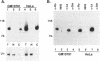Abstract
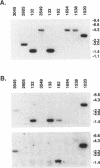
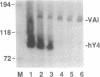
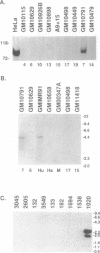
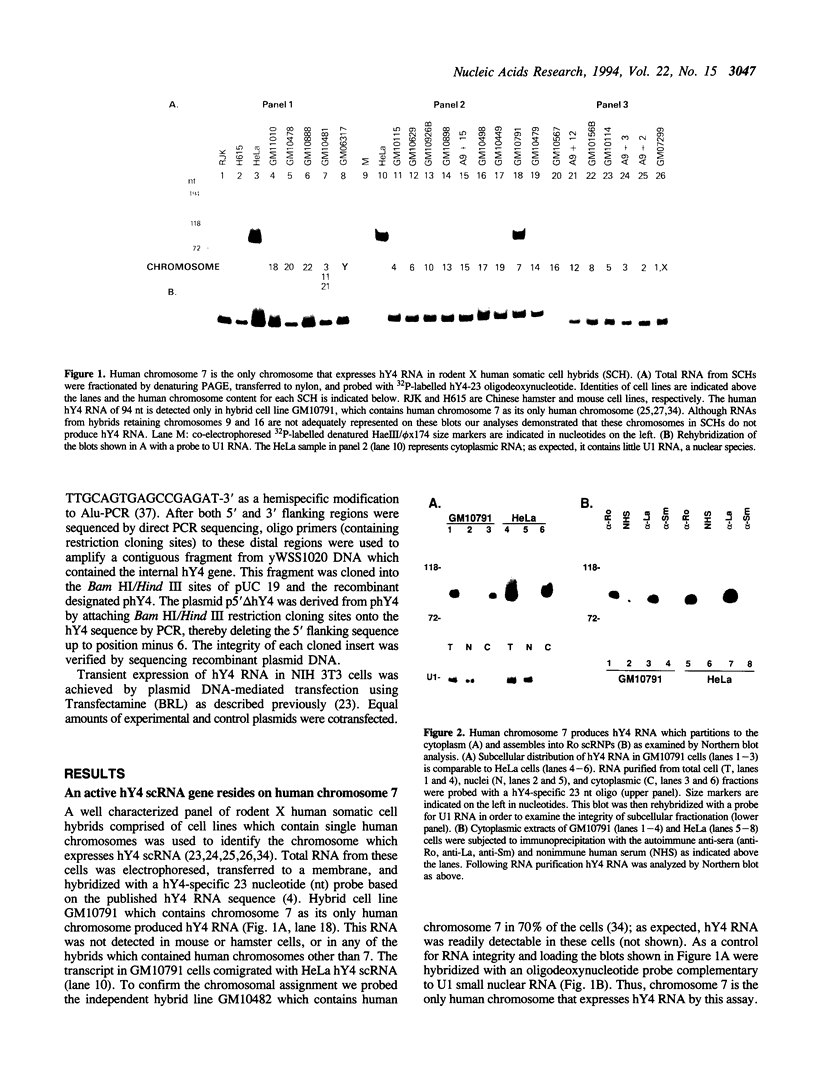
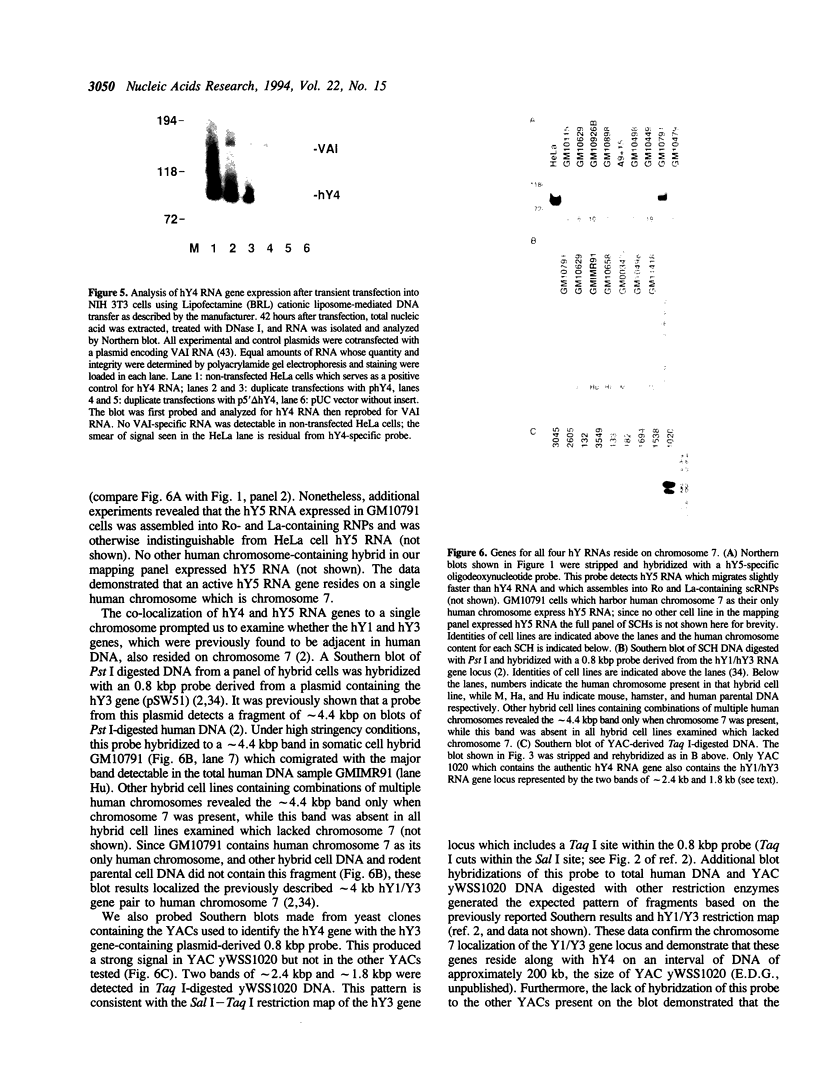
Ro ribonucleoproteins (RNP) constitute a class of evolutionarily conserved small cytoplasmic (sc) RNPs whose functions are unknown. In human cells four distinctive scRNAs designated hY1, hY3, hY4 and hY5 are synthesized by RNA polymerase III (pol III) and accumulate as components of Ro scRNPs. The previously isolated hY1 and hY3 genes contain upstream sequences similar to the class III promoters for U6 and 7SK snRNAs. Additional mammalian Y scRNA genes have been refractory to cloning due to interference from numerous hY-homologous pseudogenes and studies of hY RNA genes have been sparse. Although homologs of hY1 and hY3 RNAs exist in rodent cells, the smaller Y4 and Y5 RNAs do not which has allowed us to localize the hY4 scRNA gene to human chromosome 7 by assaying for its transcript in rodent X human somatic cell hybrids (SCH). A chromosome 7-enriched yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) library was then screened and the authentic hY4 sequence was isolated by strepavidin--biotin-mediated hybrid-selection followed by poly(dA)-tailing and hemispecific PCR. The region upstream of the hY4 sequence contains a TATAAAA motif centered at -26, a candidate proximal sequence element at -63, and three octamer-like sequences located between -260 and -200. hY4 RNA is readily detectable on Northern blots after transient transfection of the hY4 gene into mouse cells but not after transfection of a construct in which the 5' flanking region was deleted. SCHs and chromosome 7-enriched YACs were used to demonstrate that all four hY RNA genes reside on human chromosome 7.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander E., Buyon J. P., Provost T. T., Guarnieri T. Anti-Ro/SS-A antibodies in the pathophysiology of congenital heart block in neonatal lupus syndrome, an experimental model. In vitro electrophysiologic and immunocytochemical studies. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Feb;35(2):176–189. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M., Cross J. Differential staining of human and mouse chromosomes in interspecific cell hybrids. Nature. 1974 Sep 6;251(5470):77–79. doi: 10.1038/251077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. Y., Nelson B., Bilyeu T., Hsu K., Darlington G. J., Maraia R. J. A human Alu RNA-binding protein whose expression is associated with accumulation of small cytoplasmic Alu RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3949–3959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch D., Liebke E. H. The molecular cloning of a mouse Ro RNA, my1-like sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4890–4890. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels G. R., Deininger P. L. Integration site preferences of the Alu family and similar repetitive DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8939–8954. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. S., Bair L. W., Jr, Shen-Schwarz S., Ramsey-Goldman R., Medsger T., Jr Localization of Ro (SS-A) antigen in the cardiac conduction system. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1232–1238. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll C. T., Darlington G. J., Maraia R. J. The conserved 7SK snRNA gene localizes to human chromosome 6 by homolog exclusion probing of somatic cell hybrid RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 11;22(5):722–725. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Idol J. R., Mohr-Tidwell R. M., Braden V. V., Peluso D. C., Fulton R. S., Massa H. F., Magness C. L., Wilson A. M., Kimura J. Integration of physical, genetic and cytogenetic maps of human chromosome 7: isolation and analysis of yeast artificial chromosome clones for 117 mapped genetic markers. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Mar;3(3):489–501. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Mohr R. M., Idol J. R., Jones M., Buckingham J. M., Deaven L. L., Moyzis R. K., Olson M. V. Systematic generation of sequence-tagged sites for physical mapping of human chromosomes: application to the mapping of human chromosome 7 using yeast artificial chromosomes. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):548–564. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Chromosomal region of the cystic fibrosis gene in yeast artificial chromosomes: a model for human genome mapping. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):94–98. doi: 10.1126/science.2218515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Systematic screening of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wolin S. L., Rinke J., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins are a subclass of La ribonucleoproteins: further characterization of the Ro and La small ribonucleoproteins from uninfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1138–1149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Kriet J. D., Reichlin M. Organ distribution of the Ro (SS-A) antigen in the guinea pig. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Dec;33(12):1815–1821. doi: 10.1002/art.1780331209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. J., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. Biochemical and genetic analysis of the Chinese hamster mutants irs1 and irs2 and their comparison to cultured ataxia telangiectasia cells. Mutagenesis. 1990 Jan;5(1):15–23. doi: 10.1093/mutage/5.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurka J., Smith T. F., Labuda D. Small cytoplasmic Ro RNA pseudogene and an Alu repeat in the human alpha-1 globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):766–766. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Hoshino H., Harada F. Nucleotide sequence of 4.5S RNA (C8 or hY5) from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91875-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelekar A., Keene J. D. Downregulation of RNA polymerase III transcription of the hY3 gene in vitro. Mol Biol Rep. 1990;14(2-3):173–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00360463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraia R. J., Driscoll C. T., Bilyeu T., Hsu K., Darlington G. J. Multiple dispersed loci produce small cytoplasmic Alu RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4233–4241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraia R. J., Kenan D. J., Keene J. D. Eukaryotic transcription termination factor La mediates transcript release and facilitates reinitiation by RNA polymerase III. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2147–2158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraia R. J. The subset of mouse B1 (Alu-equivalent) sequences expressed as small processed cytoplasmic transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5695–5702. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner W., Wanandi I., Carbon P., Krol A., Seifart K. H. Transcription factors required for the expression of Xenopus laevis selenocysteine tRNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 25;22(4):553–559. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M. M., Slightom J. L., Goodman M. Phylogenetic relations of humans and African apes from DNA sequences in the psi eta-globin region. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):369–373. doi: 10.1126/science.3116671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon I. S., Krause M. O. Common RNA polymerase I, II, and III upstream elements in mouse 7SK gene locus revealed by the inverse polymerase chain reaction. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):23–32. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Altruda F., Ullu E., Tripodi M., Silengo L., Melli M. DNA sequences complementary to human 7 SK RNA show structural similarities to the short mobile elements of the mammalian genome. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):575–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Ledbetter S. A., Corbo L., Victoria M. F., Ramírez-Solis R., Webster T. D., Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Alu polymerase chain reaction: a method for rapid isolation of human-specific sequences from complex DNA sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6686–6690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ning Y., Lovell M., Taylor L., Pereira-Smith O. M. Isolation of monochromosomal hybrids following fusion of human diploid fibroblast-derived microcells with mouse A9 cells. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;60(1):79–80. doi: 10.1159/000133300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien C. A., Harley J. B. A subset of hY RNAs is associated with erythrocyte Ro ribonucleoproteins. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3683–3689. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien C. A., Harley J. B. Association of hY4 pseudogenes with Alu repeats and abundance of hY RNA-like sequences in the human genome. Gene. 1992 Jul 15;116(2):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90527-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien C. A., Margelot K., Wolin S. L. Xenopus Ro ribonucleoproteins: members of an evolutionarily conserved class of cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7250–7254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., Wingens P. A., Peters S. L., Thijssen J. P., van Venrooij W. J. Ro RNP associated Y RNAs are highly conserved among mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 14;1216(3):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90006-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Immunoprecipitation of ribonucleoproteins using autoantibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:468–481. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh D., Yuan Y., Henning D., Reddy R. Secondary structure of 7SK and 7-2 small RNAs. Possible origin of some 7SK pseudogenes from cDNA formed through self-priming by 7SK RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):221–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. V., Scott J. S., Gerlis L. M., Esscher E., Scott O. Maternal antibodies against fetal cardiac antigens in congenital complete heart block. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 11;315(11):667–672. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609113151103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Esposito V., Melli M. Evolutionary conservation of the human 7 S RNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 15;161(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Weiner A. M. Human genes and pseudogenes for the 7SL RNA component of signal recognition particle. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3303–3310. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Weiner A. M. Upstream sequences modulate the internal promoter of the human 7SL RNA gene. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):371–374. doi: 10.1038/318371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Genes for two small cytoplasmic Ro RNAs are adjacent and appear to be single-copy in the human genome. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):735–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. The Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins: identification of the antigenic protein and its binding site on the Ro RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]