Abstract
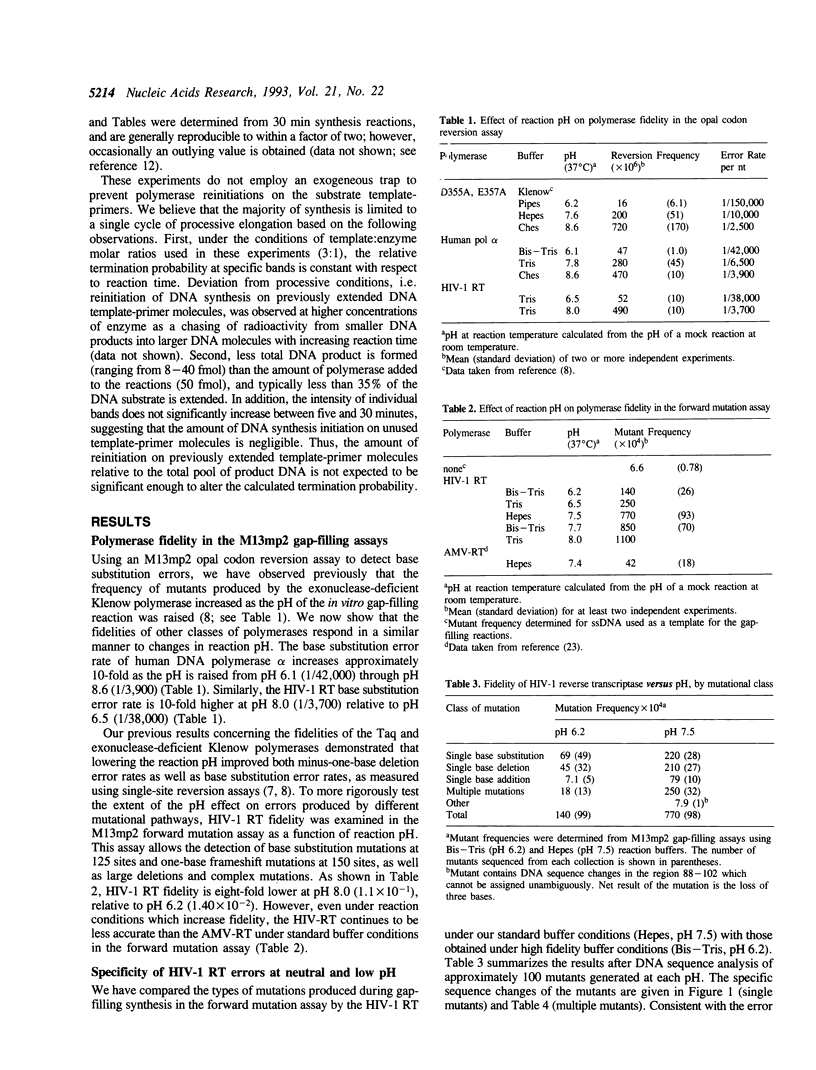
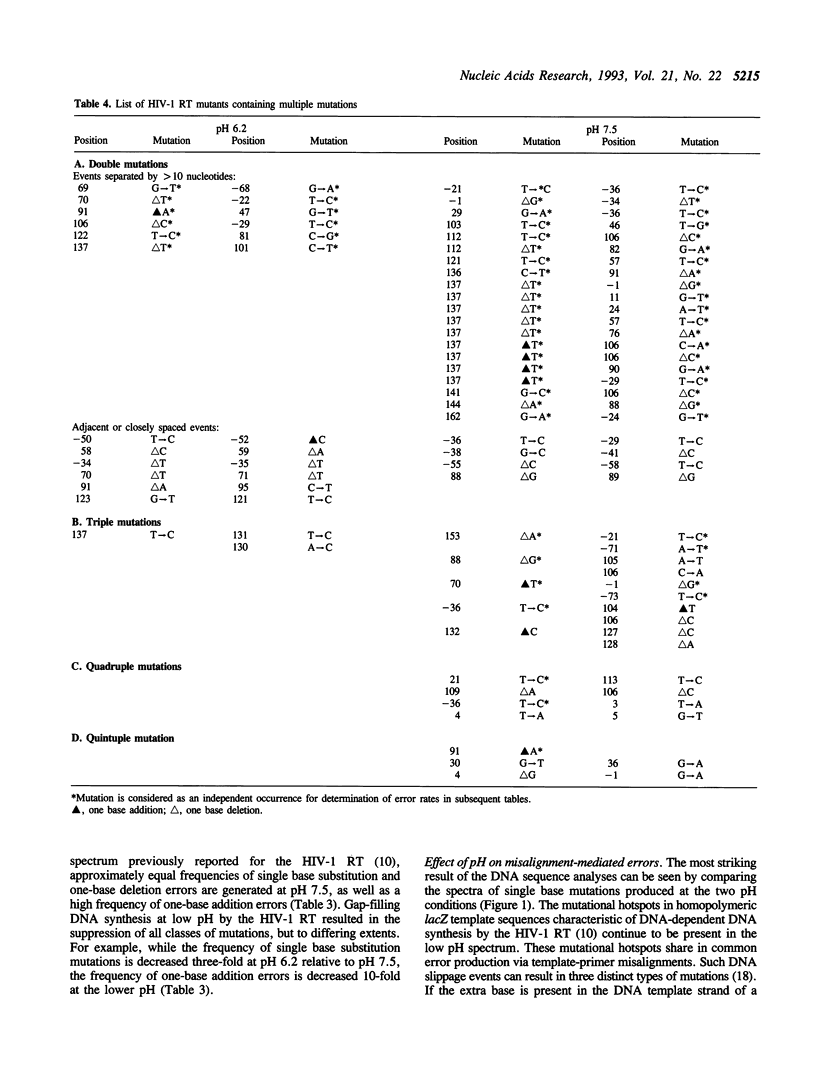
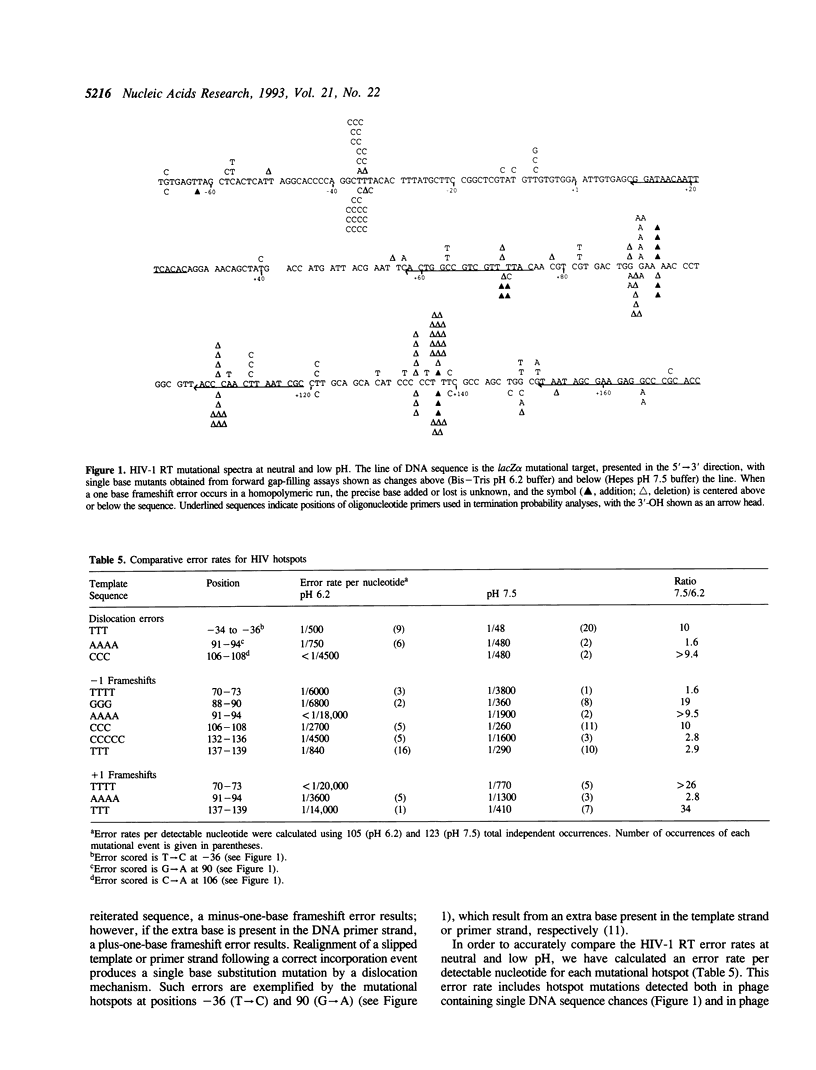
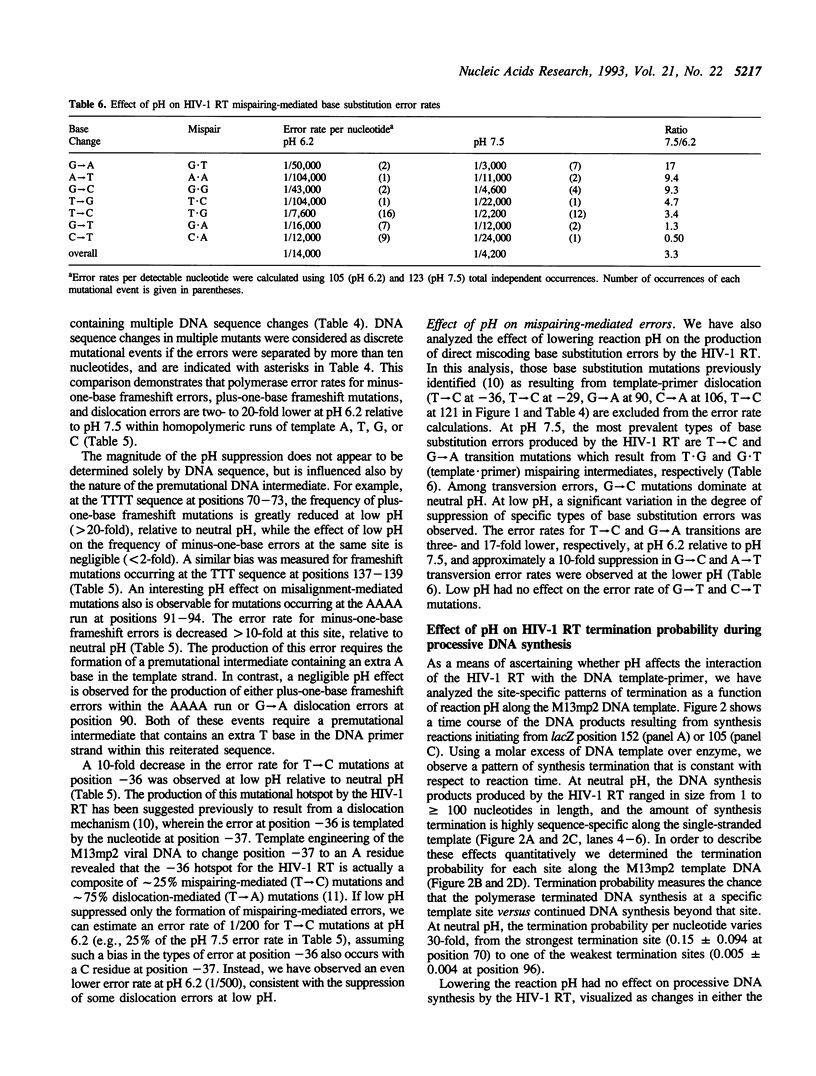
The accuracy of DNA synthesis catalyzed by the Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase and the 3'-->5' exonuclease-deficient Klenow fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I varies as a function of reaction pH (Eckert, K.A. and Kunkel, T.A. (1990) Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 3739-3744; Eckert, K.A. and Kunkel, T.A. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268, 13462-13471). In the current study, we demonstrate that the fidelity of human DNA polymerase alpha increases 10-fold when the pH of the in vitro synthesis reaction is lowered from pH 8.6 to pH 6.1 (37 degrees C), as determined using a base substitution reversion assay to score polymerase errors within the lacZ alpha gene of bacteriophage M13mp2. Similarly, the base substitution fidelity of DNA-dependent DNA synthesis by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase (HIV-1 RT) was improved nine-fold at pH 6.5 relative to pH 8.0 (37 degrees C). A detailed comparison of HIV-1 RT error specificity at neutral and low pH in a lacZ alpha forward mutation assay revealed that low pH suppresses both mispairing-mediated and misalignment-mediated mutations; however, the characteristic HIV-1 RT pattern of mutational hotspots at homopolymeric sequences is retained at the lower pH. Consistent with the presumption that these mutations result, in part, from increased termination of DNA synthesis within the hotspot sequences relative to other homopolymeric sequences, the HIV-1 RT termination pattern during processive DNA synthesis is not altered by low pH. The HIV-1 RT results are in agreement with our previous hypothesis that the observed increase in polymerase fidelity at low pH results from a decreased efficiency of continuing DNA synthesis from premutational DNA intermediates.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbotts J., Bebenek K., Kunkel T. A., Wilson S. H. Mechanism of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Termination of processive synthesis on a natural DNA template is influenced by the sequence of the template-primer stem. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10312–10323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbotts J., SenGupta D. N., Zon G., Wilson S. H. Studies on the mechanism of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I large fragment. Effect of template sequence and substrate variation on termination of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15094–15103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Abbotts J., Roberts J. D., Wilson S. H., Kunkel T. A. Specificity and mechanism of error-prone replication by human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16948–16956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Abbotts J., Wilson S. H., Kunkel T. A. Error-prone polymerization by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Contribution of template-primer misalignment, miscoding, and termination probability to mutational hot spots. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10324–10334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite D. K., Ito J. Compilation, alignment, and phylogenetic relationships of DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 25;21(4):787–802. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.4.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Leonard G. A., Booth E. D., Kneale G. Influence of pH on the conformation and stability of mismatch base-pairs in DNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 5;212(3):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90320-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland W. C., Wang T. S. Mutational analysis of the human DNA polymerase alpha. The most conserved region in alpha-like DNA polymerases is involved in metal-specific catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11028–11040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delarue M., Poch O., Tordo N., Moras D., Argos P. An attempt to unify the structure of polymerases. Protein Eng. 1990 May;3(6):461–467. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.6.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert K. A., Kunkel T. A. Effect of reaction pH on the fidelity and processivity of exonuclease-deficient Klenow polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13462–13471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert K. A., Kunkel T. A. High fidelity DNA synthesis by the Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3739–3744. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Prusty D., Frangioni J. V., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lechene C., Schwartz M. A. Control of intracellular pH and growth by fibronectin in capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1803–1811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kati W. M., Johnson K. A., Jerva L. F., Anderson K. S. Mechanism and fidelity of HIV reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25988–25997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchta R. D., Benkovic P., Benkovic S. J. Kinetic mechanism whereby DNA polymerase I (Klenow) replicates DNA with high fidelity. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6716–6725. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K. Recent studies of the fidelity of DNA synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Misalignment-mediated DNA synthesis errors. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8003–8011. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Soni A. Exonucleolytic proofreading enhances the fidelity of DNA synthesis by chick embryo DNA polymerase-gamma. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4450–4459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. The mutational specificity of DNA polymerase-beta during in vitro DNA synthesis. Production of frameshift, base substitution, and deletion mutations. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5787–5796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. The mutational specificity of DNA polymerases-alpha and -gamma during in vitro DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12866–12874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove E., Seaman M., Hedley D. Relationship between cytoplasmic pH and proliferation during exponential growth and cellular quiescence. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Sep;172(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Bebenek K., Kunkel T. A. The accuracy of reverse transcriptase from HIV-1. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1171–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.2460925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Preston B. D., Johnston L. A., Soni A., Loeb L. A., Kunkel T. A. Fidelity of two retroviral reverse transcriptases during DNA-dependent DNA synthesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):469–476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Both G., Lechene C. Effect of cell spreading on cytoplasmic pH in normal and transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4525–4529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers L. C., Shaw B. R., Veigl M. L., Sedwick W. D. DNA base modification: ionized base pairs and mutagenesis. Mutat Res. 1987 Apr;177(2):201–218. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(87)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



