Abstract
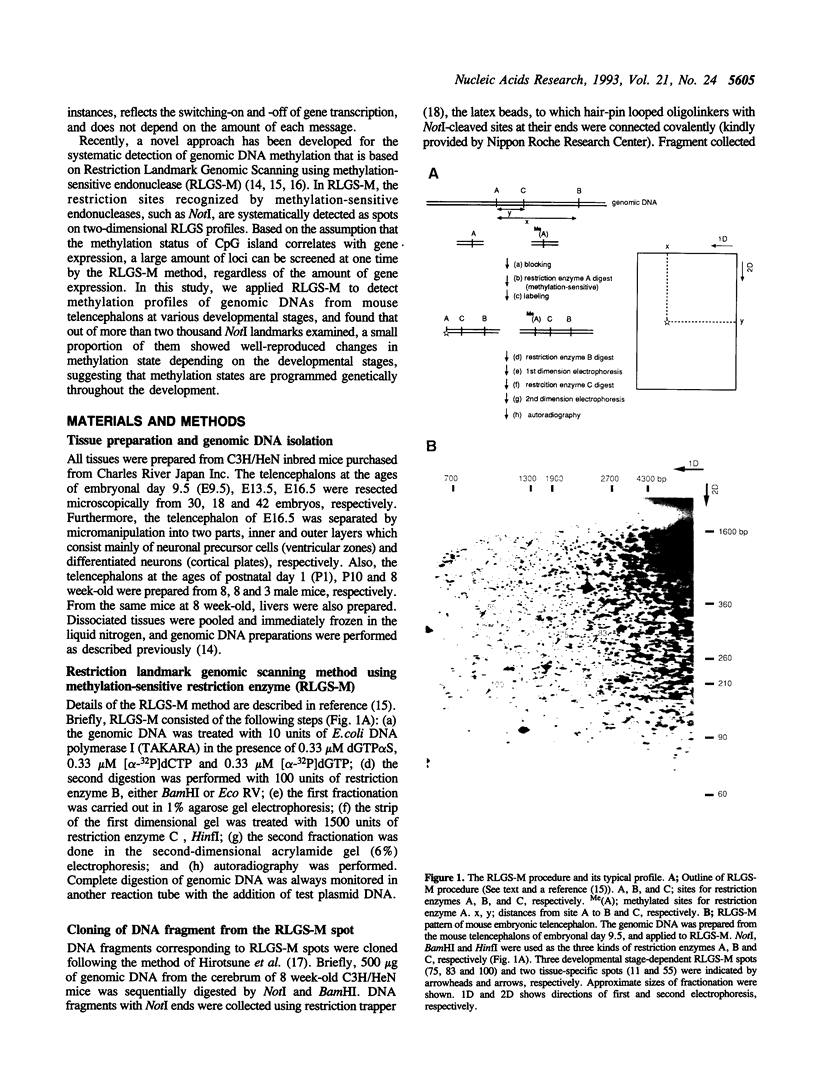
Restriction landmark genomic scanning using methylation-sensitive endonucleases (RLGS-M) is a newly developed powerful method for systematic detection of DNA methylation. Using this method, we scanned mouse brain genomic DNAs from various developmental stages to detect the transcriptionally active regions. This approach is based on the assumption that CpG methylation, particularly of CpG islands, might be associated with gene transcriptional regulation. Genomic DNAs were prepared from telencephalons of 9.5-, 13.5- and 16.5-day embryos, 1- and 10-day neonates and adults, followed by subjecting them to RLGS-M and comparing their patterns with each other or with that of the adult liver. We used NotI as a methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme and surveyed the methylation states of 2,600 NotI sites, almost of which should correspond to gene loci. Although almost all RLGS spots (98%) were present constantly at every developmental stages, only a few percent of spots reproducibly appeared and disappeared at different developmental stages of the brain (44 spots, 1.7%) and some were tissue-specific (10 spots, 0.7%). These data suggest that DNA methylation associated with gene transcription is a well-programmed event during the central nervous system (CNS) development. Thus, RLGS-M can offer a means for detecting systematically the genes in which the state of DNA methylation changes during development of the higher organism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baik J. H., Griffiths S., Giuili G., Manson M., Siegrist S., Guellaen G. DNA methylation patterns of the rat gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase gene in embryonic, adult and neoplastic liver. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Jun;12(6):1035–1039. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. The essentials of DNA methylation. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90526-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Razin A. DNA methylation and development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 24;1049(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90076-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D., Keshet I., Shani M., Levine A., Razin A., Cedar H. Demethylation of CpG islands in embryonic cells. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):239–241. doi: 10.1038/351239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatada I., Hayashizaki Y., Hirotsune S., Komatsubara H., Mukai T. A genomic scanning method for higher organisms using restriction sites as landmarks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9523–9527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashizaki Y., Hirotsune S., Hatada I., Tamatsukuri S., Miyamoto C., Furuichi Y., Mukai T. A new method for constructing NotI linking and boundary libraries using a restriction trapper. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):733–739. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashizaki Y., Hirotsune S., Okazaki Y., Hatada I., Shibata H., Kawai J., Hirose K., Watanabe S., Fushiki S., Wada S. Restriction landmark genomic scanning method and its various applications. Electrophoresis. 1993 Apr;14(4):251–258. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150140145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Cohen D. I., Nielsen E. A., Davis M. M. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding T cell-specific membrane-associated proteins. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):149–153. doi: 10.1038/308149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirotsune S., Hatada I., Komatsubara H., Nagai H., Kuma K., Kobayakawa K., Kawara T., Nakagawara A., Fujii K., Mukai T. New approach for detection of amplification in cancer DNA using restriction landmark genomic scanning. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3642–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirotsune S., Shibata H., Okazaki Y., Sugino H., Imoto H., Sasaki N., Hirose K., Okuizumi H., Muramatsu M., Plass C. Molecular cloning of polymorphic markers on RLGS gel using the spot target cloning method. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 16;194(3):1406–1412. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko M. S. An 'equalized cDNA library' by the reassociation of short double-stranded cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5705–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Bestor T. H., Jaenisch R. Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):915–926. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90611-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo K., Hori N., Matoba R., Niiyama T., Fukushima A., Kojima Y., Matsubara K. Large scale cDNA sequencing for analysis of quantitative and qualitative aspects of gene expression. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):173–179. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patanjali S. R., Parimoo S., Weissman S. M. Construction of a uniform-abundance (normalized) cDNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1943–1947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peek R., Niessen R. W., Schoenmakers J. G., Lubsen N. H. DNA methylation as a regulatory mechanism in rat gamma-crystallin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):77–83. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes K., Breindl M. Developmental changes in the methylation status of regulatory elements in the murine alpha 1(I) collagen gene. Gene Expr. 1992;2(1):59–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer R., Kafri T., O'Connell A., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L., Razin A. Methylation changes in the apolipoprotein AI gene during embryonic development of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11300–11304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





