Abstract
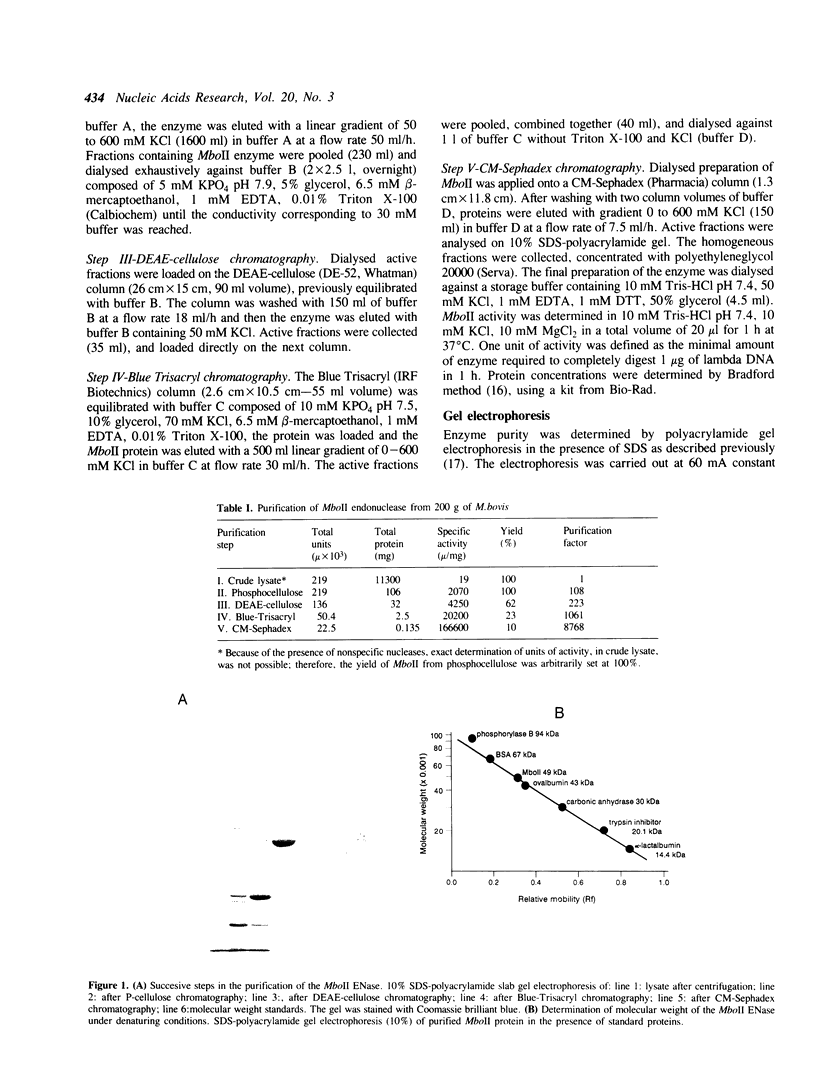
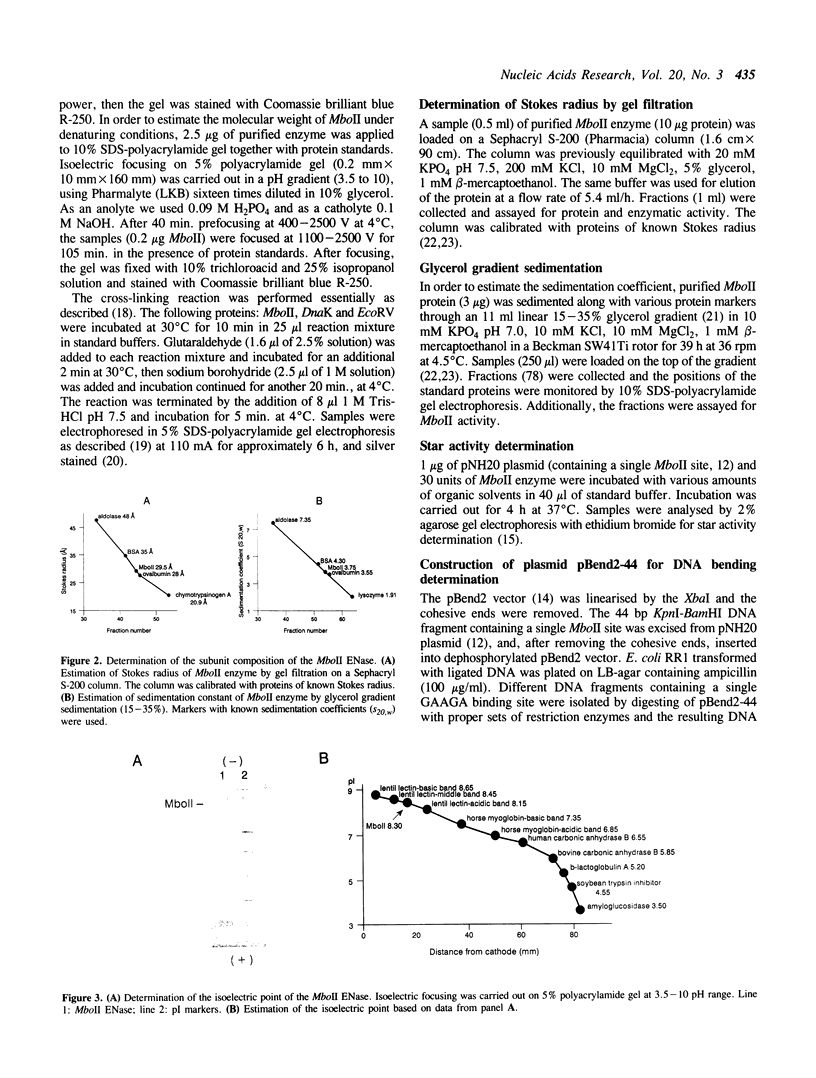
After five purification steps a homogeneous preparation of endonuclease MboII was obtained, and several properties of the enzyme were determined. MboII is a monomer, with Mr under native and denaturing conditions being 47-49 x 10(3) Da. Endonuclease MboII is a basic protein (pI 8.3) which remains active when Mg2+ is replaced by Mn2+, Co2+, Ca2+, or Fe2+. MboII exhibits a star activity in the presence of some of the following reagents or ions: DMSO, glycerol, ethanol (and Co2+ or Mn2+ at pH 6). MboII does not bend DNA and is heat sensitive, losing activity after 15 min at 50 degrees C.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bocklage H., Heeger K., Müller-Hill B. Cloning and characterization of the MboII restriction-modification system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1007–1013. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. C., Charles I. G., Keyte J. W., Brammar W. J. Isolation and computer-aided characterization of MmeI, a type II restriction endonuclease from Methylophilus methylotrophus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5255–5274. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Smith M. The specific non-symmetrical sequence recognized by restriction endonuclease MboII. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arcy A., Brown R. S., Zabeau M., van Resandt R. W., Winkler F. K. Purification and crystallization of the EcoRV restriction endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):1987–1990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayle R. B., 3rd, Auger E. A., Gough G. R., Gilham P. T., Bennett G. N. Formation of MboII vectors and cassettes using asymmetric MboII linkers. Gene. 1987;54(2-3):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90490-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelinas R. E., Myers P. A., Roberts R. J. Two sequence-specific endonucleases from Moraxella bovis. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan N., Kur J., Szybalski W. An MboII/FokI trimming plasmid allowing consecutive cycles of precise 1- to 12-base-pair deletions in cloned DNA. Gene. 1989 Oct 30;82(2):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Berg P. Altering the specificity of restriction endonuclease: effect of replacing Mg2+ with Mn2+. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):131–138. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski T., Skowron P., Podhajska A. J. Purification and characterization of the FokI restriction endonuclease. Gene. 1989 Aug 15;80(2):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. C., Podhajska A. J., Szybalski W. Cleaving DNA at any predetermined site with adapter-primers and class-IIS restriction enzymes. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):504–506. doi: 10.1126/science.2833816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita K., Kotani H., Hiraoka N., Nakamura T., Yonaha K. Overproduction and crystallization of FokI restriction endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8741–8753. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita K., Kotani H., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. The fokI restriction-modification system. I. Organization and nucleotide sequences of the restriction and modification genes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5751–5756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kur J., Hradecna Z., Hasan N., Szybalski W. The role of the direct repeat in qut-controlled antitermination in phage lambda. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):629–632. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90034-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Osipiuk J., Zylicz M., Ang D., Skorko J., Georgopoulos C. Physical interactions between bacteriophage and Escherichia coli proteins required for initiation of lambda DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3022–3029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney M. C., Moran L. S., Jack W. E., Feehery G. R., Benner J. S., Slatko B. E., Wilson G. G. Nucleotide sequence of the FokI restriction-modification system: separate strand-specificity domains in the methyltransferase. Gene. 1989 Aug 15;80(2):193–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luke P. A., McCallum S. A., Halford S. E. The EcoR V restriction endonuclease. Gene Amplif Anal. 1987;5:185–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malyguine E., Vannier P., Yot P. Alteration of the specificity of restriction endonucleases in the presence of organic solvents. Gene. 1980 Jan;8(2):163–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasri M., Thomas D. Alteration of the specificity of PvuII restriction endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7677–7687. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwankwo D., Wilson G. Cloning of two type II methylase genes that recognise asymmetric nucleotide sequences: FokI and HgaI. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):570–574. doi: 10.1007/BF00331164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podhajska A. J., Szybalski W. Conversion of the FokI endonuclease to a universal restriction enzyme: cleavage of phage M13mp7 DNA at predetermined sites. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., Greene P., Garfin D. E., McCarthy B. J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Specificity of substrate recognition by the EcoRI restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3310–3314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlossman D. M., Schmid S. L., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. An enzyme that removes clathrin coats: purification of an uncoating ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):723–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki H., Kanazawa S. New restriction endonucleases from Flavobacterium okeanokoites (FokI) and Micrococcus luteus (MluI). Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szybalski W., Kim S. C., Hasan N., Podhajska A. J. Class-IIS restriction enzymes--a review. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:13–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90345-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovar K., Hillen W. Tet repressor binding induced curvature of tet operator DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6515–6522. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfes H., Fliess A., Winkler F., Pingoud A. Cross-linking of bromodeoxyuridine-substituted oligonucleotides to the EcoRI and EcoRV restriction endonucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury C. P., Jr, Hagenbüchle O., von Hippel P. H. DNA site recognition and reduced specificity of the Eco RI endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11534–11548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead J. L., Bhave N., Malcolm A. D. Cation dependence of restriction endonuclease EcoRI activity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):293–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli dnaK replication protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- le Maire M., Rivas E., Møller J. V. Use of gel chromatography for determination of size and molecular weight of proteins: further caution. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 15;106(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]