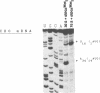
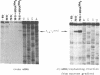
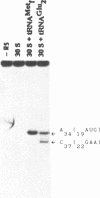
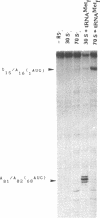
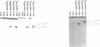Abstract
The mRNA encoding repressor cI of phage lambda is the only known E. coli message which starts directly with the initiation AUG codon. The ability of in vitro synthesized cI mRNA fragments (150 or 400 nts) to form ternary initiation complexes has been studied using the toeprint method. In the presence of tRNA(Met)f, these fragments are capable of forming the ternary complexes at the 5'-terminal AUG codon not only with 30S subunits but also with undissociated 70S ribosomes (70S tight couples). In the latter case, no binding at other positions of cI mRNA can be detected at all. The starting region of cI mRNA has a single stranded conformation and is highly enriched in A-residues. This feature of cI mRNA RBS is suggested to be the main factor which allows cI mRNA to form the initiation complex with the ribosome. Unlike 30S subunits, the binding to 70S tight couples is not affected by any of the initiation factors, although it is as efficient as that to 30S subunits supplemented with the factors. 30S subunits prefer to associate with the internal RBSs of the preformed mRNA molecules, provided that they are not sequestered by the secondary structure. In contrast, 70S tight couples tend to avoid extra sequences upstream of the codon directed to the P site and occupy a position as close as possible to the 5'-end of the message. This has been found to be the case both for tRNA(Met)f and for elongator tRNA(Glu)2. The structural features of mRNA RBSs which influence their different binding for 30S subunits and 70S ribosomes are discussed.
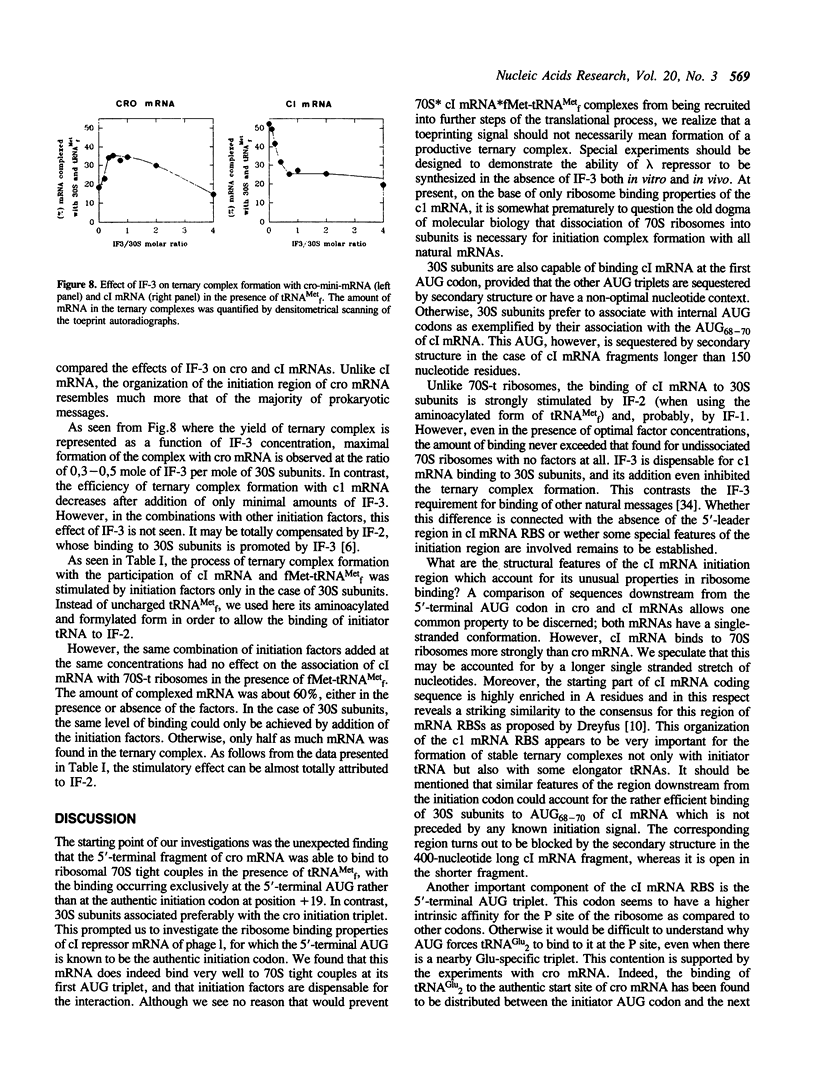
Full text
PDF

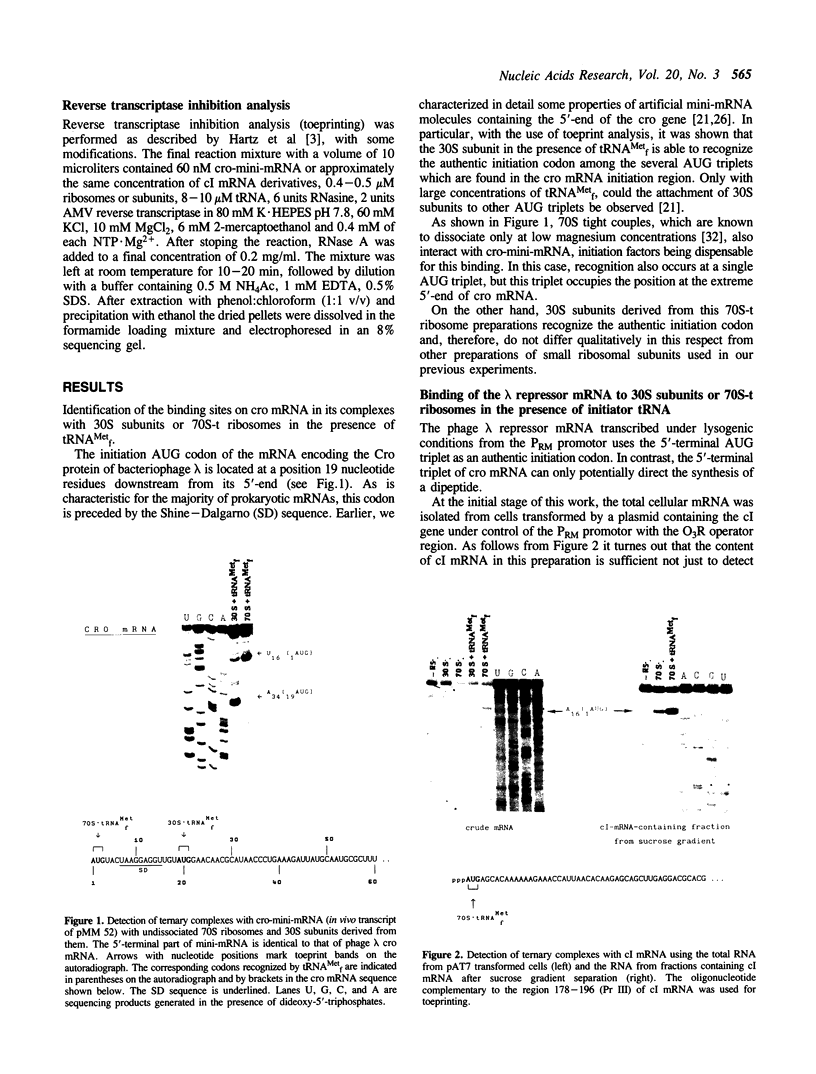

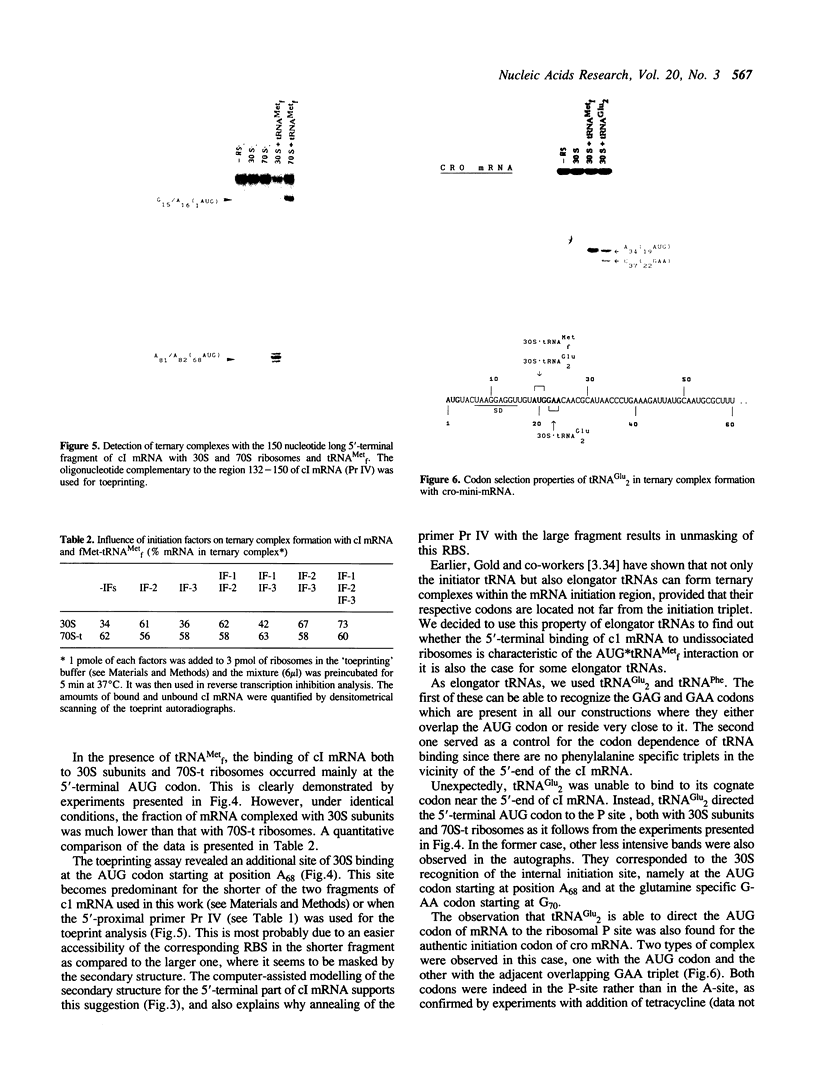
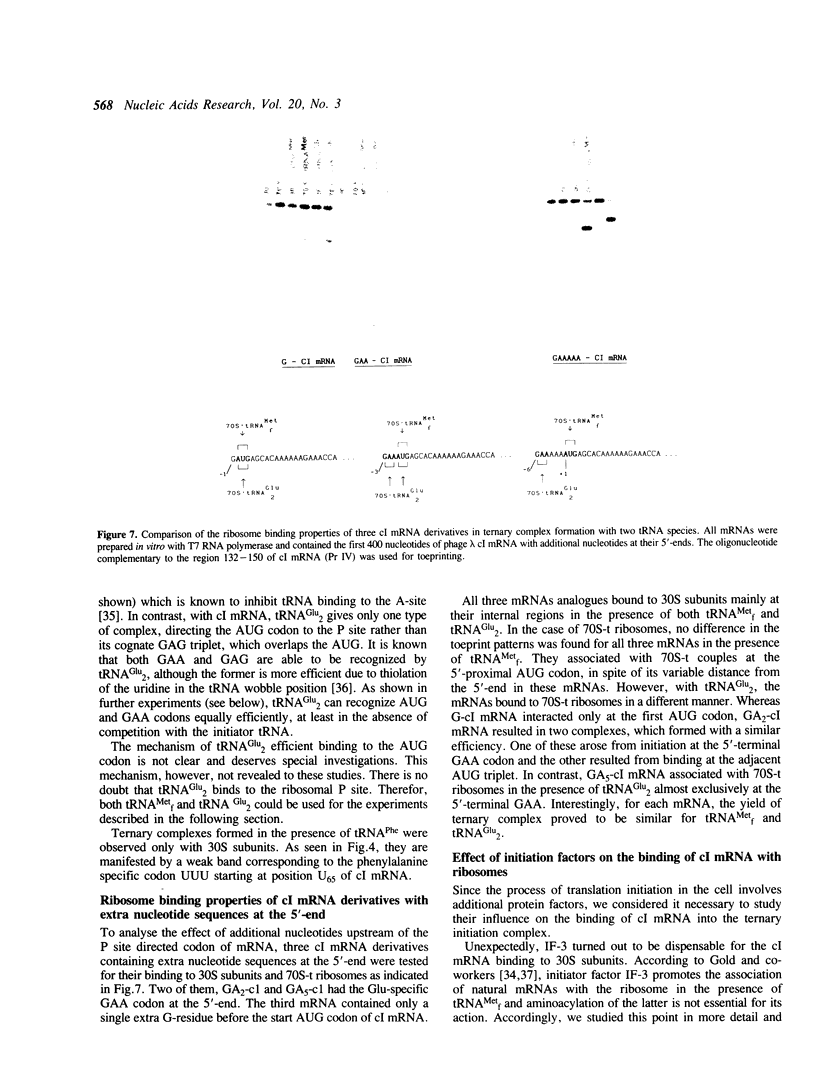


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agranovsky A. A., Boyko V. P., Karasev A. V., Lunina N. A., Koonin E. V., Dolja V. V. Nucleotide sequence of the 3'-terminal half of beet yellows closterovirus RNA genome: unique arrangement of eight virus genes. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jan;72(Pt 1):15–23. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi G. Animal mitochondrial DNA: an extreme example of genetic economy. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:93–145. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61373-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balakin A. G., Skripkin E. A., Shatskii I. N., Van Duin Ia, Bogdanov A. A. Lokalizatsiia uchastkov mRNK, ékraniruemykh ribosomami v initsiatornykh kompleksakh, pri pomoshchi reaktsii obratnoi transkriptsii. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1989;305(4):1000–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balakin A., Skripkin E., Shatsky I., Bogdanov A. Transition of the mRNA sequence downstream from the initiation codon into a single-stranded conformation is strongly promoted by binding of the initiator tRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90151-Q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta A., Steiner G., Brosius J., Noller H. F., Kuechler E. Identification of a site on 23S ribosomal RNA located at the peptidyl transferase center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3607–3611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boni I. V., Isaeva D. M., Musychenko M. L., Tzareva N. V. Ribosome-messenger recognition: mRNA target sites for ribosomal protein S1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):155–162. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Daniels C. J., Reeve J. N. Gene structure, organization, and expression in archaebacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;16(4):287–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denslow N. D., Michaels G. S., Montoya J., Attardi G., O'Brien T. W. Mechanism of mRNA binding to bovine mitochondrial ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8328–8338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M. What constitutes the signal for the initiation of protein synthesis on Escherichia coli mRNAs? J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):79–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evstafieva A. G., Ugarova T. Y., Chernov B. K., Shatsky I. N. A complex RNA sequence determines the internal initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):665–671. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C. O., Pon C. L. Initiation of mRNA translation in prokaryotes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):5881–5889. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., Binkley J., Hollingsworth T., Gold L. Domains of initiator tRNA and initiation codon crucial for initiator tRNA selection by Escherichia coli IF3. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1790–1800. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Gold L. Selection of the initiator tRNA by Escherichia coli initiation factors. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1899–1912. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Traut R., Gold L. Extension inhibition analysis of translation initiation complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:419–425. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques N., Dreyfus M. Translation initiation in Escherichia coli: old and new questions. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1063–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinks-Robertson S., Gourse R. L., Nomura M. Expression of rRNA and tRNA genes in Escherichia coli: evidence for feedback regulation by products of rRNA operons. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):865–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao H. X., Spremulli L. L. Effects of length and mRNA secondary structure on the interaction of bovine mitochondrial ribosomes with messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11761–11765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao H. X., Spremulli L. L. Interaction of bovine mitochondrial ribosomes with messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7518–7522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhno V. I., Peshin N. N., Semenkov Iu P., Kirillov S. V. Modifitsirovannyi sposob polucheniia "tight" 70S ribosom iz Escherichia coli, vysokoaktivnykh v otdel'nykh stadiiakh tsikla élongatsii. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1988 May-Jun;22(3):670–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. E., Gualerzi C. Translational control of prokaryotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90098-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Traut R. R., Noller H., Pearson P., Delius H. Ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. II. Proteins from the 30 s subunit. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):441–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. V. Magnesium-dependent dissociation of tight couples into subunits: measurements of dissociation constants and exchange rates. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):111–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojala D. K., Montoya J., Attardi G. The putative mRNA for subunit II of human cytochrome c oxidase starts directly at the translation initiator codon. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):79–82. doi: 10.1038/287079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G. B., Stockwell P. A., Hill D. F. Messenger RNA recognition in Escherichia coli: a possible second site of interaction with 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3957–3962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatsky I. N., Bakin A. V., Bogdanov A. A., Vasiliev V. D. How does the mRNA pass through the ribosome? Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):937–945. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90135-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelness G. S., Williams D. L. Secondary structure analysis of apolipoprotein II mRNA using enzymatic probes and reverse transcriptase. Evaluation of primer extension for high resolution structure mapping of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8637–8646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skripkin E. A., Bogdanova S. L., Kopylov A. M., Bogdanov A. A. Konstruirovanie i ékspressiia genov, kodiruiushchikh korotkie gibridnye mRNK Escherichia coli. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1986 Mar-Apr;287(1):237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Guertin D., Lee K. A. Capped mRNAs with reduced secondary structure can function in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1633–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengart M. L., Fatscher H. P., Fuchs E. The initiation of translation in E. coli: apparent base pairing between the 16srRNA and downstream sequences of the mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1719–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Nucleotide sequences of the ribosomal binding sites of bacteriophage R17 RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:621–630. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M., Reitmeier H., Oesterhelt D. Biosynthesis of the purple membrane of halobacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1976 Apr;15(4):187–194. doi: 10.1002/anie.197601871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]