Abstract
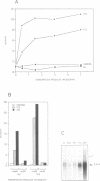
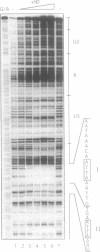
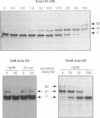
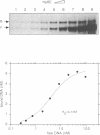
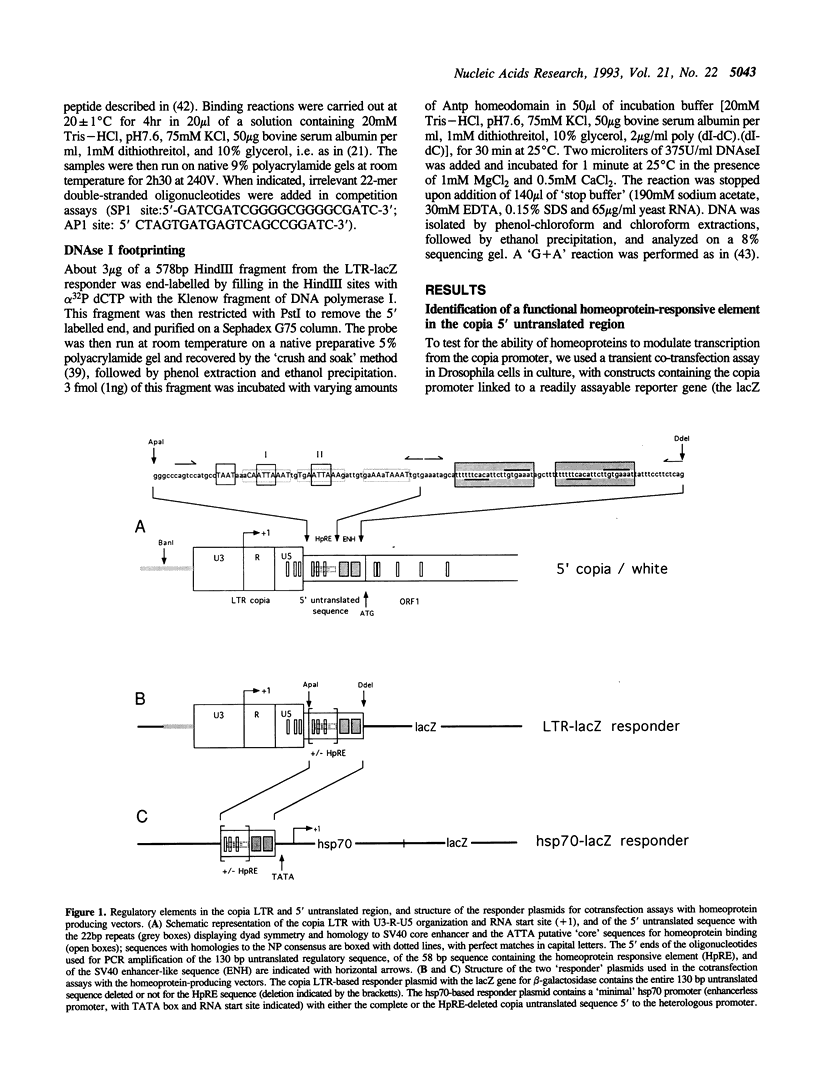
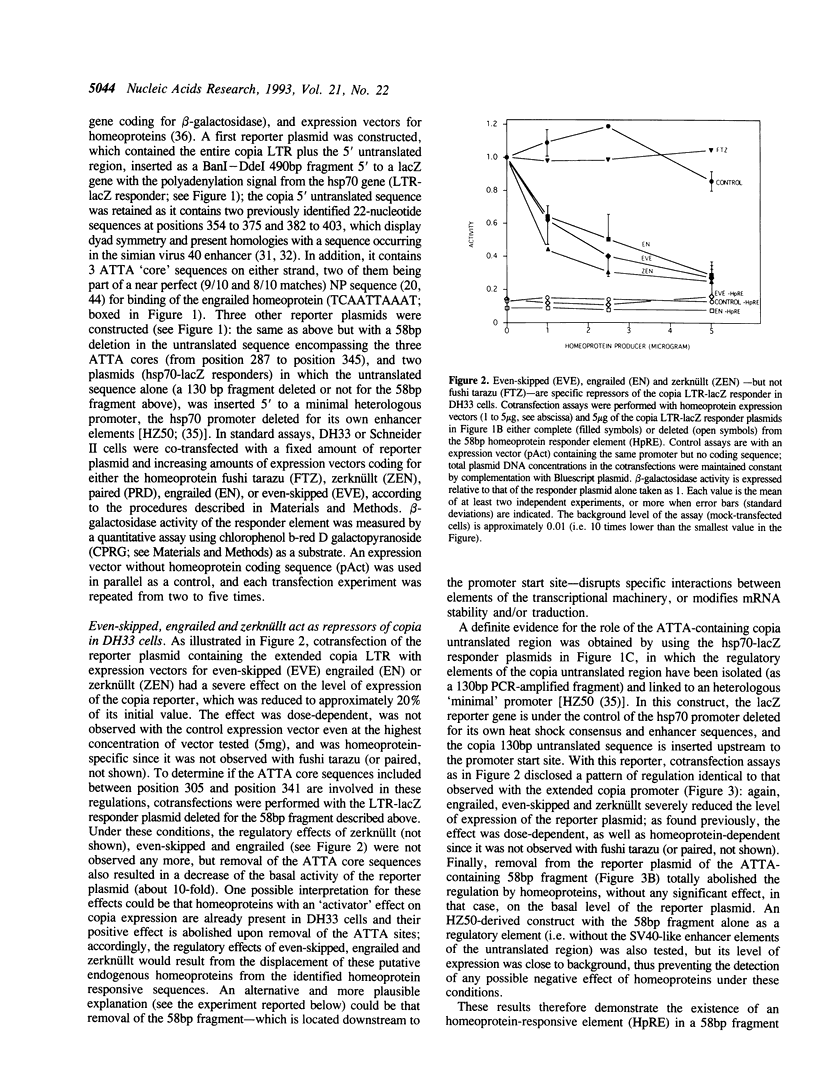
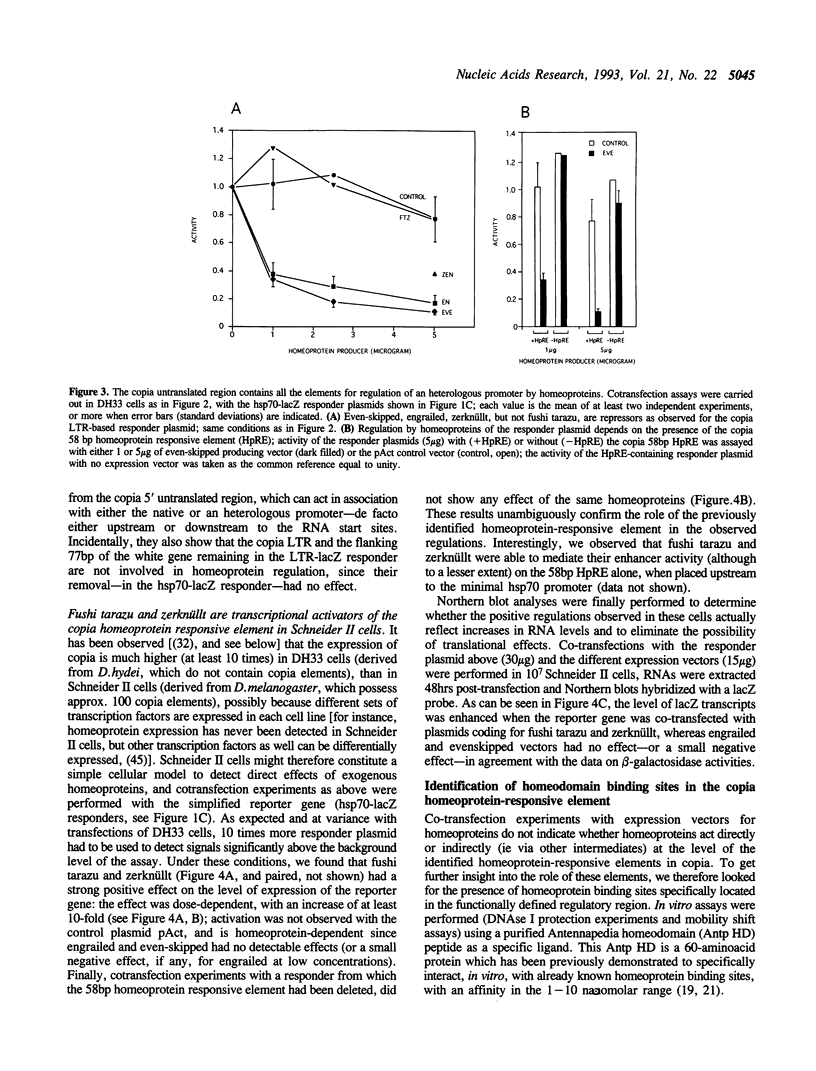
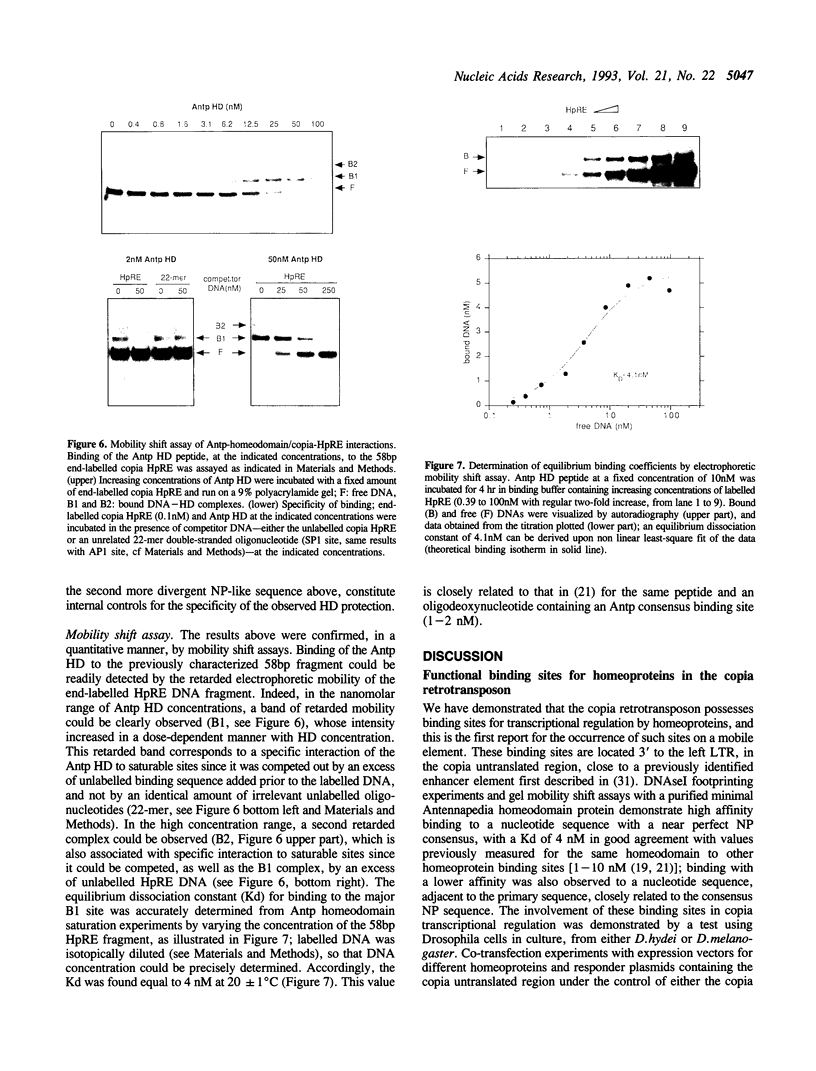
We have identified in the 5' untranslated region of the Drosophila copia retrotransposon, 3' to the left LTR, a sequence for transcriptional regulation by homeoproteins. Co-transfection assays using expression vectors for homeoproteins and reporter vectors containing the lacZ gene under the control of either the entire copia LTR with 5' untranslated sequence, or a minimal heterologous promoter flanked with a 130 bp fragment containing the copia untranslated region, disclosed both positive and negative modulations of promoter activity in Drosophila cells in culture: a 5-10 fold decrease with engrailed, even-skipped and zerknüllt in DH33 cells, and a 10-30 fold increase with fushi tarazu and zerknüllt in Schneider II cells. In all cases, the regulatory effects were abolished with reporter plasmids deleted for a 58 bp fragment encompassing the putative homeoprotein binding sites. Mobility shift assays with a purified homeodomain-containing peptide demonstrated direct interaction with the 58 bp fragment, with an affinity in the 1-10 nM range as reported with the same peptide for other well characterized homeodomain binding regulatory sites. Foot-printing experiments with the extended LTR demonstrated protection of 'consensus' sequences, located within the 58 bp fragment. These homeodomain binding sites could be involved in the developmental regulation of the copia retrotransposon.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Leupin W., Gehring W. J. DNA binding properties of the purified Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4093–4097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Affolter M., Schier A., Gehring W. J. Homeodomain proteins and the regulation of gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhipova I. R., Ilyin Y. V. Properties of promoter regions of mdg1 Drosophila retrotransposon indicate that it belongs to a specific class of promoters. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1169–1177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M., Qian Y., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Determination of the three-dimensional structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain from Drosophila in solution by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):183–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90155-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Rocancourt D., Briand P., Grimber G., Nicolas J. F. A beta-galactosidase hybrid protein targeted to nuclei as a marker for developmental studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6795–6799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant L. A., Brierley C., Flavell A. J., Sinclair J. H. The retrotransposon copia regulates Drosophila gene expression both positively and negatively. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5533–5536. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brûlet P., Condamine H., Jacob F. Spatial distribution of transcripts of the long repeated ETn sequence during early mouse embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2054–2058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucheton A. I transposable elements and I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila. Trends Genet. 1990 Jan;6(1):16–21. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G. Drosophila retrotransposons: interactions with genome. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:33–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Optimal DNA sequence recognition by the Ultrabithorax homeodomain of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Differential DNA sequence recognition is a determinant of specificity in homeotic gene action. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4059–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P., Liao X. B., Belcourt M., Zhao H., Kapakos J., Clare J. Enhancer and silencerlike sites within the transcribed portion of a Ty2 transposable element of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4824–4834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J. Transposable elements and DNA transposition in eukaryotes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florence B., Handrow R., Laughon A. DNA-binding specificity of the fushi tarazu homeodomain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3613–3623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton A. M., Rathjen P. D., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Upstream and downstream transcriptional control signals in the yeast retrotransposon, TY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5439–5458. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Poole S., Kornberg T. Association of the Drosophila melanogaster engrailed protein with specific soluble nuclear protein complexes. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4291–4297. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Müller M., Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Billeter M., Qian Y. Q., Otting G., Wüthrich K. The structure of the homeodomain and its functional implications. Trends Genet. 1990 Oct;6(10):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Levine M. S., Manley J. L. Synergistic activation and repression of transcription by Drosophila homeobox proteins. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. A genetic model for interaction of the homeodomain recognition helix with DNA. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):426–430. doi: 10.1126/science.1671176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Heidmann T. Retrotransposition of a mouse IAP sequence tagged with an indicator gene. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90217-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J. Regulation and function of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., O'Farrell P. H. Activation and repression of transcription by homoeodomain-containing proteins that bind a common site. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):744–749. doi: 10.1038/336744a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S., Heidmann T. An indicator gene for detection of germline retrotransposition in transgenic Drosophila demonstrates RNA-mediated transposition of the LINE I element. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1927–1937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joliot A., Pernelle C., Deagostini-Bazin H., Prochiantz A. Antennapedia homeobox peptide regulates neural morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1864–1868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K. The intracisternal A-particle gene family: structure and functional aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:183–276. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Bingham P. M., Rubin G. M. Physical map of the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):564–568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L. LINEs. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Dec;1(4):505–508. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W., Wüthrich K. Secondary structure determination for the Antennapedia homeodomain by nuclear magnetic resonance and evidence for a helix-turn-helix motif. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4305–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D., Courey A. J. The same dorsal binding site mediates both activation and repression in a context-dependent manner. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1837–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst S. M., Corces V. G. Developmental expression of Drosophila melanogaster retrovirus-like transposable elements. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):419–424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Elble R., Tye B. K. A protein involved in minichromosome maintenance in yeast binds a transcriptional enhancer conserved in eukaryotes. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):921–935. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pélisson A., Finnegan D. J., Bucheton A. Evidence for retrotransposition of the I factor, a LINE element of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4907–4910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. A., Lis J. T. A germline transformation analysis reveals flexibility in the organization of heat shock consensus elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2971–2988. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon A., Flavell A. J. The transcriptional control regions of the copia retrotransposon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4025–4035. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondermeijer P. J., Derksen J. W., Lubsen N. H. New cell line: established cell lines of Drosophila hydei. In Vitro. 1980 Nov;16(11):913–914. doi: 10.1007/BF02619327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Tanaka M., Herr W. The Oct-1 homoeodomain directs formation of a multiprotein-DNA complex with the HSV transactivator VP16. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):624–630. doi: 10.1038/341624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TenHarmsel A., Austin R. J., Savenelli N., Biggin M. D. Cooperative binding at a distance by even-skipped protein correlates with repression and suggests a mechanism of silencing. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2742–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]