Abstract
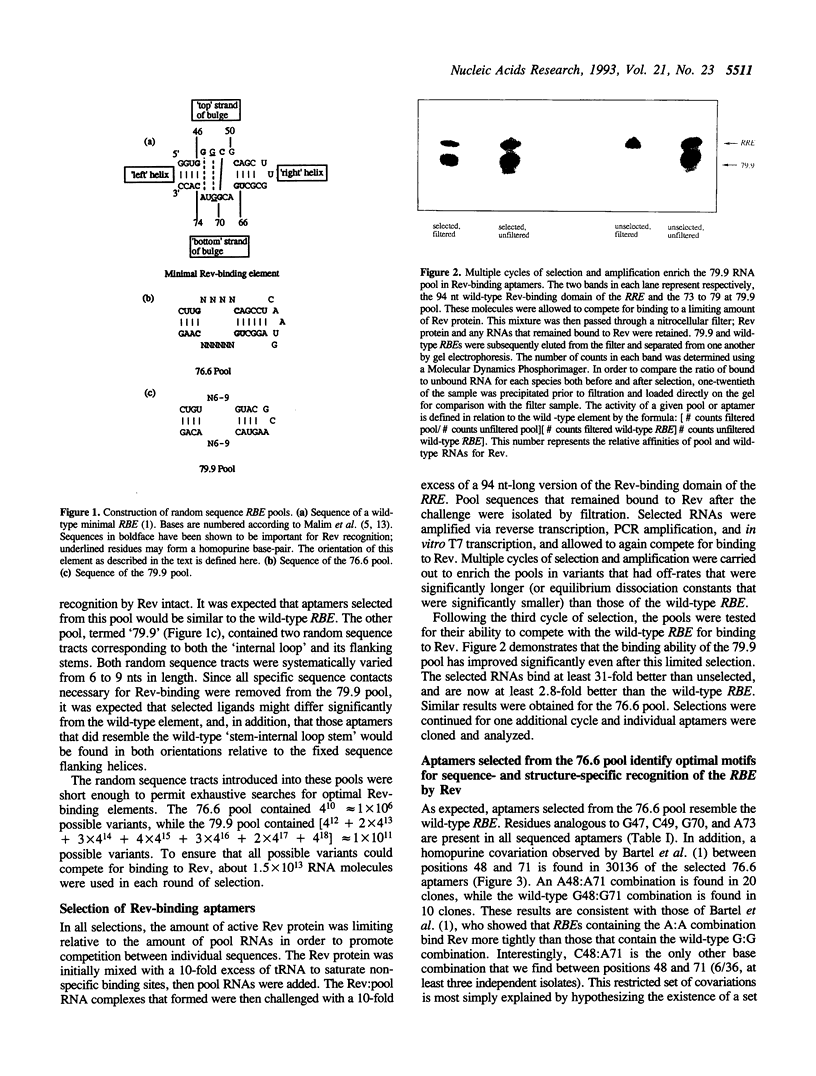
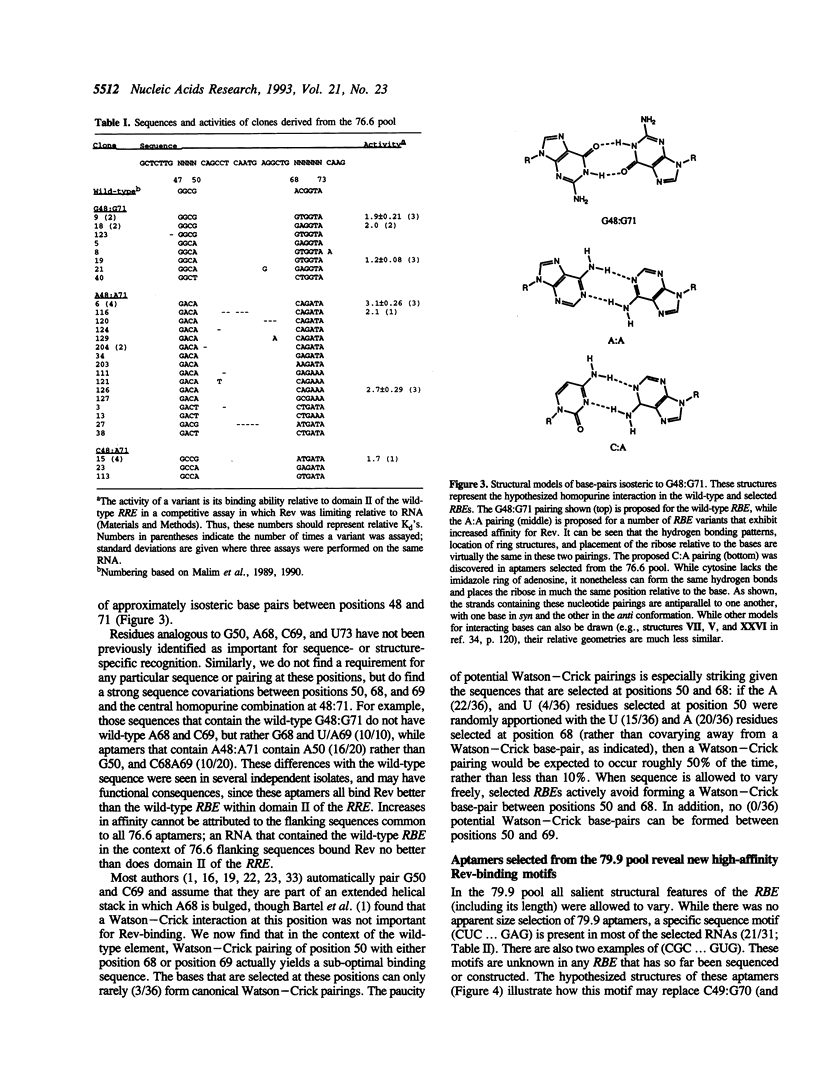
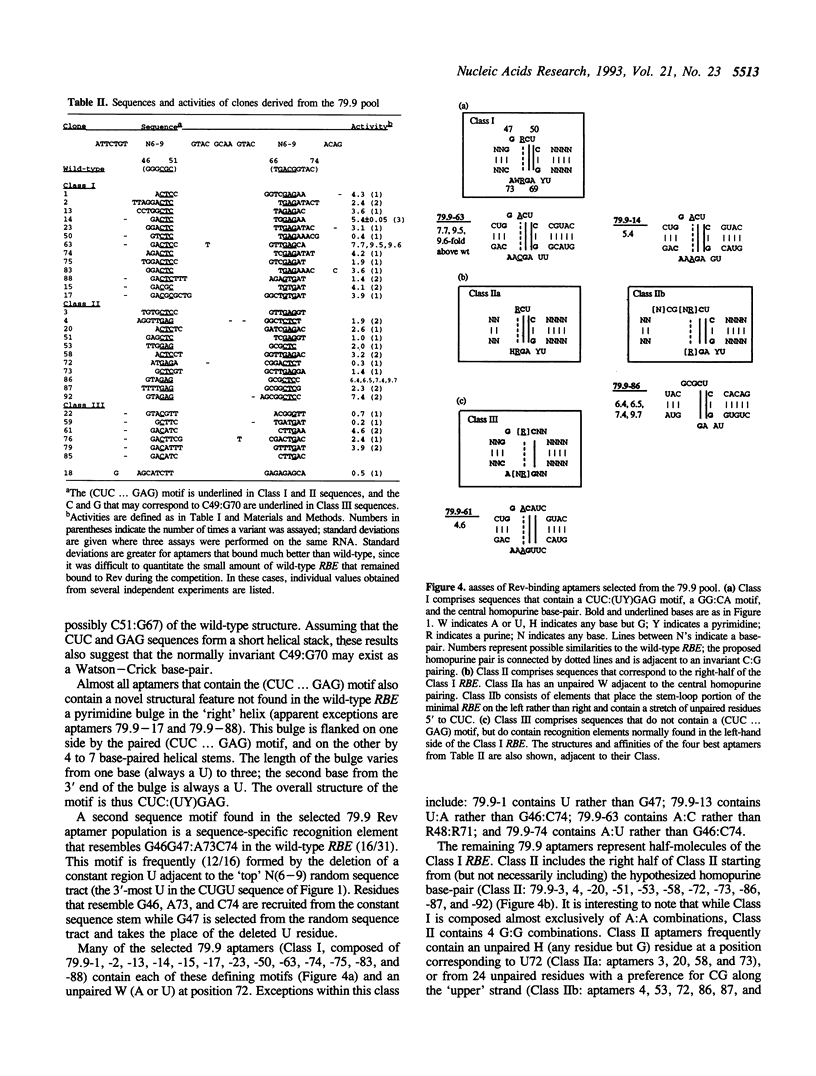
RNA molecules that can bind to the Rev protein of HIV-1 have been isolated from random sequence nucleic acid pools based on a minimal Rev-binding element (RBE) found within the Rev Responsive Element (RRE). While the selected sequences are related to the wild-type element, they also contain substitutions that allow them to bind Rev up to 10-fold better in vitro. A hypothesized homopurine pairing at G48:G71 is generally replaced by A48:A71; the occasional selection of C48:A71 suggests that R71 may be in a syn conformation. These data support the structural model for the RBE originally proposed by Bartel et al. (1). Additional interactions with the Rev protein are promoted by the sequence CUC ... UYGAG, found in one class of high-affinity aptamers, but absent from the wild-type element. Within each class of aptamers different residues and substructures covary with one another to generate optimal Rev-binding surfaces. The interdependencies of different nucleotide substitutions suggest structural models for both the wild-type RBE and the selected high-affinity aptamers.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Gene therapy. Intracellular immunization. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):395–396. doi: 10.1038/335395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P., Zapp M. L., Green M. R., Szostak J. W. HIV-1 Rev regulation involves recognition of non-Watson-Crick base pairs in viral RNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90527-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Specific interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein with a structured region in the env mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1198–1202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook K. S., Fisk G. J., Hauber J., Usman N., Daly T. J., Rusche J. R. Characterization of HIV-1 REV protein: binding stoichiometry and minimal RNA substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1577–1583. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couture S., Ellington A. D., Gerber A. S., Cherry J. M., Doudna J. A., Green R., Hanna M., Pace U., Rajagopal J., Szostak J. W. Mutational analysis of conserved nucleotides in a self-splicing group I intron. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):345–358. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton E. T., Konings D. A., Powell D. M., Shapiro B. A., Butini L., Maizel J. V., Dayton A. I. Extensive sequence-specific information throughout the CAR/RRE, the target sequence of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev protein. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1139–1151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1139-1151.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton E. T., Powell D. M., Dayton A. I. Functional analysis of CAR, the target sequence for the Rev protein of HIV-1. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1625–1629. doi: 10.1126/science.2688093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Vazeux R., Peden K. The rev gene product of the human immunodeficiency virus affects envelope-specific RNA localization. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1155–1165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Cladaras C., Copeland T., Pavlakis G. N. rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects the stability and transport of the viral mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Woese C. R. Higher order structural elements in ribosomal RNAs: pseudo-knots and the use of noncanonical pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Heimer J., Hammarskjöld B., Sangwan I., Albert L., Rekosh D. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus env expression by the rev gene product. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1959-1966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 regulator of virion expression (Rev) protein binds to an RNA stem-loop structure located within the Rev response element region. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Finch J. T., Gait M. J., Karn J., Singh M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 regulator of virion expression, rev, forms nucleoprotein filaments after binding to a purine-rich "bubble" located within the rev-responsive region of viral mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7366–7370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland S. M., Ahmad N., Maitra R. K., Wingfield P., Venkatesan S. Human immunodeficiency virus rev protein recognizes a target sequence in rev-responsive element RNA within the context of RNA secondary structure. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5966–5975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5966-5975.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland S. M., Chavez M., Gerstberger S., Venkatesan S. A specific sequence with a bulged guanosine residue(s) in a stem-bulge-stem structure of Rev-responsive element RNA is required for trans activation by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3699–3706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3699-3706.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X. J., Hope T. J., Bond B. L., McDonald D., Grahl K., Parslow T. G. Minimal Rev-response element for type 1 human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2131–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2131-2134.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai S., Pritchard C., Mann D. A., Karn J., Gait M. J. Recognition of the high affinity binding site in rev-response element RNA by the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 rev protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6465–6472. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Dingwall C., Finch J. T., Heaphy S., Gait M. J. RNA binding by the tat and rev proteins of HIV-1. Biochimie. 1991 Jan;73(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90068-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Brown M., Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Structural analysis of the interaction between the human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein and the Rev response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):683–687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Sharp P. A. Specific binding of a basic peptide from HIV-1 Rev. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1119–1129. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of RRE-derived sequences inhibits HIV-1 replication in CEM cells. New Biol. 1992 Jan;4(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisziewicz J., Sun D., Klotman M., Agrawal S., Zamecnik P., Gallo R. Specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by antisense oligonucleotides: an in vitro model for treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11209–11213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Tiley L. S., McCarn D. F., Rusche J. R., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires binding of the Rev trans-activator to its RNA target sequence. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90670-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Nelbock P., Cochrane A. W., Rosen C. A. Secondary structure is the major determinant for interaction of HIV rev protein with RNA. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):845–848. doi: 10.1126/science.2406903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G. Evidence for an essential non-Watson-Crick interaction between the first and last nucleotides of a nuclear pre-mRNA intron. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):660–662. doi: 10.1038/361660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Intragenic cis-acting art gene-responsive sequences of the human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of TAR sequences renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90455-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiley L. S., Malim M. H., Tewary H. K., Stockley P. G., Cullen B. R. Identification of a high-affinity RNA-binding site for the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):758–762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Sequence-specific RNA binding by the HIV-1 Rev protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):714–716. doi: 10.1038/342714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Hope T. J., Parslow T. G., Green M. R. Oligomerization and RNA binding domains of the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein: a dual function for an arginine-rich binding motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7734–7738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



