Abstract
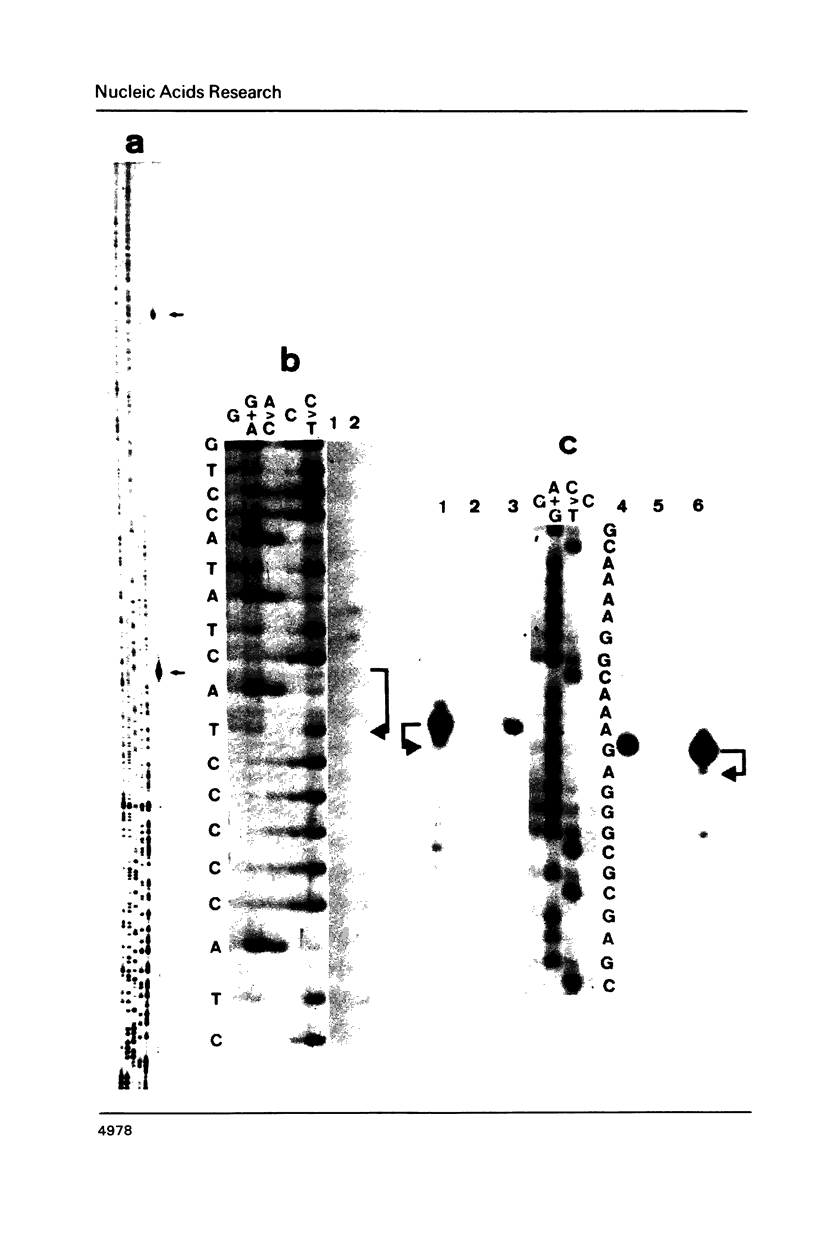
A 14 kb maize DNA fragment carrying nuclear rRNA genes and spacer regions was isolated and characterised by restriction enzyme mapping. A complete 3020 bp long external spacer region was sequenced and revealed 9 tandemly arranged 200 bp long repeat units with high homology. The repeat units lie upstream from two prominent S1 mapping signals. The sequence of a typical repeat unit is compared to a corresponding 130 bp long wheat repeat unit. The possible functional relevance of the repeat units is discussed.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W., Barker R. System for DNA sequencing with resolution of up to 600 base pairs. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Mar;9(1):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E. Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R., Allet B., Crippa M. Sequence organization of the spacer in the ribosomal genes of Xenopus clivii and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5311–5330. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R., Grummt I., Allet B. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation region of the ribosomal transcription unit from mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1559–1569. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Gene conversion: some implications for immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):592–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buescher P. J., Phillips R. L., Brambl R. Ribosomal RNA contents of maize genotypes with different ribosomal RNA gene numbers. Biochem Genet. 1984 Oct;22(9-10):923–930. doi: 10.1007/BF00499483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. VI. Plasmid pBR329, a new derivative of pBR328 lacking the 482-base-pair inverted duplication. Gene. 1982 Jan;17(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. Spacer promoters are essential for efficient enhancement of X. laevis ribosomal transcription. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90765-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Hirsh D. Ribosomal DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Human ribosomal RNA gene: nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region and comparison of three mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K. C., Stafford D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region for rRNA in the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus. Gene. 1985;39(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelewski N., Schmidt E. R. Spacer size heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA of Chironomus thummi is due to a 120 bp repeat homologous to a predominantly centromeric repeated sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7689–7700. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Urano Y., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Organization of ribosomal RNA gene repeats of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3219–3233. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M., Arnheim N. Nucleotide sequence of the genetically labile repeated elements 5' to the origin of mouse rRNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):211–224. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Volpe A., Simeone A., D'Esposito M., Scotto L., Fidanza V., de Falco A., Boncinelli E. Molecular analysis of the heterogeneity region of the human ribosomal spacer. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Penman S. Processing steps and methylation in the formation of the ribosomal RNA of cultured Drosophila cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):219–238. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Rebbert M. L., Dawid I. B. Nucleotide sequence of the initiation site for ribosomal RNA transcription in Drosophila melanogaster: comparison of genes with and without insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1513–1517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Carlson J., Hagen G., Rubenstein I., Oleson A. Cloning and sequencing of the ribosomal RNA genes in maize: the 17S region. DNA. 1984;3(1):31–40. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Enhancers and ribosomal gene spacers. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G., Dunaway M. Spacer regulation of Xenopus ribosomal gene transcription: competition in oocytes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Sollner-Webb B., Wahn H. L. Sites of transcription initiation in vivo on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Reddy R., Cassidy B. Transcription initiation site of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7345–7362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., La Volpe A., Boncinelli E. Nucleotide sequence of a complete ribosomal spacer of D. melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1089–1101. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skryabin K. G., Eldarov M. A., Larionov V. L., Bayev A. A., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Veldman G. M., Planta R. J., Georgiev O. I., Hadjiolov A. A. Structure and function of the nontranscribed spacer regions of yeast rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2955–2968. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]