Abstract
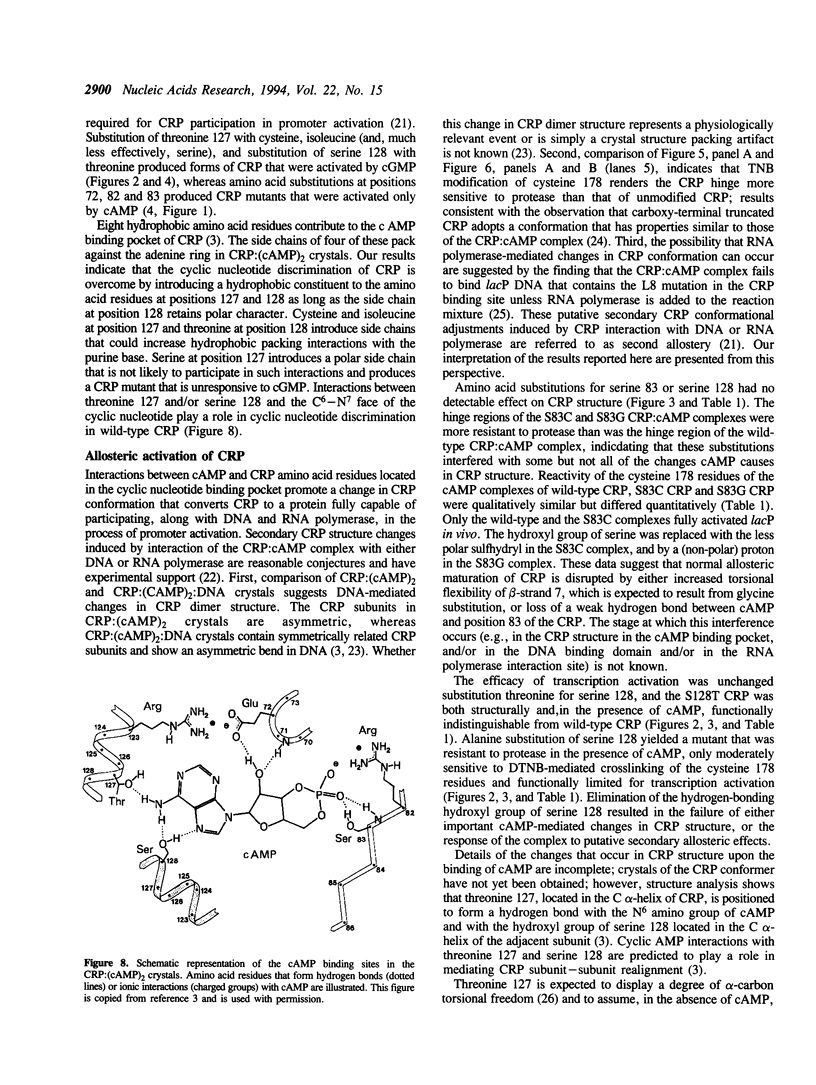
The cyclic 3', 5' adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) binding pocket of the cAMP receptor protein (CRP) of Escherichia coli was mutagenized to substitute cysteine or glycine for serine 83; cysteine, glycine, isoleucine, or serine for threonine 127; and threonine or alanine for serine 128. Cells that expressed the binding pocket residue-substituted forms of CRP were characterized by measurements of beta-galactosidase activity. Purified wild-type and mutant CRP preparations were characterized by measurement of cAMP binding activity and by their capacity to support lacP activation in vitro. CRP structure was assessed by measurement of sensitivity to protease and DTNB-mediated subunit crosslinking. The results of this study show that cAMP interactions with serine 83, threonine 127 and serine 128 contribute to CRP activation and have little effect on cAMP binding. Amino acid substitutions that introduce hydrophobic amino acid side chain constituents at either position 127 or 128 decrease CRP discrimination of cAMP and cGMP. Finally, cAMP-induced CRP structural change(s) that occur in or near the CRP hinge region result from cAMP interaction with threonine 127; substitution of threonine 127 by cysteine, glycine, isoleucine, or serine produced forms of CRP that contained, independently of cAMP binding, structural changes similar to those of the wild-type CRP:cAMP complex.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. B., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Effect of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate analogues on the activity of the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2717–2722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belduz A. O., Lee E. J., Harman J. G. Mutagenesis of the cyclic AMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli: targeting positions 72 and 82 of the cyclic nucleotide binding pocket. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1827–1835. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Helinski D. R. Use of the lambda phage promoter PL to promote gene expression in hybrid plasmid cloning vehicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:482–492. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botsford J. L., Harman J. G. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):100–122. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.100-122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Le Grice S. F., Miller J. P., Krakow J. S. Analogs of cyclic AMP that elicit the biochemically defined conformational change in catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) but do not stimulate binding to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):91–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilen E., Krakow J. S. Cyclic AMP-mediated intersubunit disulfide crosslinking of the cyclic AMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garges S., Adhya S. Cyclic AMP-induced conformational change of cyclic AMP receptor protein (CRP): intragenic suppressors of cyclic AMP-independent CRP mutations. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1417–1422. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1417-1422.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Sandulache R., Gärtner S., Clore G. M. Mutations in the cyclic AMP binding site of the cyclic AMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):801–807. doi: 10.1042/bj2530801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman J. G., McKenney K., Peterkofsky A. Structure-function analysis of three cAMP-independent forms of the cAMP receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16332–16339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Adhya S., Garges S. Allosteric changes in the cAMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli: hinge reorientation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9700–9704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. S. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor: effect of cyclic AMP analogues on DNA binding and proteolytic inactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 2;383(4):345–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90303-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Peterkofsky A., McKenney K. Hyperexpression and purification of Escherichia coli adenylate cyclase using a vector designed for expression of lethal gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10473–10488. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S. Catabolite gene activator protein activation of lac transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):655–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.655-658.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riftina F., DeFalco E., Krakow J. S. Effects of an anti-alpha monoclonal antibody on interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with lac promoters. Biochemistry. 1990 May 8;29(18):4440–4446. doi: 10.1021/bi00470a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S., Kim J., Adhya S., Garges S. Pivotal role of amino acid at position 138 in the allosteric hinge reorientation of cAMP receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):75–79. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santa-Coloma T. A., Rossi R. J., Charreau E. H. Solid-phase assay for determination of binding parameters of ligand-protein complexes with high dissociation rates. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):367–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90550-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of a complex of catabolite gene activator protein and cyclic AMP refined at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. H., Bobin S., Krakow J. S. Characterization of the CRPCY core formed after treatment with carboxypeptidase Y. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4253–4257. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M., Patterson T. A., Court D. L. Analysis of nutR, a site required for transcription antitermination in phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]