Vadas M. A. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor/interleukin 3 locus is regulated by an inducible cyclosporin A-sensitive enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eustice D. C., Feldman P. A., Colberg-Poley A. M., Buckery R. M., Neubauer R. H. A sensitive method for the detection of beta-galactosidase in transfected mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):739-40, 742-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Becker K. G., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Driggers P. H., Levi B. Z., Appella E., Ozato K. Cloning of a negative transcription factor that binds to the upstream conserved region of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. K., Guerra J. J., Nguyen C. Y., Indes J. E., Gasson J. C., Nimer S. D. Characterization of a cell-type-restricted negative regulatory activity of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2213–2221. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C. Molecular physiology of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1991 Mar 15;77(6):1131–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P., Tan T. H., Rice N. R., Sica A., Young H. A. The interleukin 2 CD28-responsive complex contains at least three members of the NF kappa B family: c-Rel, p50, and p65. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1696–1700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto A., LePage D., Pons G., Mader S. L., Park K., Atchison M. L., Walsh K. Functional antagonism between YY1 and the serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4209–4214. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Delta, a transcription factor that binds to downstream elements in several polymerase II promoters, is a functionally versatile zinc finger protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9799–9803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye C. J., Seto E. Relief of YY1-induced transcriptional repression by protein-protein interaction with the nucleolar phosphoprotein B23. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6506–6510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Galvin K. M., Shi Y. Evidence for physical interaction between the zinc-finger transcription factors YY1 and Sp1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6145–6149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Shi Y., Schwartz R. J. Displacement of BrdUrd-induced YY1 by serum response factor activates skeletal alpha-actin transcription in embryonic myoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9814–9818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Zhang Y., Schwartz R. J. Bifunctional transcriptional properties of YY1 in regulating muscle actin and c-myc gene expression during myogenesis. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1047–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda E. S., Tokumitsu H., Tsuboi A., Shlomai J., Hung P., Arai K., Arai N. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promoter cis-acting element CLE0 mediates induction signals in T cells and is recognized by factors related to AP1 and NFAT. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7399–7407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier V. S., Groner B. The nuclear factor YY1 participates in repression of the beta-casein gene promoter in mammary epithelial cells and is counteracted by mammary gland factor during lactogenic hormone induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):128–137. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Shlomai J., Arai K., Arai N. Characterization of the mouse granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) gene promoter: nuclear factors that interact with an element shared by three lymphokine genes--those for GM-CSF, interleukin-4 (IL-4), and IL-5. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5894–5901. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimer S. D., Morita E. A., Martis M. J., Wachsman W., Gasson J. C. Characterization of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promoter region by genetic analysis: correlation with DNase I footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1979–1984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimer S., Fraser J., Richards J., Lynch M., Gasson J. The repeated sequence CATT(A/T) is required for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promoter activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6084–6088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomiyama H., Hieshima K., Hirokawa K., Hattori T., Takatsuki K., Miura R. Characterization of cytokine LD78 gene promoters: positive and negative transcriptional factors bind to a negative regulatory element common to LD78, interleukin-3, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2787–2801. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K., Atchison M. L. Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9804–9808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penix L., Weaver W. M., Pang Y., Young H. A., Wilson C. B. Two essential regulatory elements in the human interferon gamma promoter confer activation specific expression in T cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1483–1496. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs K. J., Merrell K. T., Wilson G., Calame K. Common factor 1 is a transcriptional activator which binds in the c-myc promoter, the skeletal alpha-actin promoter, and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1765–1769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Jäckle H. Concentration-dependent transcriptional activation or repression by Krüppel from a single binding site. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):563–566. doi: 10.1038/353563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Lewis B., Shenk T. Interaction between transcription factors Sp1 and YY1. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):462–464. doi: 10.1038/365462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Shi Y., Shenk T. YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):241–245. doi: 10.1038/354241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava A., Saleque S., Kalpana G. V., Artandi S., Goff S. P., Calame K. Inhibition of transcriptional regulator Yin-Yang-1 by association with c-Myc. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1889–1892. doi: 10.1126/science.8266081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi A., Muramatsu M., Tsutsumi A., Arai K., Arai N. Calcineurin activates transcription from the GM-CSF promoter in synergy with either protein kinase C or NF-kappa B/AP-1 in T cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):1064–1072. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usheva A., Shenk T. TATA-binding protein-independent initiation: YY1, TFIIB, and RNA polymerase II direct basal transcription on supercoiled template DNA. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1115–1121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90387-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Belle I., Walker P. R., Smith I. C., Sikorska M. Identification of a multiprotein complex interacting with the c-fos serum response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2752–2759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]