Abstract
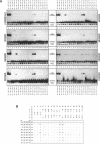
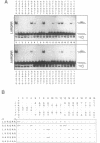
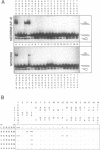
We exchanged specific amino acids in the basic region of the murine N-Myc protein and tested the mutant proteins for their DNA binding specificity. The amino acids we exchanged were chosen in analogy to residues of the homologous basic regions of bHLH and bZIP proteins. Mutant N-Myc peptides were expressed in Escherichia coli and specific DNA binding was monitored by gel shift experiments. For this we used palindromic target sequences with systematic base pair exchanges. Several mutants with altered DNA binding specificity were identified. Amino acid exchanges of residues -14 or -10 of the basic region lead to specificity changes (we define leucine 402 of N-Myc as +1; comparable to GCN4 see (1)). The palindromic N-Myc recognition sequence 5'CACGTG is no longer recognized by the mutant proteins, but DNA fragments with symmetrical exchanges of the target sequence are. Exchanges at position -15 broaden the binding specificity. These data were used to build a computer based model of the putative interactions of the N-Myc basic DNA binding region with its target sequence.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alex R., Sözeri O., Meyer S., Dildrop R. Determination of the DNA sequence recognized by the bHLH-zip domain of the N-Myc protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20(9):2257–2263. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.9.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Dalton S., Brooks M. W., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):423–426. doi: 10.1038/359423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Sharp P. A. A helix-loop-helix protein related to the immunoglobulin E box-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4384–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Barrett J., Villa-Garcia M., Resar L. M., Kato G. J., Fearon E. R. Intracellular leucine zipper interactions suggest c-Myc hetero-oligomerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):954–962. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildrop R., Ma A., Zimmerman K., Hsu E., Tesfaye A., DePinho R., Alt F. W. IgH enhancer-mediated deregulation of N-myc gene expression in transgenic mice: generation of lymphoid neoplasias that lack c-myc expression. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1121–1128. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré-D'Amaré A. R., Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B., Burley S. K. Recognition by Max of its cognate DNA through a dimeric b/HLH/Z domain. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):38–45. doi: 10.1038/363038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Parent L. A., Sharp P. A. Myc/Max and other helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper proteins bend DNA toward the minor groove. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11779–11783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Predicted structural similarities of the DNA binding domains of c-Myc and endonuclease Eco RI. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.1734524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkhoff E., Bister K., Klempnauer K. H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by Myc proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4323–4327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Tzamarias D., Ellenberger T., Harrison S. C., Struhl K. Adaptability at the protein-DNA interface is an important aspect of sequence recognition by bZIP proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4513–4517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisters-Woike B., Lehming N., Sartorius J., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. A model of the lac repressor-operator complex based on physical and genetic data. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jun 1;198(2):411–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Gee C. E., Alt F. W. Activated expression of the N-myc gene in human neuroblastomas and related tumors. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1335–1337. doi: 10.1126/science.6505694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Kanda N., Schreck R. R., Bruns G., Latt S. A., Gilbert F., Alt F. W. Transposition and amplification of oncogene-related sequences in human neuroblastomas. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Murphree A. L., Benedict W. F. Expression and amplification of the N-myc gene in primary retinoblastoma. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):458–460. doi: 10.1038/309458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehming N., Sartorius J., Kisters-Woike B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Mutant lac repressors with new specificities hint at rules for protein--DNA recognition. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):615–621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma A., Moroy T., Collum R., Weintraub H., Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K. DNA binding by N- and L-Myc proteins. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):1093–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens C. B., Auerbach A. B., Conlon R. A., Joyner A. L., Rossant J. A targeted mutation reveals a role for N-myc in branching morphogenesis in the embryonic mouse lung. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):691–704. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambu J. R., Lewis J. O., Wharton K. A., Jr, Crews S. T. The Drosophila single-minded gene encodes a helix-loop-helix protein that acts as a master regulator of CNS midline development. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1157–1167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeda K., Salinas J., Chua N. H. A tobacco bZip transcription activator (TAF-1) binds to a G-box-like motif conserved in plant genes. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1793–1802. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum H., Webb E., Adams J. M., Cory S., Harris A. W. N-myc transgene promotes B lymphoid proliferation, elicits lymphomas and reveals cross-regulation with c-myc. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):749–755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. R., Perkins A. S., Tessarollo L., Sassoon D. A., Parada L. F. Loss of N-myc function results in embryonic lethality and failure of the epithelial component of the embryo to develop. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2235–2247. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckow M., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Identification of three residues in the basic regions of the bZIP proteins GCN4, C/EBP and TAF-1 that are involved in specific DNA binding. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1193–1200. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suckow M., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. The DNA binding specificity of the basic region of the yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 can be changed by substitution of a single amino acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2081–2086. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lohuizen M., Breuer M., Berns A. N-myc is frequently activated by proviral insertion in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):133–136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]