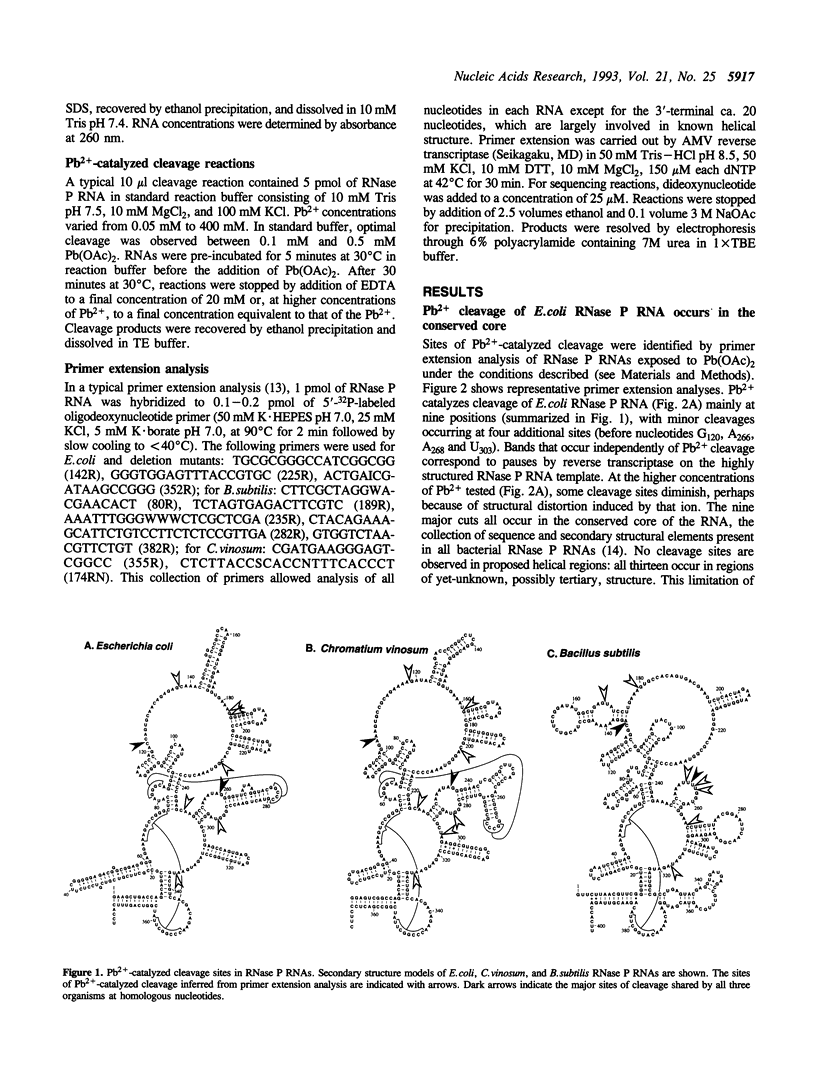
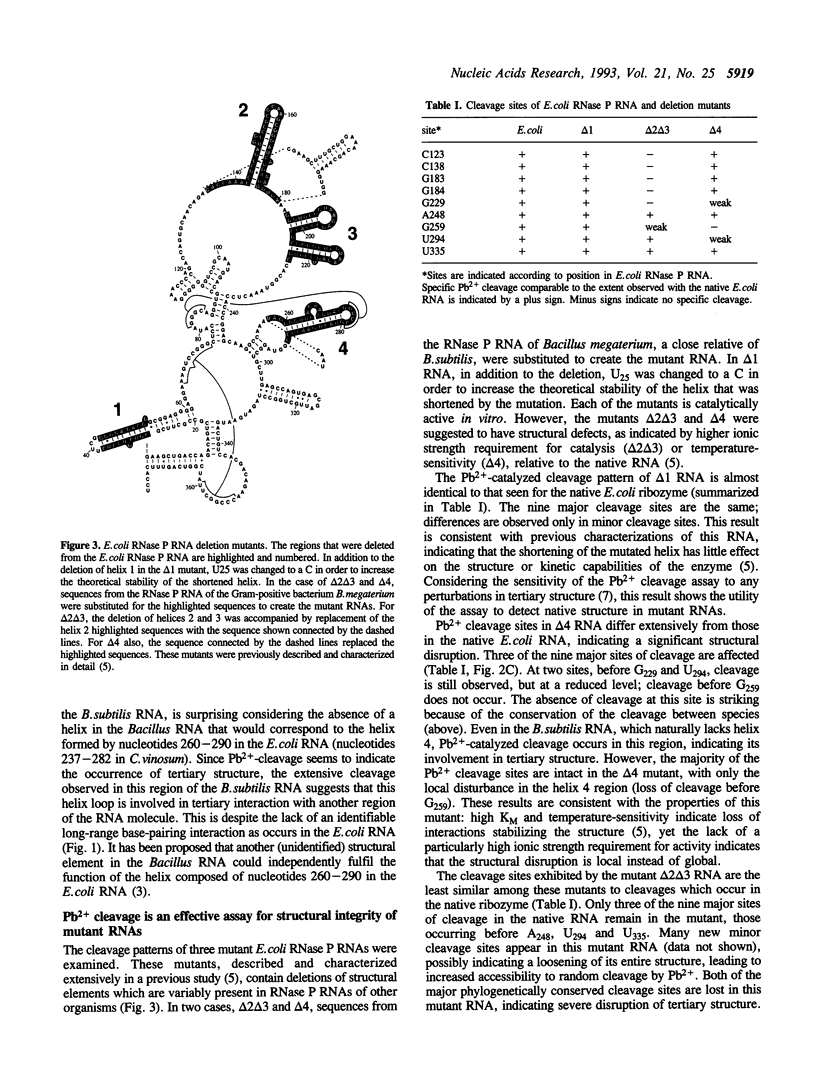
Abstract
Pb(2+)-catalyzed cleavage of RNA has been shown previously to be a useful probe for tertiary structure. In the present study, Pb2+ cleavage patterns were identified for ribonuclease P RNAs from three phylogenetically disparate organisms, Escherichia coli, Chromatium vinosum, Bacillus subtilis, and for E. coli RNase P RNAs that had been altered by deletions. Each of the native RNAs undergoes cleavage at several sites in the core structure that is common to all bacterial RNase P RNAs. All the cleavages occur in non-paired regions of the secondary structure models of the RNAs, in regions likely to be involved in tertiary interactions. Two cleavage sites occur at homologous positions in all the native RNAs, regardless of sequence variation, suggesting common tertiary structural features. The Pb2+ cleavage sites in four deletion mutants of E. coli RNase P RNA differed from the native pattern, indicating alterations in the tertiary structures of the mutant RNAs. This conclusion is consistent with previously characterized properties of the mutant RNAs. The Pb2+ cleavage assay is thus a useful probe to reveal alteration of tertiary structure in RNase P RNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behlen L. S., Sampson J. R., DiRenzo A. B., Uhlenbeck O. C. Lead-catalyzed cleavage of yeast tRNAPhe mutants. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2515–2523. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Pace N. R. Ribonuclease P RNA and protein subunits from bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1451–1456. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Dewan J. C., Klug A. Crystallographic and biochemical investigation of the lead(II)-catalyzed hydrolysis of yeast phenylalanine tRNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4785–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Hingerty B. E., Dewan J. C., Klug A. Pb(II)-catalysed cleavage of the sugar-phosphate backbone of yeast tRNAPhe--implications for lead toxicity and self-splicing RNA. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):543–546. doi: 10.1038/303543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgin A. B., Pace N. R. Mapping the active site of ribonuclease P RNA using a substrate containing a photoaffinity agent. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4111–4118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darr S. C., Zito K., Smith D., Pace N. R. Contributions of phylogenetically variable structural elements to the function of the ribozyme ribonuclease P. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):328–333. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E. S., Morse D. P., Brown J. W., Schmidt F. J., Pace N. R. Long-range structure in ribonuclease P RNA. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):853–856. doi: 10.1126/science.1719634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Ladner J. E., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Klug A. A crystallographic study of metal-binding to yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 15;111(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James B. D., Olsen G. J., Liu J. S., Pace N. R. The secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA, the catalytic element of a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov S., Altman S. Site-specific cleavage by metal ion cofactors and inhibitors of M1 RNA, the catalytic subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9193–9197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzosiak W. J., Marciniec T., Wiewiorowski M., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Giegé R. Characterization of the lead(II)-induced cleavages in tRNAs in solution and effect of the Y-base removal in yeast tRNAPhe. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5771–5777. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumelsky N., Altman S. Selection and characterization of randomly produced mutants in the gene coding for M1 RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Uhlenbeck O. C. Synthesis of small RNAs using T7 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:51–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Gutell R. R., Uhlenbeck O. C. Folding of circularly permuted transfer RNAs. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1361–1364. doi: 10.1126/science.1720569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Burgin A. B., Haas E. S., Pace N. R. Influence of metal ions on the ribonuclease P reaction. Distinguishing substrate binding from catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Pace N. R. Multiple magnesium ions in the ribonuclease P reaction mechanism. Biochemistry. 1993 May 25;32(20):5273–5281. doi: 10.1021/bi00071a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streicher B., von Ahsen U., Schroeder R. Lead cleavage sites in the core structure of group I intron-RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):311–317. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh D. S., Green C. J., Pace N. R. The design and catalytic properties of a simplified ribonuclease P RNA. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1569–1571. doi: 10.1126/science.2472671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]