Abstract
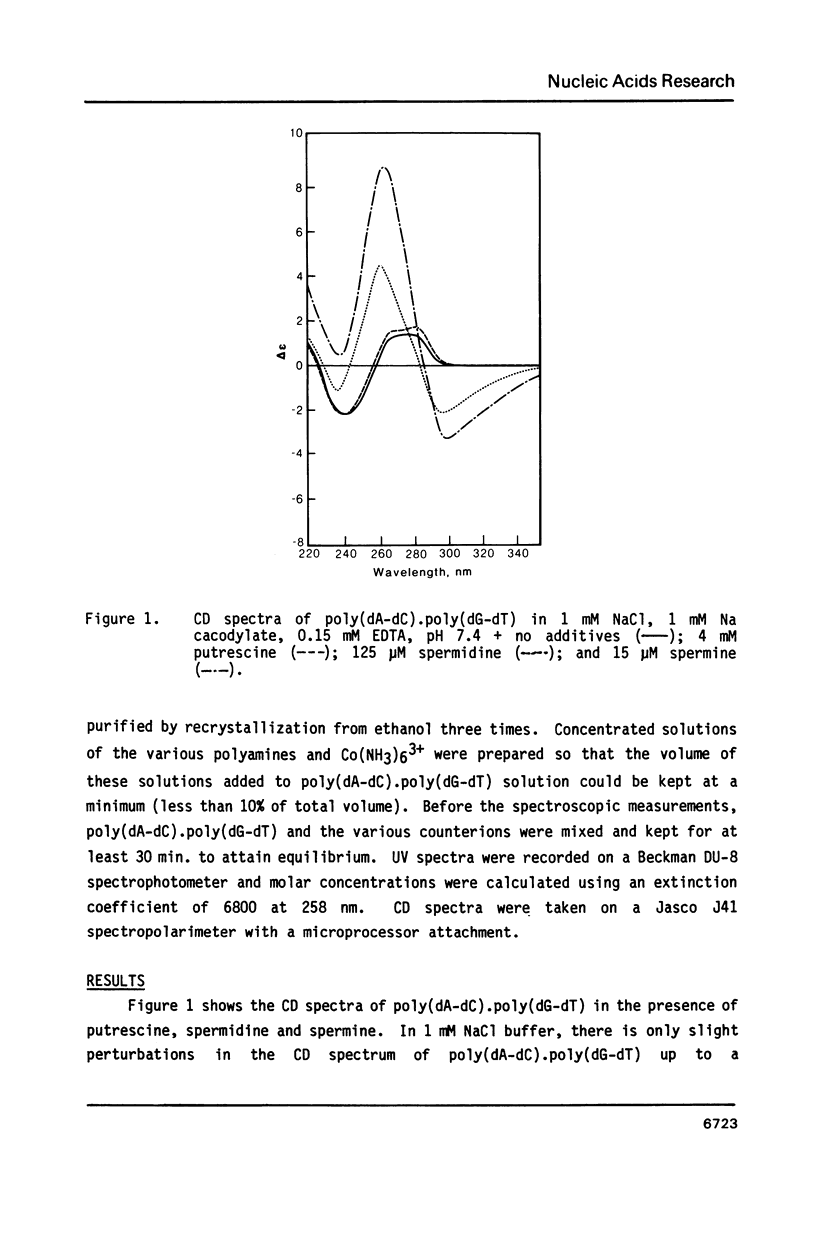
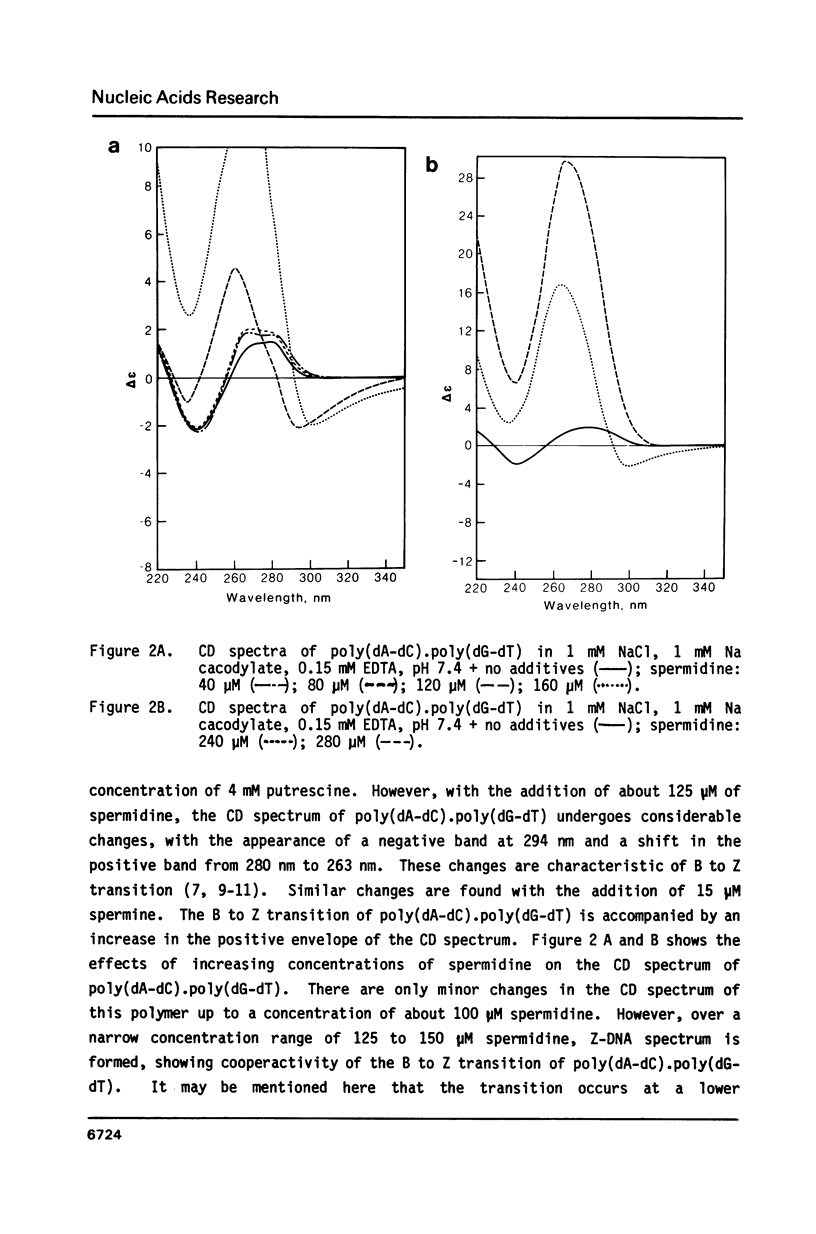
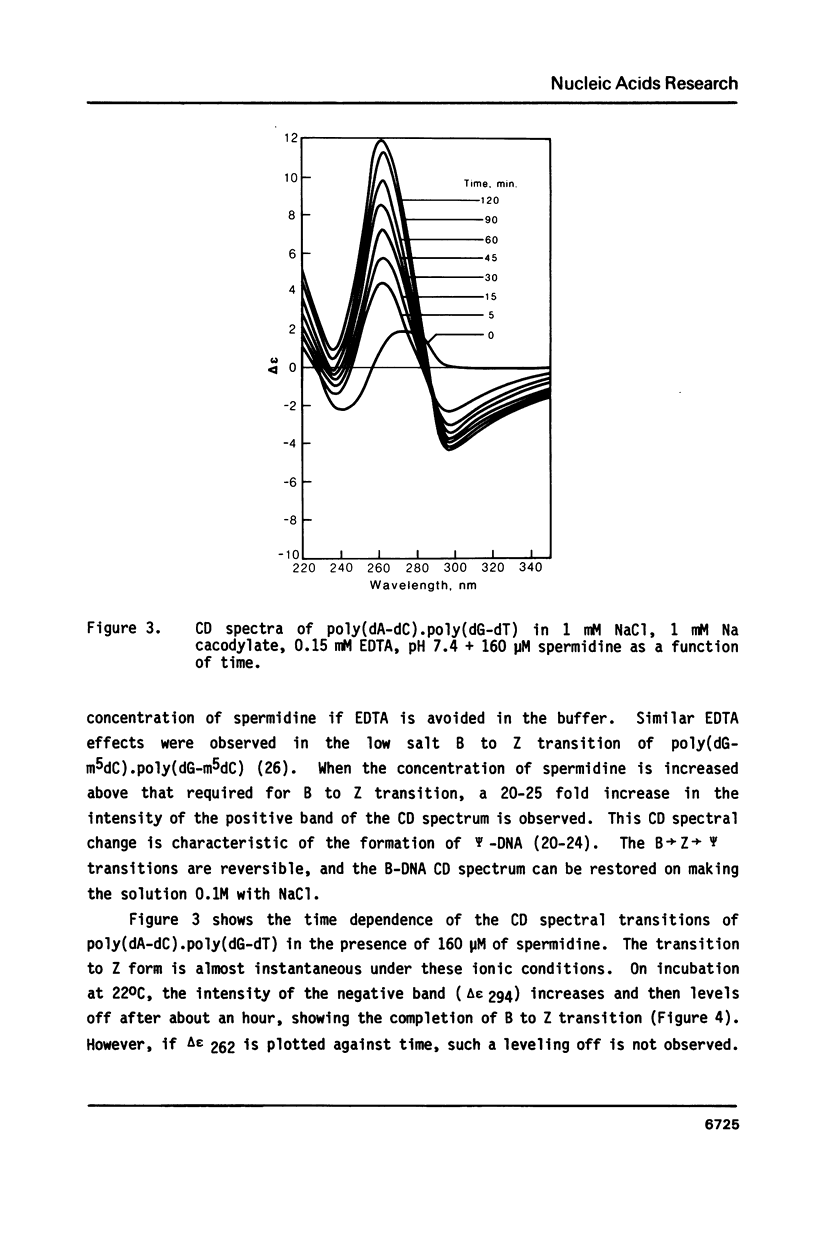
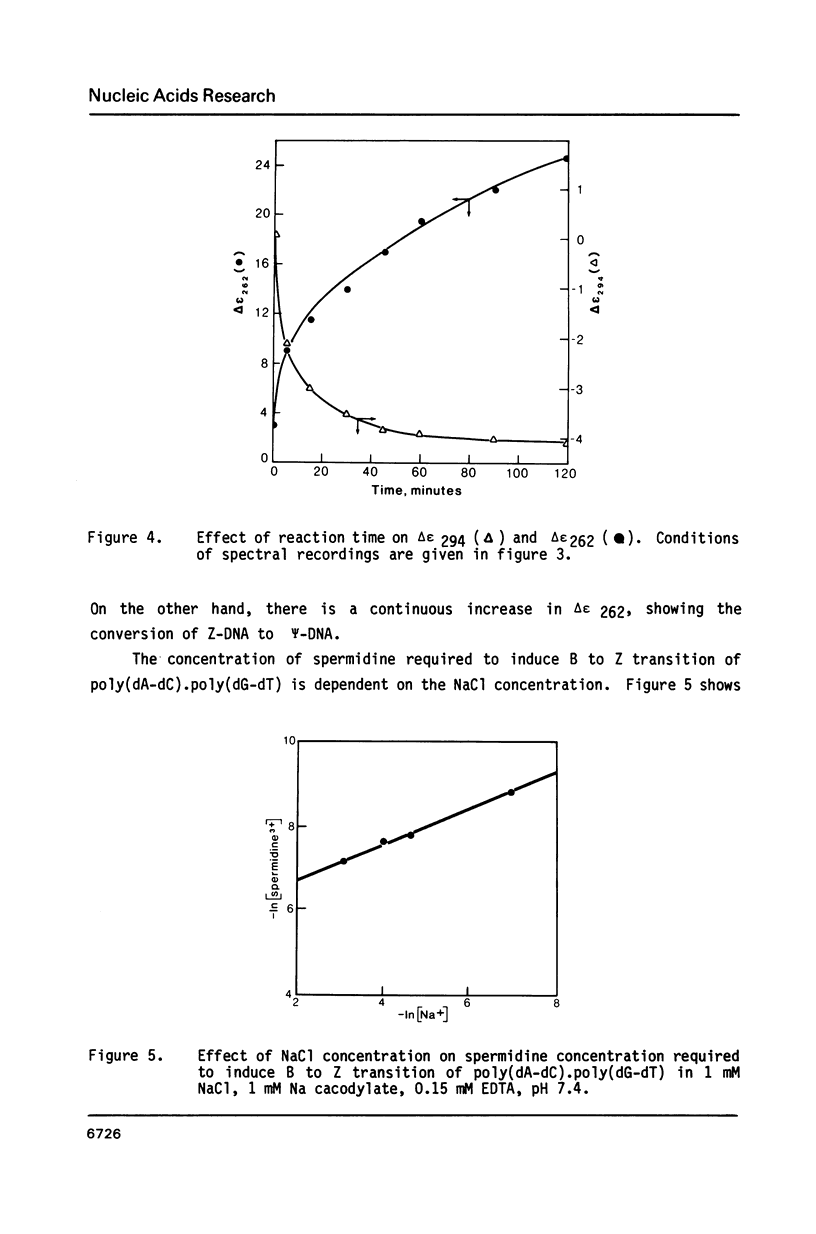
Blocks of potential Z-DNA forming alternating purine-pyrimidine (APP) sequences are widely dispersed in native DNAs. We have studied the effects of naturally occurring polyamines on the conformation of a synthetic APP sequence, poly(dA-dC).poly(dG-dT) by circular dichroism spectroscopy. In the presence of micromolar concentrations of spermidine (125 microM) and spermine (16 microM), this polymer undergoes B to Z transition in low ionic strength (2 mM Na+) buffers. The concentration of polyamines required for B to Z transition increases with Na+ in the buffer and a straight line is obtained on plotting ln[Na+] vs. ln [spermidine 3+]. However, at concentrations of polyamines higher than those necessary to induce B to Z transition, Z-DNA converts to psi-DNA, an ordered, twisted, tight packing arrangement of the double helix. These results suggest a pathway for the transient formation of Z-DNA segments in vivo by interaction of the ubiquitous polyamines with naturally occurring blocks of APP sequences.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
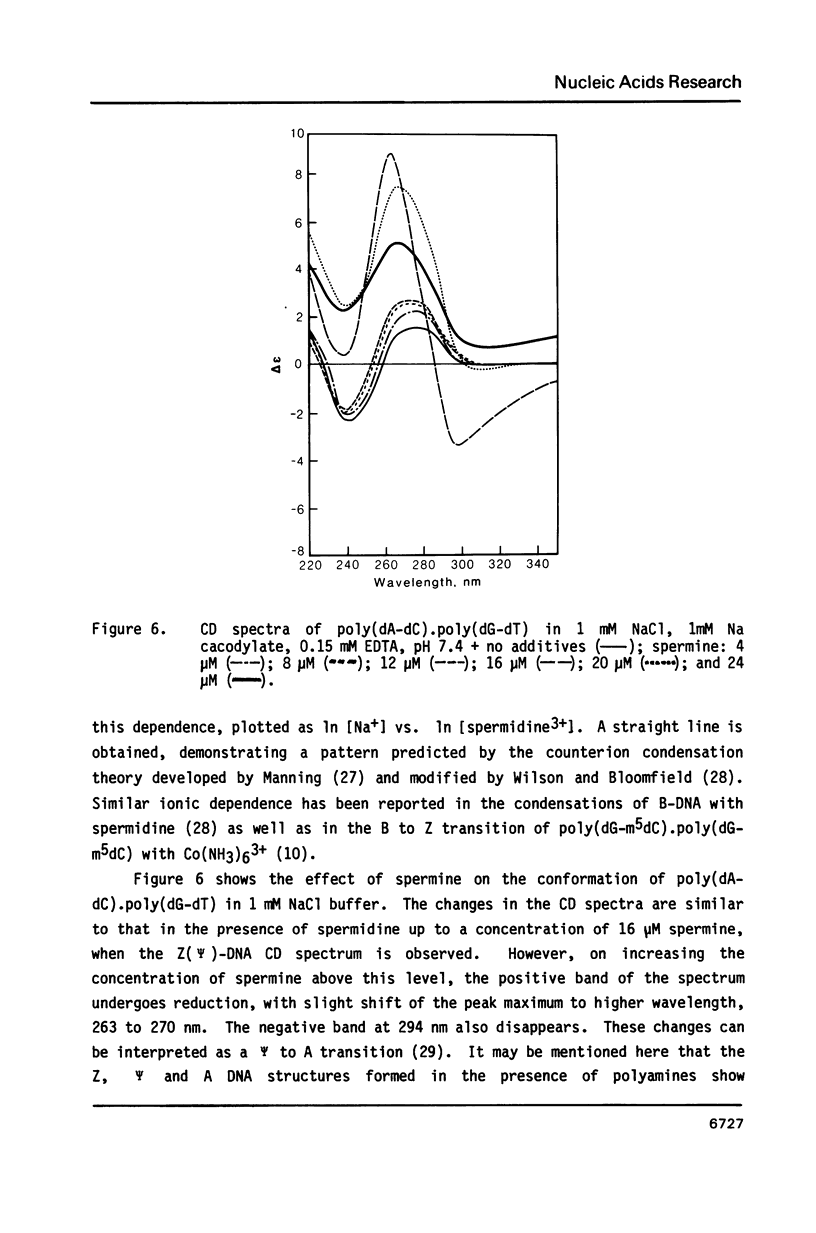
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
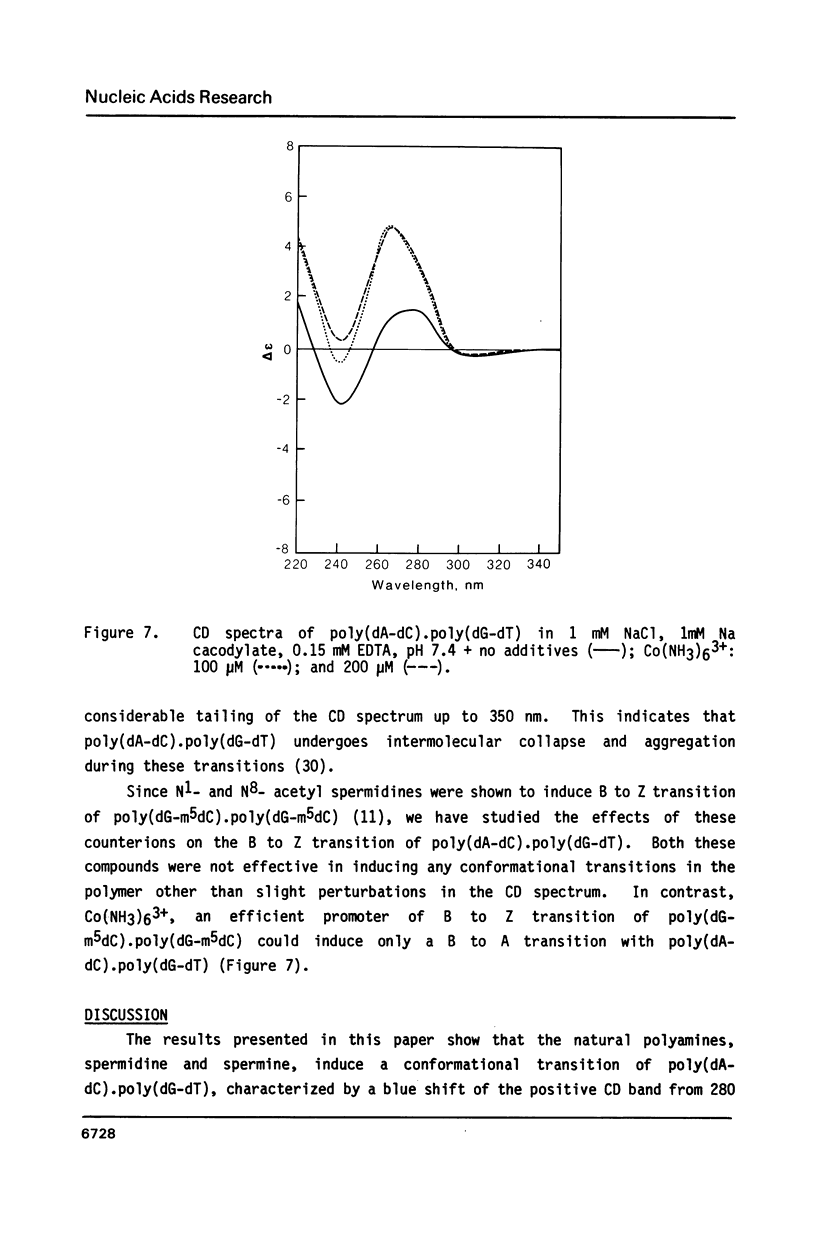
- Braunlin W. H., Strick T. J., Record M. T., Jr Equilibrium dialysis studies of polyamine binding to DNA. Biopolymers. 1982 Jul;21(7):1301–1314. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damaschun H., Damaschun G., Becker M., Buder E., Misselwitz R., Zirwer D. Study of DNA-spermine interactions by use of small-angle and wide-angle X-ray scattering and circular dichroism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3801–3809. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R., Conner B. N., Wing R. M., Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L. The anatomy of A-, B-, and Z-DNA. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):475–485. doi: 10.1126/science.7071593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granados E. N., Bello J. Interactions of poly (N epsilon , N epsilon , N epsilon ,-trimethyllysine) and poly(lysine) with polynucleotides: circular dichroism and A-T sequence selectivity. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4761–4765. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Kakunaga T. Potential Z-DNA forming sequences are highly dispersed in the human genome. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):396–398. doi: 10.1038/298396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Facile transition of poly[d(TG) x d(CA)] into a left-handed helix in physiological conditions. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):632–634. doi: 10.1038/302632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Dixon J. E. Z-DNA in the rat somatostatin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8145–8156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan C. F., Lerman L. S., Venable J. H. Structure and circular dichroism of DNA in concentrated polymer solutions. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 22;236(64):67–70. doi: 10.1038/newbio236067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., McIntosh L. P., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Zarling D. A., Robert-Nicoud M., van de Sande J. H., Jorgenson K. F., Eckstein F. Left-handed DNA: from synthetic polymers to chromosomes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):21–57. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Klysik J., Singleton C. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Hanau L. H., Erlanger B. F., Wells R. D. Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7268–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Larson J. E., Hart P. A., Wells R. D. Left-handed DNA in restriction fragments and a recombinant plasmid. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):672–677. doi: 10.1038/290672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Valle R. P., Möller A., Nordheim A., Schur P. H., Rich A., Stollar B. D. Z-DNA-specific antibodies in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):314–321. doi: 10.1172/JCI110771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestre M. F., Reich C. Contribution of light scattering to the circular dichroism of deoxyribonucleic acid films, deoxyribonucleic acid-polylysine complexes, and deoxyribonucleic acid particles in ethanolic buffers. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5214–5223. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh L. P., Grieger I., Eckstein F., Zarling D. A., van de Sande J. H., Jovin T. M. Left-handed helical conformation of poly[d(A-m5C).d(G-T)]. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):83–86. doi: 10.1038/304083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minyat E. E., Ivanov V. I., Kritzyn A. M., Minchenkova L. E., Schyolkina A. K. Spermine and spermidine-induced B to A transition of DNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Nordheim A., Rich A. Right-handed and left-handed DNA: studies of B- and Z-DNA by using proton nuclear Overhauser effect and P NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1413–1417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl F. M., Jovin T. M. Salt-induced co-operative conformational change of a synthetic DNA: equilibrium and kinetic studies with poly (dG-dC). J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):375–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revet B., Delain E., Dante R., Niveleau A. Three dimensional association of double-stranded helices are produced in conditions for Z-DNA formation. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(4):857–871. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. H. Clinical relevance of polyamines. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1983;18(3):261–311. doi: 10.3109/10408368209085073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin Y. A., Eichhorn G. L. Formation of psi (+) and psi (-) DNA. Biopolymers. 1984 Feb;23(2):325–335. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley J. T., Lee J. S., Decoteau W. E. Left-handed "Z" DNA antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1984 Oct;11(5):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taillandier E., Taboury J. A., Adam S., Liquier J. Left-handed helical structure of poly[d(A-C)].poly[d(G-T)] studied by infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5703–5706. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A., Canellakis Z. N. Differential effects on the B-to-Z transition of poly(dG-me5dC).poly(dG-me5dC) produced by N1- and N8-acetyl spermidine. Biopolymers. 1985 Apr;24(4):725–729. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A. Collapse of DNA caused by trivalent cations: pH and ionic specificity effects. Biopolymers. 1983 Apr;22(4):1097–1106. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A. Ionic and structural effects on the thermal helix-coil transition of DNA complexed with natural and synthetic polyamines. Biopolymers. 1984 Jul;23(7):1295–1306. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A. Quasielastic laser light scattering and electron microscopy studies of the conformational transitions and condensation of poly(dA-dT).poly(dA-dT). Biopolymers. 1985 Dec;24(12):2185–2194. doi: 10.1002/bip.360241203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A. Toroidal condensation of Z DNA and identification of an intermediate in the B to Z transition of poly(dG-m5dC) X poly(dG-m5dC). Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):713–719. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Bustamante C., Maestre M. F. The optical activity of nucleic acids and their aggregates. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:107–141. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Helden P. D. Potential Z-DNA-forming elements in serum DNA from human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorlíckovă M., Kypr J., Stokrová S., Sponar J. A Z-like form of poly(dA-dC).poly(dG-dT) in solution? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):1071–1080. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Brennan R., Chapman K. A., Goodman T. C., Hart P. A., Hillen W., Kellogg D. R., Kilpatrick M. W., Klein R. D., Klysik J. Left-handed DNA helices, supercoiling, and the B-Z junction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Goodman T. C., Hillen W., Horn G. T., Klein R. D., Larson J. E., Müller U. R., Neuendorf S. K., Panayotatos N., Stirdivant S. M. DNA structure and gene regulation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:167–267. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60674-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Miglietta J. J., Kłysik J., Larson J. E., Stirdivant S. M., Zacharias W. Spectroscopic studies on acetylaminofluorene-modified (dT-dG)n . (dC-dA)n suggest a left-handed conformation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10166–10171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. W., Bloomfield V. A. Counterion-induced condesation of deoxyribonucleic acid. a light-scattering study. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2192–2196. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisard A., Fazakerley G. V. Ultrapolymorphic DNA: B, A, Z, and Z* conformations of poly(dA-dC).poly(dG-dT). Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2672–2676. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias W., Martin J. C., Wells R. D. Condensed form of (dG-dC)n X (dG-dC)n as an intermediate between the B- and Z-type conformations induced by sodium acetate. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2398–2405. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling D. A., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Robert-Nicoud M., McIntosh L. P., Thomae R., Jovin T. M. Immunoglobulin recognition of synthetic and natural left-handed Z DNA conformations and sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):369–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


