Abstract
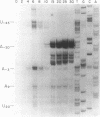
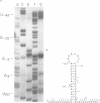
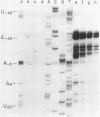
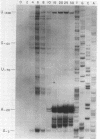
The bacteriophage T4 lysozyme gene is transcribed at early and late times after infection of E. coli, but the early mRNA is not translated. DNA sequence analysis and mapping of the 5' ends of the lysozyme transcripts produced at different times after T4 infection show that the early mRNA is initiated some distance upstream from the gene. The early mRNA is not translated because of a stable secondary structure which blocks the translational initiation site. The stable RNA structure has been demonstrated by nuclease protection in vivo. After DNA replication begins, two late promoters are activated; the late transcripts are initiated at sites such that the secondary structure can not form, and translation of the late messages occurs.
Full text
PDF



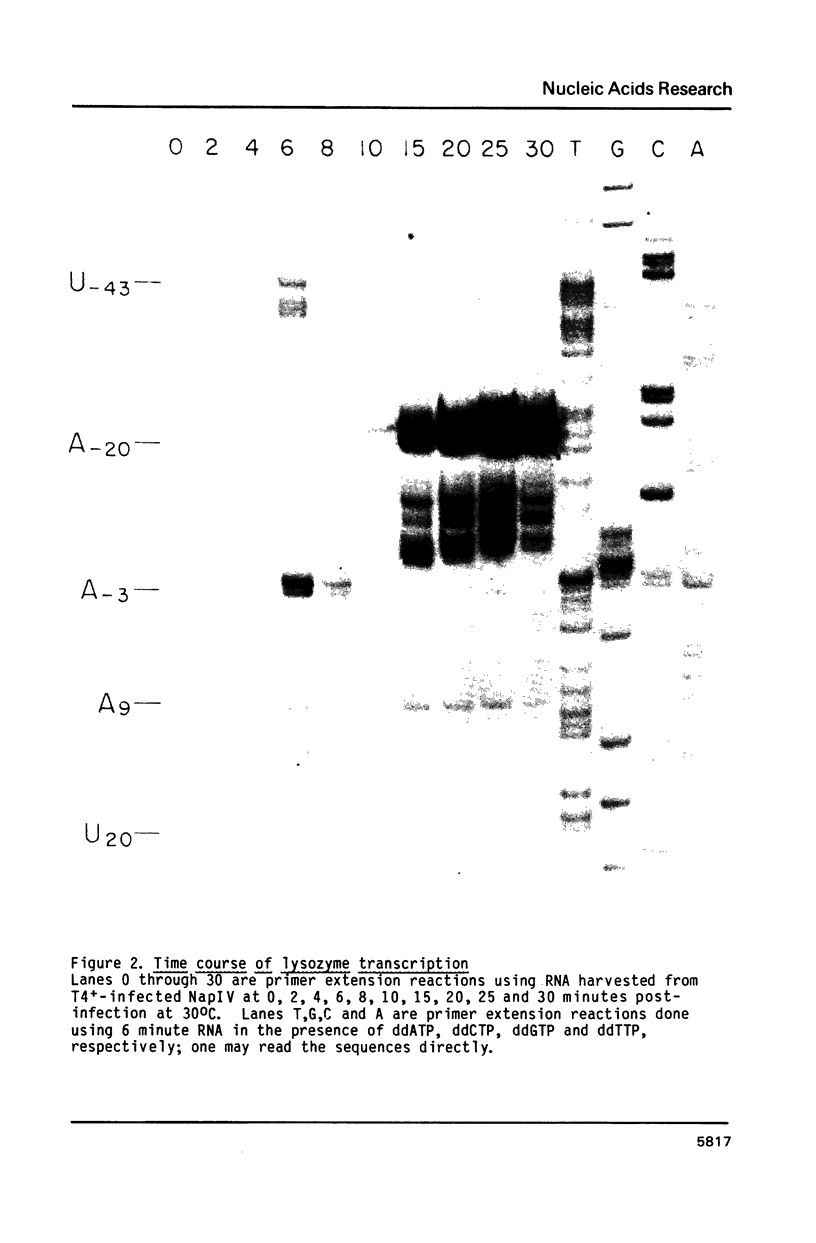
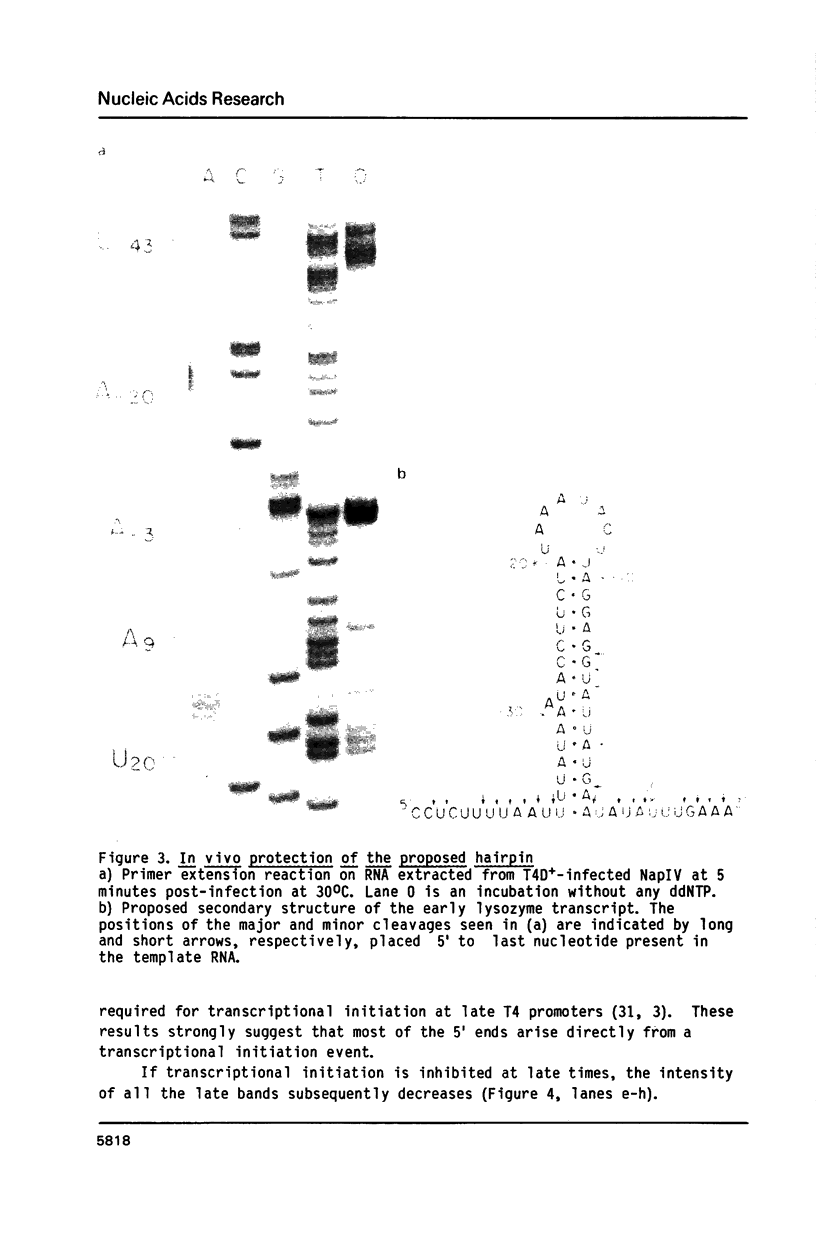

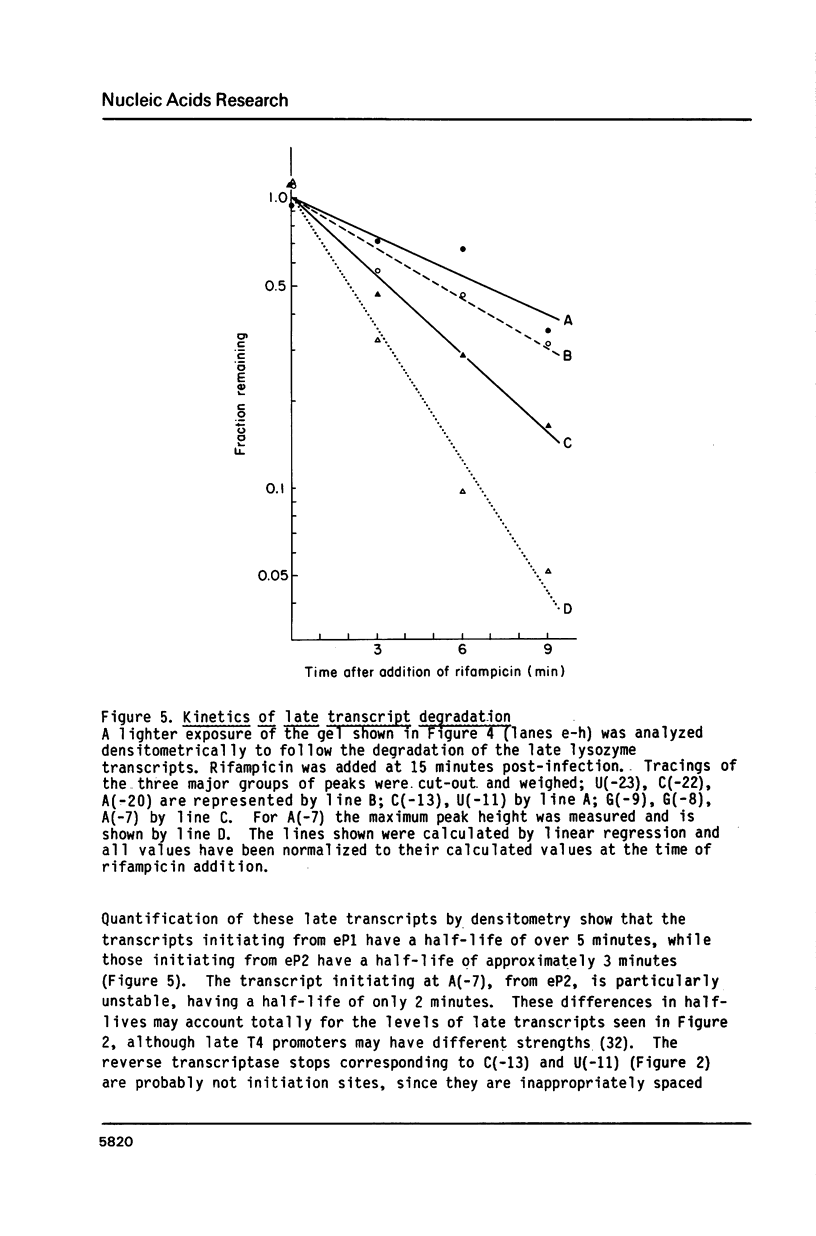

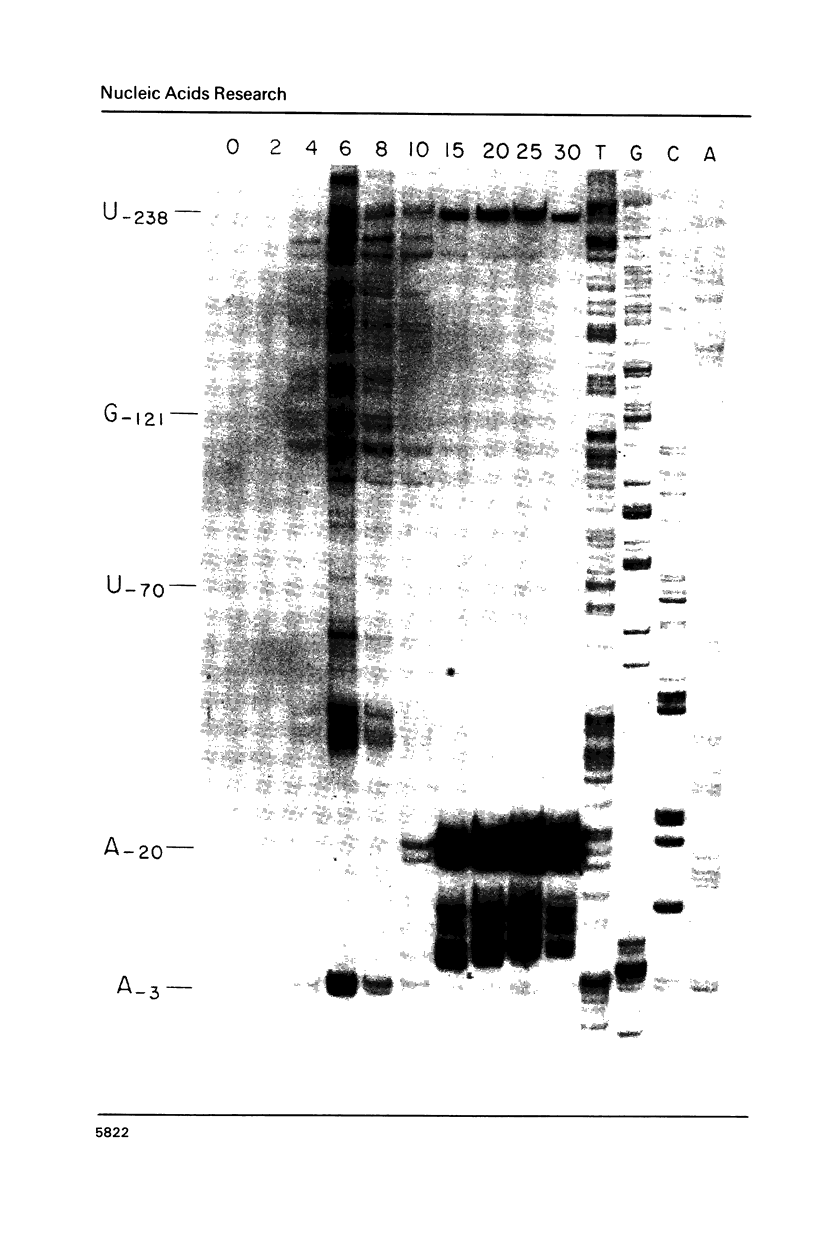




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bautz E. K., Kasai T., Reilly E., Bautz F. A. Gene-specific mRNA. II. Regulation of mRNA synthesis in E. coli after infection with bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1081–1088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L. W., Gold L. M. Pre-replicative development of the bacteriophage T4: RNA and protein synthesis in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):365–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. C., Young E. T. T4 late transcripts are initiated near a conserved DNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):369–371. doi: 10.1038/299369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. A., Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Tn10 protects itself at two levels from fortuitous activation by external promoters. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. The complex pattern of transcription in the segment of the bacteriophage T4 genome containing three of the head protein genes. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):260–282. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F., Salser W. Bacteriophage T4 lysozyme mRNA. Genetics. 1969;61(1 Suppl):429–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. M., Schweiger M. Control of beta-glucosyltransferase and lysozyme synthesis during T4 deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2255–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram H., Liebig H. D., Hack A., Niggemann E., Rüger W. A physical map of bacteriophage T4 including the positions of strong promoters and terminators recognized in vitro. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(1-2):232–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00383522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Young E. T. Effect of RNase III on efficiency of translation of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme mRNA. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):793–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.793-804.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Débarbouillé M., Schwartz M. A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):616–618. doi: 10.1038/295616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Simons R. W., Way J. C., Walsh R. B., Kleckner N. DNA sequence organization of IS10-right of Tn10 and comparison with IS10-left. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2608–2612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Cech T. R. Secondary structure of the circular form of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: a technique for RNA structure analysis using chemical probes and reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karam J., Gold L., Singer B. S., Dawson M. Translational regulation: identification of the site on bacteriophage T4 rIIB mRNA recognized by the regA gene function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4669–4673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai T., Bautz E. K. Regulation of gene-specific RNA synthesis in bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):401–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Bacteriophage T4 late promoters: mapping 5' ends of T4 gene 23 mRNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):107–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: bacteriophage T4 gene 55 protein suffices for directing late promoter recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5101–5105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire G., Gold L., Yarus M. Autogenous translational repression of bacteriophage T4 gene 32 expression in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):73–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Kutter E., Mosig G. Regulation of a bacteriophage T4 late gene, soc, which maps in an early region. Genetics. 1984 Jan;106(1):17–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson L. M., Stormo G. D., Niece R. L., Reznikoff W. S. lacZ translation initiation mutations. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):663–683. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Gold L. M. Bacteriophage T4 gene expression. Evidence for two classes of prereplicative cistrons. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5502–5511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. E., Schultz D. W., Taylor A., Smith G. R. Nucleotide sequence of the lysozyme gene of bacteriophage T4. Analysis of mutations involving repeated sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):229–248. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80255-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Heyneker H. L., Wetzel R. Non-toxic expression in Escherichia coli of a plasmid-encoded gene for phage T4 lysozyme. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulitzer J. F., Geiduschek E. P. Function of T4 gene 55. II. RNA synthesis by temperature-sensitive gene 55 mutants. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):489–507. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Gesteland R. F., Bolle A. In vitro synthesis of bacteriophage lysozyme. Nature. 1967 Aug 5;215(5101):588–591. doi: 10.1038/215588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger M., Gold L. M. Bacteriophage T4 DNA-dependent in vitro synthesis of lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1351–1358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. T., 2nd, van Houwe G. Control of synthesis of glucosyl transferase and lysozyme messengers after T4 infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):605–619. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Kowalczykowski S. C., Lonberg N., Newport J. W., Paul L. S., Stormo G. D., Gold L. Autoregulation of gene expression. Quantitative evaluation of the expression and function of the bacteriophage T4 gene 32 (single-stranded DNA binding) protein system. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):795–818. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]