Abstract
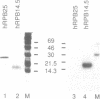
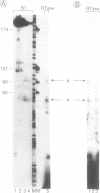
The structure of the gene encoding the 14.5 kDa subunit of the human RNA polymerase II (or B) has been elucidated. The gene consists of six exons, ranging from 52 to over 101 bp, interspaced with five introns ranging from 84 to 246 bp. It is transcribed into three major RNA species, present at low abundance in exponentially growing HeLa cells. The corresponding messenger RNAs contain the same open reading frame encoding a 125 amino acid residue protein, with a calculated molecular weight of 14,523 Da. This protein (named hRPB14.5) shares strong homologies with the homologous polymerase subunits encoded by the Drosophila (RpII15) and yeast (RPB9) genes. Cysteines characteristic of two zinc fingers are conserved in all three corresponding sequences and, like the yeast protein, the hRPB14.5 subunit exhibits zinc-binding activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker J., Wintzerith M., Vigneron M., Kédinger C. Primary structure of the second largest subunit of human RNA polymerase II (or B). J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1295–1299. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91071-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahearn J. M., Jr, Bartolomei M. S., West M. L., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the mouse genomic locus encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10695–10705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird D. M., Riddle D. L. Molecular cloning and sequencing of ama-1, the gene encoding the largest subunit of Caenorhabditis elegans RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4119–4130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carles C., Treich I., Bouet F., Riva M., Sentenac A. Two additional common subunits, ABC10 alpha and ABC10 beta, are shared by yeast RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24092–24096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg D., Dworniczak B., Faust D. M., Bautz E. K. RNA polymerase II of Drosophila. Relation of its 140,000 Mr subunit to the beta subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90496-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham J., Steger G., Yaniv M. How do eukaryotic activator proteins stimulate the rate of transcription by RNA polymerase II? FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 27;307(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80906-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. A., Mortin M. A., Corces V. G. The RNA polymerase II 15-kilodalton subunit is essential for viability in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):928–935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokerst R. S., Weeks J. R., Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. Analysis of the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):266–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00339727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II subunit RPB3 is an essential component of the mRNA transcription apparatus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5387–5394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. A consideration of alternative models for the initiation of translation in eukaryotes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(4-5):385–402. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Gropp F., Lottspeich F., Zillig W., Garrett R. A. Sequence, organization, transcription and evolution of RNA polymerase subunit genes from the archaebacterial extreme halophiles Halobacterium halobium and Halococcus morrhuae. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisitsyn N. A., Monastyrskaya G. S., Sverdlov E. D. Genes coding for RNA polymerase beta subunit in bacteria. Structure/function analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):363–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazen A., Gradwohl G., de Murcia G. Zinc-binding proteins detected by protein blotting. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKune K., Richards K. L., Edwards A. M., Young R. A., Woychik N. A. RPB7, one of two dissociable subunits of yeast RNA polymerase II, is essential for cell viability. Yeast. 1993 Mar;9(3):295–299. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Monastyrskaya G. S., Gubanov V. V., Guryev S. O., Salomatina I. S., Shuvaeva T. M., Lipkin V. M., Sverdlov E. D. The primary structure of E. coli RNA polymerase, Nucleotide sequence of the rpoC gene and amino acid sequence of the beta'-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):4035–4044. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pati U. K., Weissman S. M. Isolation and molecular characterization of a cDNA encoding the 23-kDa subunit of human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13114–13121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pati U. K., Weissman S. M. The amino acid sequence of the human RNA polymerase II 33-kDa subunit hRPB 33 is highly conserved among eukaryotes. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8400–8403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pühler G., Leffers H., Gropp F., Palm P., Klenk H. P., Lottspeich F., Garrett R. A., Zillig W. Archaebacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerases testify to the evolution of the eukaryotic nuclear genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4569–4573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. L., Levin J. R., Ingles C. J., Agabian N. In trypanosomes the homolog of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II is encoded by two genes and has a highly unusual C-terminal domain structure. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):815–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90686-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D., Nonet M., Young R. A. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases have homologous core subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treich I., Carles C., Riva M., Sentenac A. RPC10 encodes a new mini subunit shared by yeast nuclear RNA polymerases. Gene Expr. 1992;2(1):31–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treich I., Riva M., Sentenac A. Zinc-binding subunits of yeast RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21971–21976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintzerith M., Acker J., Vicaire S., Vigneron M., Kedinger C. Complete sequence of the human RNA polymerase II largest subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):910–910. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Lane W. S., Young R. A. Yeast RNA polymerase II subunit RPB9 is essential for growth at temperature extremes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19053–19055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Liao S. M., Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Subunits shared by eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):313–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., McKune K., Lane W. S., Young R. A. Yeast RNA polymerase II subunit RPB11 is related to a subunit shared by RNA polymerase I and III. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):77–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II subunit RPB10 is essential for yeast cell viability. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17816–17819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II subunit RPB4 is essential for high- and low-temperature yeast cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2854–2859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajchowski D. A., Boeuf H., Kédinger C. E1a inducibility of the adenoviral early E2a promoter is determined by specific combinations of sequence elements. Gene. 1987;58(2-3):243–256. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajchowski D. A., Boeuf H., Kédinger C. The adenovirus-2 early EIIa transcription unit possesses two overlapping promoters with different sequence requirements for EIa-dependent stimulation. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1293–1300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Advances in RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):488–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]