Abstract
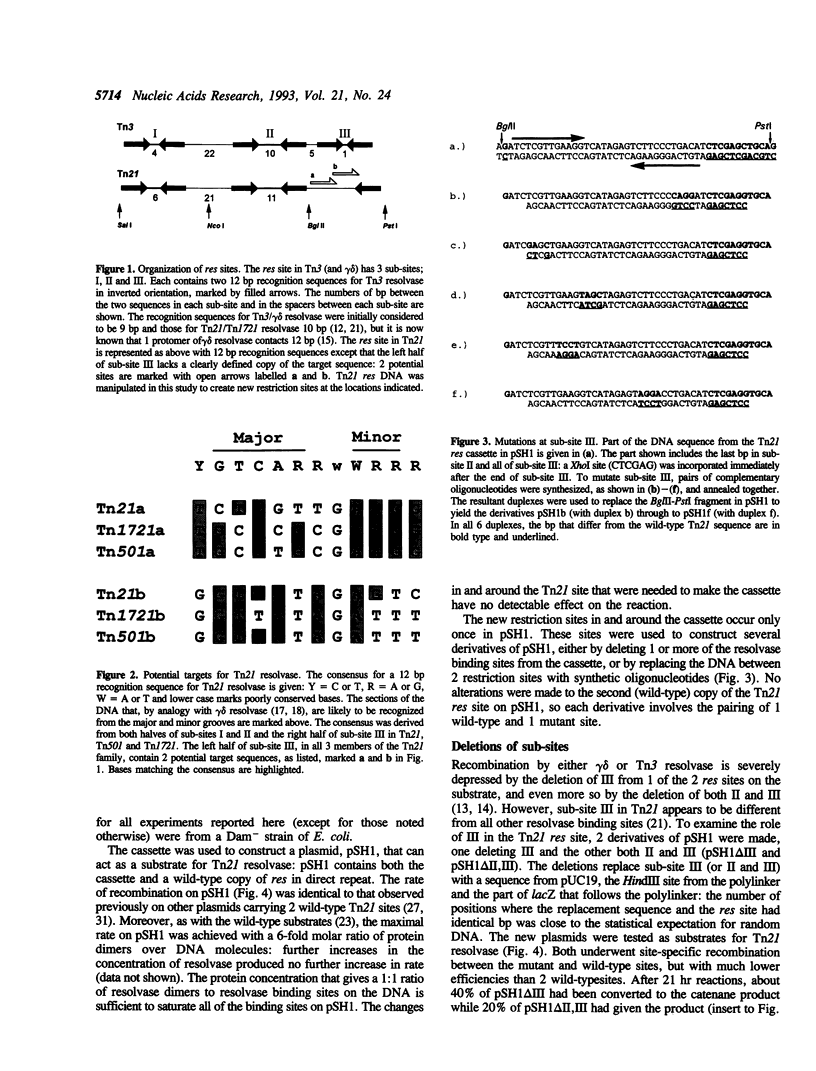
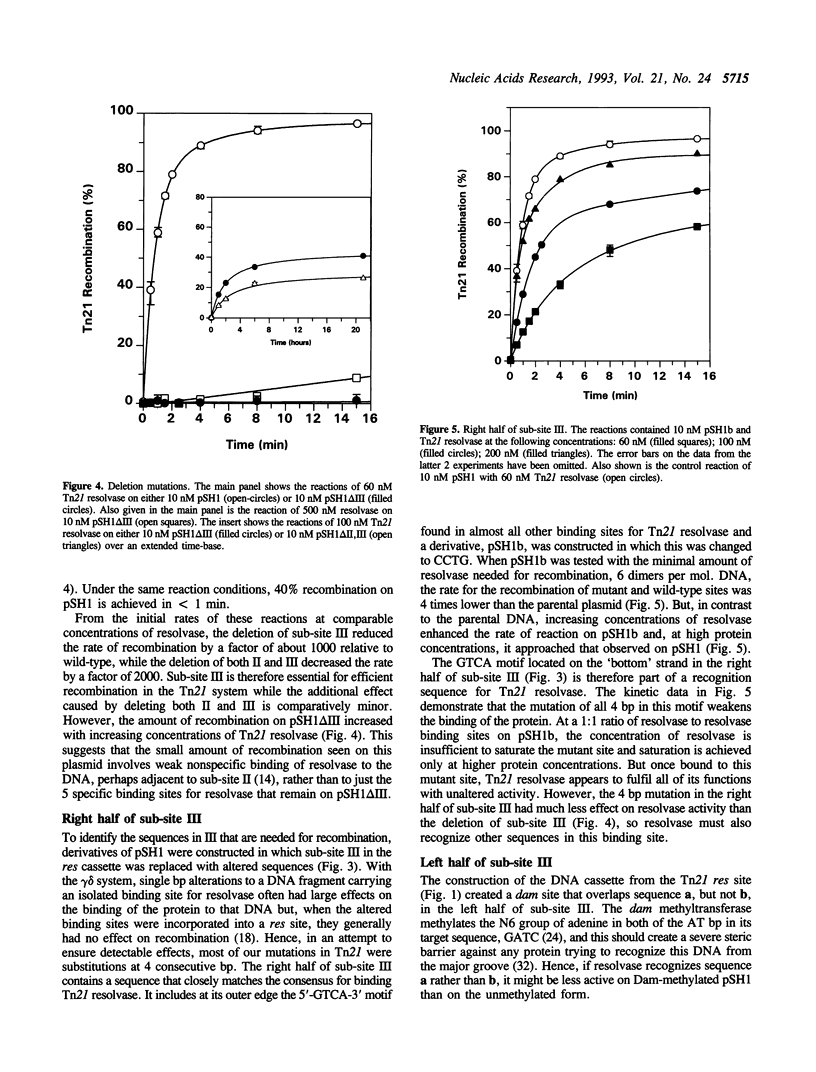
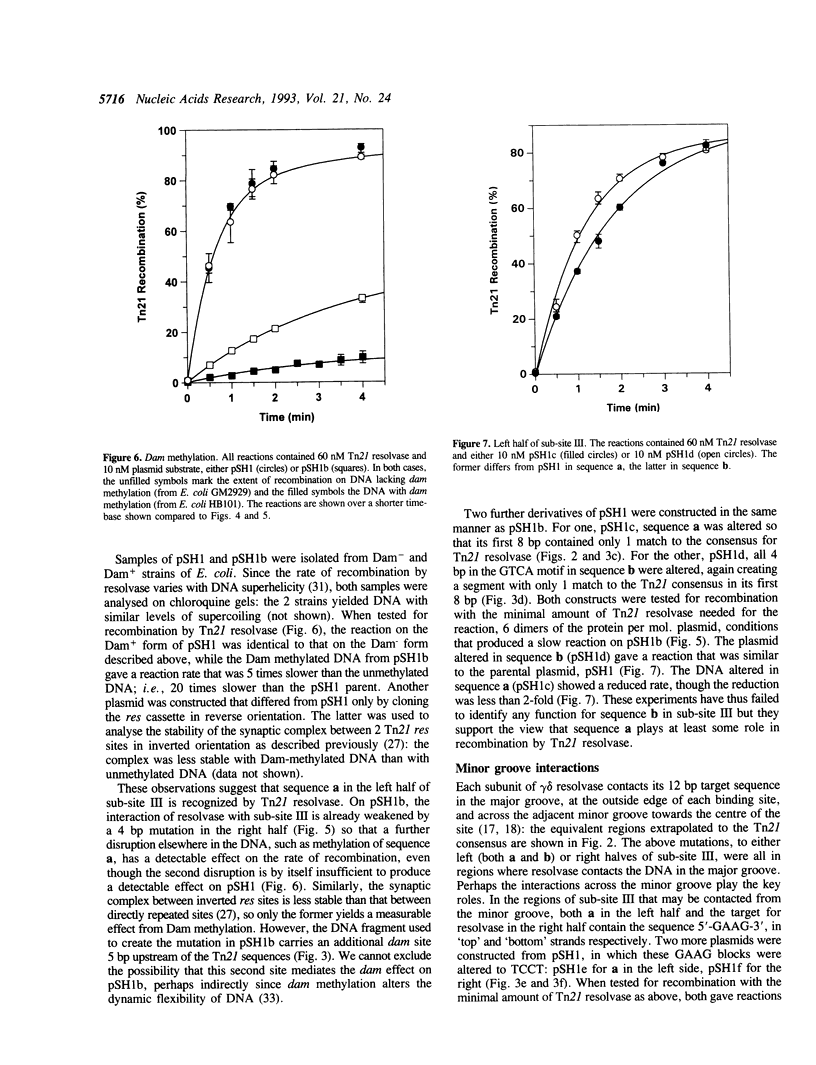
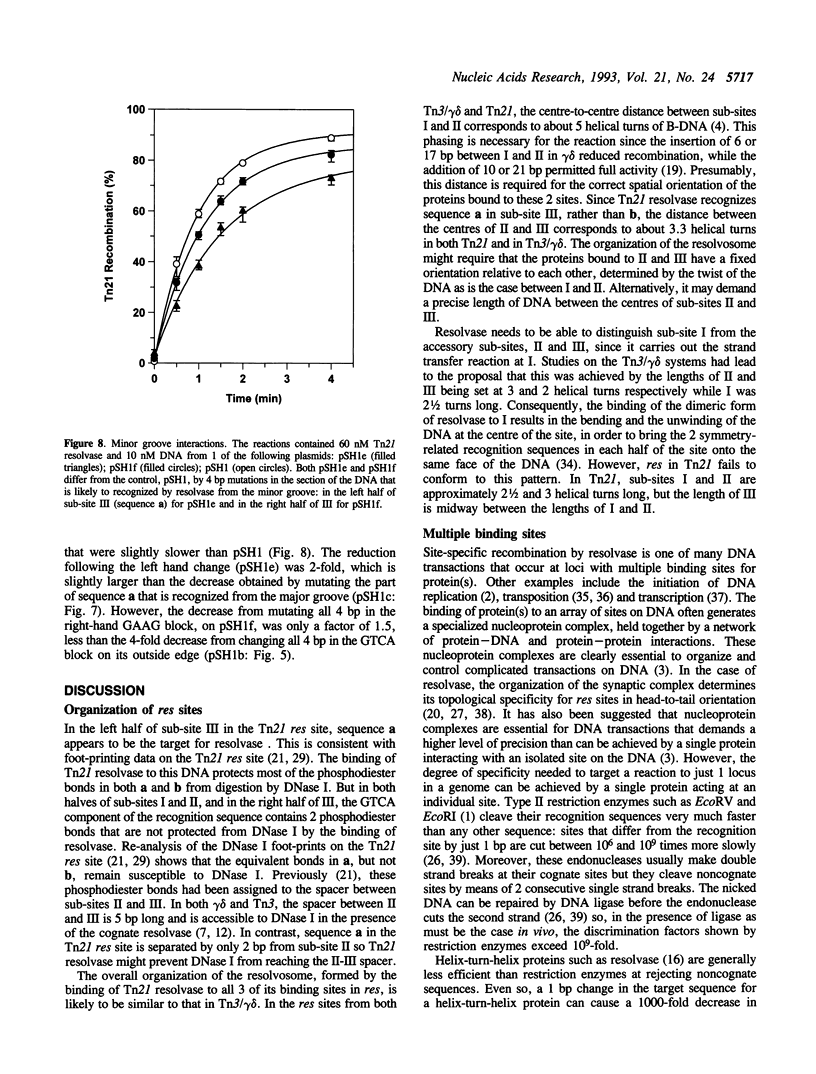
Resolvases from Tn3-like transposons catalyse site-specific recombination at res sites. Each res site has 3 binding sites for resolvase, I, II, and III. The res sites in Tn3 and Tn21 have similar structures at I and II but they differ at III. Mutagenesis of the Tn21 res site showed that sub-site III is essential for recombination though the sequences in III that are recognized by Tn21 resolvase are positioned differently from the equivalent sequences in the Tn3 site. The deletion of III caused a 1,000-fold drop in the rate of recombination. But other mutations at III, changing 3 or 4 consecutive base pairs, caused only 1.5- to 4-fold decreases in rate, even when the mutations were in target sequences for this helix-turn-helix protein. The reason why Tn21 resolvase has similar activities at a number of different DNA sequences may be due to the multiplicity of protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions in its recombinogenic complex. This lack of precision may be a general feature of nucleoprotein complexes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Grindley N. D., Templeton N. S., Steitz T. A. Cleavage of the site-specific recombination protein gamma delta resolvase: the smaller of two fragments binds DNA specifically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2001–2005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackroyd A. J., Avila P., Parker C. N., Halford S. E. Site-specific recombination by mutants of Tn21 resolvase with DNA recognition functions from Tn3 resolvase. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90388-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila P., Ackroyd A. J., Halford S. E. DNA binding by mutants of Tn21 resolvase with DNA recognition functions from Tn3 resolvase. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):645–655. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90389-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton R. J., Kubo K. M., Feng J. N., Craig N. L. Tn7 transposition: target DNA recognition is mediated by multiple Tn7-encoded proteins in a purified in vitro system. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):931–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90581-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barras F., Marinus M. G. The great GATC: DNA methylation in E. coli. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarz A. L., Boocock M. R., Sherratt D. J. Determinants of correct res site alignment in site-specific recombination by Tn3 resolvase. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2366–2375. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Cozzarelli N. R. Isolation and characterization of the Tn3 resolvase synaptic intermediate. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1897–1905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell S. E., Halford S. E. DNA supercoiling determines the activation energy barrier for site specific recombination by Tn21 resolvase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):7045–7058. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.7045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell S. E., Jordan S. L., Halford S. E. Site-specific recombination and topoisomerization by Tn21 resolvase: role of metal ions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7213–7226. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.18.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diver W. P., Grinsted J., Fritzinger D. C., Brown N. L., Altenbuchner J., Rogowsky P., Schmitt R. DNA sequences of and complementation by the tnpR genes of Tn21, Tn501 and Tn1721. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(2):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00334812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Multiple DNA-protein interactions governing high-precision DNA transactions. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1050–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.2943018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley G. V., Quignard E., Teoule R., Guy A., Guschlbauer W. A two-dimensional 1H-NMR study of the dam methylase site: comparison between the hemimethylated GATC sequence, its unmethylated analogue and a hemimethylated CATG sequence. The sequence dependence of methylation upon base-pair lifetimes. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 15;167(3):397–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick C. A., Quigley G. J., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Wang A. H., Rich A. Methylation of the EcoRI recognition site does not alter DNA conformation: the crystal structure of d(CGCGAm6ATTCGCG) at 2.0-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17872–17879. doi: 10.2210/pdb4dnb/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham K. S., Dervan P. B. Structural motif of the DNA binding domain of gamma delta-resolvase characterized by affinity cleaving. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16534–16540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Lauth M. R., Wells R. G., Wityk R. J., Salvo J. J., Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: identification of three binding sites for resolvase at the res sites of gamma delta and Tn3. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Brown N. L. A Tn21 terminal sequence within Tn501: complementation of tnpA gene function and transposon evolution. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(3):497–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00329949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., de la Cruz F., Schmitt R. The Tn21 subgroup of bacterial transposable elements. Plasmid. 1990 Nov;24(3):163–189. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90001-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halford S. E., Jordan S. L., Kirkbride E. A. The resolvase protein from the transposon Tn21. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):169–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00383331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Noble S. M., Grindley N. D. The gamma delta resolvase induces an unusual DNA structure at the recombinational crossover point. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90760-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J. How the EcoRI endonuclease recognizes and cleaves DNA. Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):445–454. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Symington L. S., Dyson P., Sherratt D. J. Transposon-encoded site-specific recombination: nature of the Tn3 DNA sequences which constitute the recombination site res. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1055–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., de la Cruz F. Genetic elements involved in Tn21 site-specific integration, a novel mechanism for the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1275–1281. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi M., Baker T. A., Mizuuchi K. Assembly of the active form of the transposase-Mu DNA complex: a critical control point in Mu transposition. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90104-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numrych T. E., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. A comparison of the effects of single-base and triple-base changes in the integrase arm-type binding sites on the site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3953–3959. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. N., Halford S. E. Dynamics of long-range interactions on DNA: the speed of synapsis during site-specific recombination by resolvase. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):781–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90121-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimphanitchayakit V., Grindley N. D. Saturation mutagenesis of the DNA site bound by the small carboxy-terminal domain of gamma delta resolvase. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):719–725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimphanitchayakit V., Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D. The 43 residue DNA binding domain of gamma delta resolvase binds adjacent major and minor grooves of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1035–1050. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P., Halford S. E., Schmitt R. Definition of three resolvase binding sites at the res loci of Tn21 and Tn1721. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2135–2141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P., Schmitt R. Tn1721-encoded resolvase: structure of the tnpR gene and its in vitro functions. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):176–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00383332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. The gamma delta resolvase bends the res site into a recombinogenic complex. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3609–3616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai A., Takeda Y. Lambda repressor recognizes the approximately 2-fold symmetric half-operator sequences asymmetrically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6513–6517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Opsomer C., McKeown Y. M., Kramer W., Zabeau M., Fritz H. J. Efficient oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations in expression vectors by the gapped duplex DNA method using alternating selectable markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4441–4454. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark W. M., Boocock M. R., Sherratt D. J. Site-specific recombination by Tn3 resolvase. Trends Genet. 1989 Sep;5(9):304–309. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vipond I. B., Halford S. E. Structure-function correlation for the EcoRV restriction enzyme: from non-specific binding to specific DNA cleavage. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(2):225–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Grindley N. D. Analysis of the gamma delta res site. Sites required for site-specific recombination and gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 15;179(4):667–687. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


