Abstract
We have isolated and sequenced a gene encoding a late H1 histone subtype from the sea urchin species L. pictus. The primary structure of the late H1 subtype encoded by this gene is 209 amino acids in length, and has a net positive charge of 67. This gene is present in a single copy per haploid genome and encodes an mRNA of 752 nucleotides. Late H1 transcripts are detected in the unfertilized egg and are most prevalent in gastrulating embryos. Comparison of 375 bp of 5' flanking sequences of the L. pictus late H1 gene and the H1-gamma gene of a distantly related sea urchin species, S. purpuratus, reveals large blocks of sequences that are identical between the two genes. To determine if these conserved 5' sequences are present in other members of the sea urchin H1 gene family, the analogous region of S. purpuratus H1-alpha, an early H1 gene, was sequenced. The homology between the flanking sequences of the early and late families was limited to consensus sequences which are found upstream of all H1 genes. The possible regulatory implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Cetta A., Davidson E. H. The single-copy DNA sequence polymorphism of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D. The role of stable complexes that repress and activate eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Cole R. D. Species and organ specificity in very lysine-rich histones. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4500–4505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Kedes L. H. Histone gene expression during sea urchin embryogenesis: isolation and characterization of early and late messenger RNAs of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus by gene-specific hybridization and template activity. Dev Biol. 1979 Nov;73(1):153–173. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
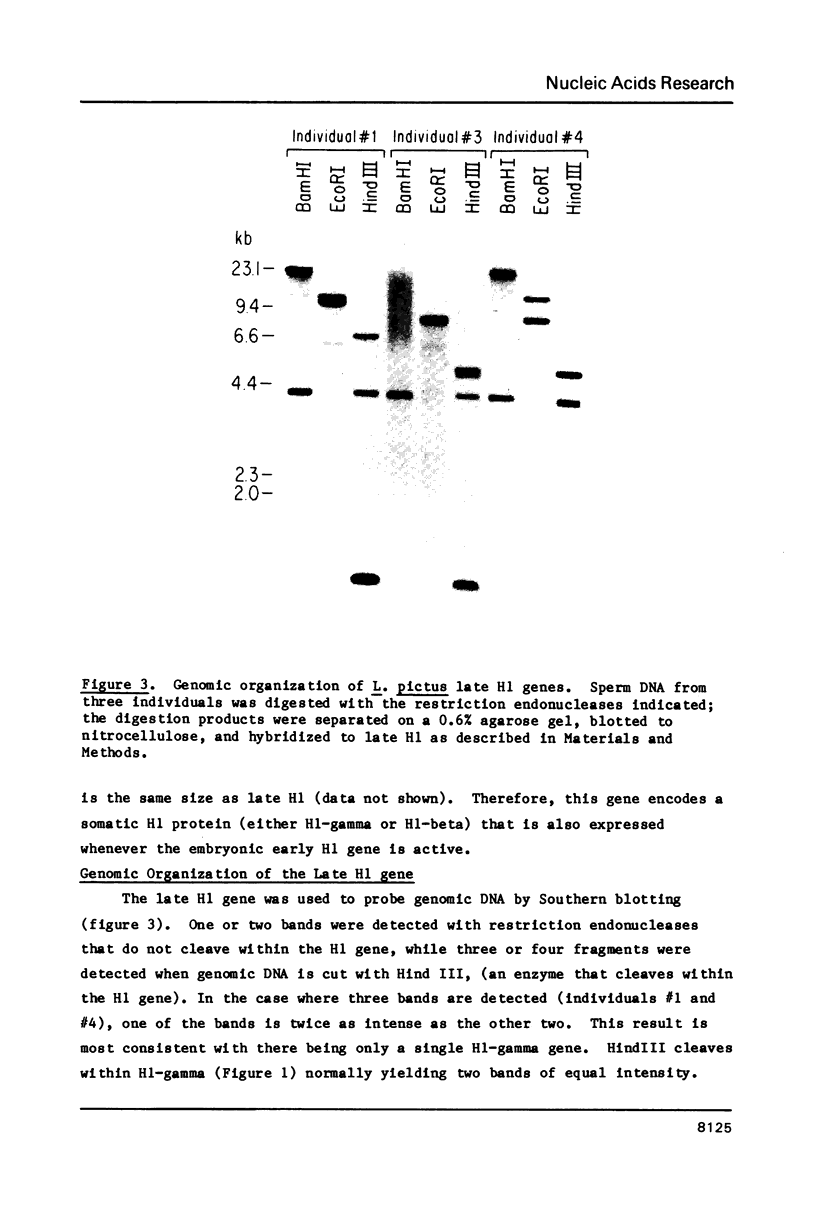
- Childs G., Nocente-McGrath C., Lieber T., Holt C., Knowles J. A. Sea urchin (lytechinus pictus) late-stage histone H3 and H4 genes: characterization and mapping of a clustered but nontandemly linked multigene family. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. H., Newrock K. M., Zweidler A. Stage-specific switches in histone synthesis during embryogenesis of the sea urchin. Science. 1975 Dec 5;190(4218):994–997. doi: 10.1126/science.1237932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H. Nonallelic histone gene clusters of individual sea urchins (Lytechinus pictus): mapping of homologies in coding and spacer DNA. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):855–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H. Nonallelic histone gene clusters of individual sea urchins (Lytechinus pictus): polarity and gene organization. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Lowry J. C., Kedes L. H. Histone genes of the sea urchin (S. purpuratus) cloned in E coli: order, polarity, and strandedness of the five histone-coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):147–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles L. S., Wells J. R. An H1 histone gene-specific 5' element and evolution of H1 and H5 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):585–594. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. G., Chapman G. E., Moss T., Bradbury E. M. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 in eukaryote chromatin. The three structural regions of the histone H1 molecule. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt C. A., Childs G. A new family of tandem repetitive early histone genes in the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus: evidence for concerted evolution within tandem arrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6455–6471. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumeyer J. F., Weinberg E. S. Sequence, organization and expression of late embryonic H3 and H4 histone genes from the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4557–4576. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. A., Childs G. J. Temporal expression of late histone messenger RNA in the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2411–2415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
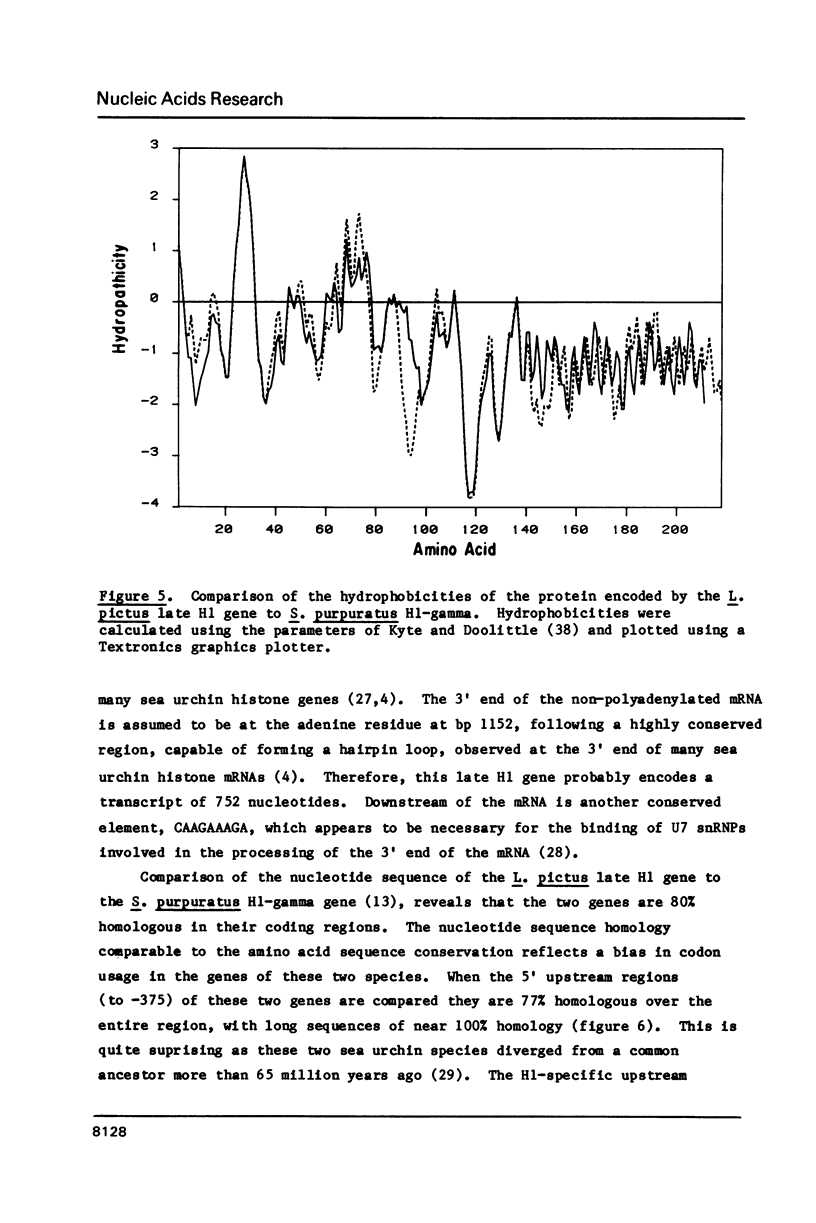
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Mohun T., Gormezano G., Childs G., Kedes L. Distinct organizations and patterns of expression of early and late histone gene sets in the sea urchin. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):120–125. doi: 10.1038/301120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Novak T. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Inducible expression of a cloned heat shock fusion gene in sea urchin embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7490–7494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Price D. H., Marzluff W. F. Synthesis of U1 RNA in a DNA-dependent system from sea urchin embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3674–3678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Thomsen G. H., Roeder R. G. Genomic organization and nucleotide sequence of two distinct histone gene clusters from Xenopus laevis. Identification of novel conserved upstream sequence elements. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):479–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G. The mechanism of nucleolar dominance in Xenopus hybrids. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90524-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. B., Weisser K. E., Childs G. Sequence comparisons of non-allelic late histone genes and their early stage counterparts. Evidence for gene conversion within the sea urchin late stage gene family. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):647–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Gross P. R. Histones and histone synthesis in sea urchin development. Dev Biol. 1974 Feb;36(2):286–298. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Gross K., Telford J., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of psammechinus miliaris: II. The arrangement of the five histone-coding and spacer sequences. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Galli G., Busslinger M., Birnstiel M. L. The cDNA sequences of the sea urchin U7 small nuclear RNA suggest specific contacts between histone mRNA precursor and U7 RNA during RNA processing. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2801–2807. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Levy S., Kedes L. H. Leader sequences of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus histone mRNAs start at a unique heptanucleotide common to all five histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]