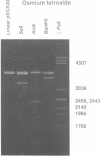
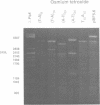
Abstract
Alternating d(A-T)n sequences which are contiguous with DNA of effectively random sequence have an abnormal conformation in linear DNA molecules. These regions are strongly reactive towards chemical modification by osmium tetroxide, and are preferentially cleaved by micrococcal nuclease. Both the chemical modification and the enzymic cutting occur uniformly through the alternating tract, and there is no evidence for enzyme or chemical sensitivity in the interfaces between the tract and DNA of normal conformation. These reactivities have a requirement for an alternating sequence. In addition to chemical reactivity, alternating (A-T)n sequences exhibit anomalously small twist changes on cruciform formation, suggesting that the pre-extruded DNA is underwound. We propose that the alternating sequences adopt an altered conformation which is subject to easy torsional deformation.
Full text
PDF








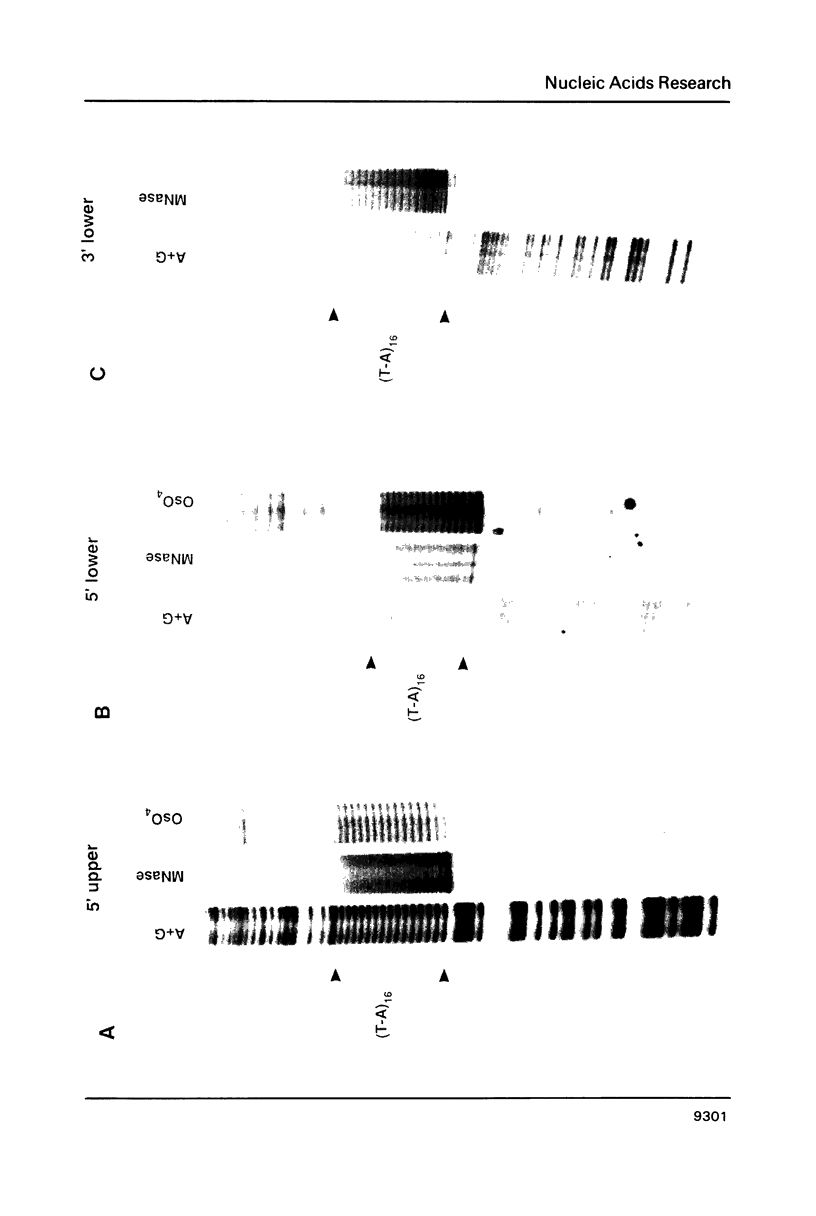








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Negative control requiring sequences both 5' and 3' to the regulated region. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):307–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G. S., Storti R. V. Structure and DNA sequence of the tropomyosin I gene from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):817–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Mengler R., Okada K., Auffray C., Strominger J. L. Sequence analysis of the human major histocompatibility gene SX alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2677–2683. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning K. S., RajBhandary U. L. Cytochrome oxidase subunit III gene in Neurospora crassa mitochondria. Location and sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5253–5256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. W., Cohen J. S. Salt- and sequence-dependence of the secondary structure of DNA in solution by 31P-NMR spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1983 Mar;22(3):879–893. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Wolstenholme D. R. A cluster of six tRNA genes in Drosophila mitochondrial DNA that includes a gene for an unusual tRNAserAGY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2367–2379. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Goodwin G. H. Demonstration of an S1-nuclease sensitive site near the human beta-globin gene, and its protection by HMG 1 and 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):547–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Effron K., Rechavi G., Ben-Neriah Y., Zakut R., Givol D. Simple DNA sequences in homologous flanking regions near immunoglobulin VH genes: a role in gene interaction? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3353–3370. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Wang J. C. Cruciform formation in a negatively supercoiled DNA may be kinetically forbidden under physiological conditions. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Conserved sequences flank variable tandem repeats in two S-antigen genes of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lange T., Berkvens T. M., Veerman H. J., Frasch A. C., Barry J. D., Borst P. Comparison of the genes coding for the common 5' terminal sequence of messenger RNAs in three trypanosome species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaese P., De Greve H., Gielen J., Seurinck L., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Identification of sequences involved in the polyadenylation of higher plant nuclear transcripts using Agrobacterium T-DNA genes as models. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):419–426. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Burke D. J., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. The 5- flanking sequences of Drosophila tRNAArg genes control their in vitro transcription in a Drosophila cell extract. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14738–14744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Lomonossoff G. P., Laskey R. A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2659–2673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Jovin T. M. Assignment of resonances in the phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of poly[d(A-T)] from phosphorothioate substitution. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4546–4550. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Schon E., Gora-Maslak G., Patterson J., Efstratiadis A. S1-hypersensitive sites in eukaryotic promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8043–8058. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galazka G., Palecek E., Wells R. D., Klysik J. Site-specific OsO4 modification of the B-Z junctions formed at the (dA-dC)32 region in supercoiled DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7093–7098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Mizuuchi K. Slow cruciform transitions in palindromic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5545–5549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Walker P., ten Heggeler B., Brown-Luedi M., de Bony E., Wahli W. Evolution of vitellogenin genes: comparative analysis of the nucleotide sequences downstream of the transcription initiation site of four Xenopus laevis and one chicken gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8595–8609. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Vojtískova M., Rena-Descalzi L., Palecek E. Osmium tetroxide: a new probe for site-specific distortions in supercoiled DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1725–1735. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
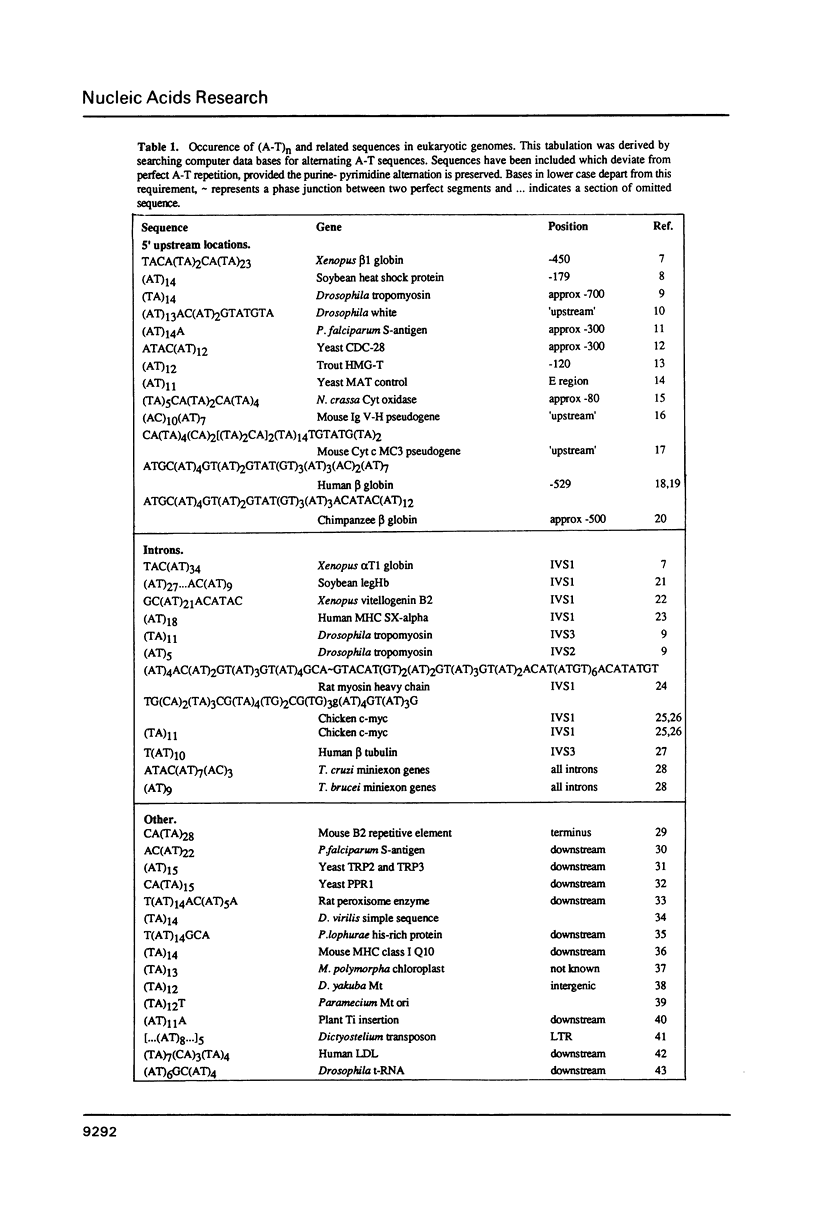
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K. (AT)n is an interspersed repeat in the Xenopus genome. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2617–2626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K., Lilley D. M. Facile cruciform formation by an (A-T)34 sequence from a Xenopus globin gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):461–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Lockyer M. J., Odink K. G., Sandhu J. S., Riveros-Moreno V., Nicholls S. C., Hillman Y., Davey L. S., Tizard M. L., Schwarz R. T. Primary structure of the precursor to the three major surface antigens of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):270–273. doi: 10.1038/317270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Jensen E. O., Paludan K., Wiborg O., Garrett R., Jørgensen P., Marcker K. A. The primary structures of two leghemoglobin genes from soybean. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):689–701. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H., Rich A. Chemical probes of DNA conformation: detection of Z-DNA at nucleotide resolution. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer B., Guyonvarch A., Hubert J. C. Yeast regulatory gene PPR1. I. Nucleotide sequence, restriction map and codon usage. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang D. S., Wells R. D. B-Z DNA junctions contain few, if any, nonpaired bases at physiological superhelical densities. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7783–7790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T. A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Loomis C., Cowan N. J. Sequence of an expressed human beta-tubulin gene containing ten Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5823–5836. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Hallam L. R. Thermodynamics of the ColE1 cruciform. Comparisons between probing and topological experiments using single topoisomers. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):179–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Palecek E. The supercoil-stabilised cruciform of ColE1 is hyper-reactive to osmium tetroxide. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbach K. J., Wu R. Characterization of a mouse somatic cytochrome c gene and three cytochrome c pseudogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):617–630. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukásová E., Vojtísková M., Jelen F., Sticzay T., Palecek E. Osmium-induced alteration in DNA structure. Gen Physiol Biophys. 1984 Apr;3(2):175–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. A pH-dependent structural transition in the homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Oct;3(2):327–338. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Reed S. I. Primary structure homology between the product of yeast cell division control gene CDC28 and vertebrate oncogenes. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):183–185. doi: 10.1038/307183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor A. L., Weiss E. H., Kress M., Jay G., Flavell R. A. A nonpolymorphic class I gene in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschonas N., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. The DNA sequence of the 5' flanking region of the human beta-globin gene: evolutionary conservation and polymorphic differences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2109–2120. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao R. T., Czarnecka E., Gurley W. B., Schöffl F., Key J. L. Genes for low-molecular-weight heat shock proteins of soybeans: sequence analysis of a multigene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3417–3428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nejedlý K., Kwinkowski M., Gałazka G., Kłysik J., Palecek E. Recognition of the structural distortions at the junctions between B and Z segments in negatively supercoiled DNA by osmium tetroxide. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Dec;3(3):467–478. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Murphy C., Levis R., Rubin G. M. DNA sequence of the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):437–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osumi T., Ishii N., Hijikata M., Kamijo K., Ozasa H., Furuta S., Miyazawa S., Kondo K., Inoue K., Kagamiyama H. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the cDNA for rat peroxisomal enoyl-CoA: hydratase-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase bifunctional enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8905–8910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Suggs J. W., Cox S. D. Right-handed alternating DNA conformation: poly(dA-dT) adopts the same dinucleotide repeat with cesium, tetraalkylammonium, and 3 alpha, 5 beta, 17 beta-dipyrrolidinium steroid dimethiodide cations in aqueous solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4063–4067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patient R. K., Harris R., Walmsley M. E., Williams J. G. The complete nucleotide sequence of the major adult beta globin gene of Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8521–8523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M. A., Nicolas R. H., Wright C. A., Goodwin G. H. Multiple sequence-specific DNA binding activities are eluted from chicken nuclei at low ionic strengths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4047–4065. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Schwartz E., Ballantine M., Surrey S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the delta beta-globin gene region in humans. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11599–11609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Laping J. L., Seilhamer J. J., Cummings D. J. Inter-species sequence diversity in the replication initiation region of Paramecium mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Feder R., Pavlovec A., Blobel G. Primary structure and genomic organization of the histidine-rich protein of the malaria parasite Plasmodium lophurae. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):616–620. doi: 10.1038/312616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Helical periodicity of DNA determined by enzyme digestion. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):573–578. doi: 10.1038/286573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Sequence-dependent helical periodicity of DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):378–380. doi: 10.1038/292378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E., Sivertsen A., Firtel R. A. An unusual transposon encoding heat shock inducible and developmentally regulated transcripts in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savatier P., Trabuchet G., Faure C., Chebloune Y., Gouy M., Verdier G., Nigon V. M. Evolution of the primate beta-globin gene region. High rate of variation in CpG dinucleotides and in short repeated sequences between man and chimpanzee. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H. 13C NMR study of conformation and mobility of 145-base-pair poly(dA-dT) . poly(dA-dT) in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):309–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Simpson R. T., Cohen J. S. An alternating conformation characterizes the phosphodiester backbone of poly(dA-dT) in solution. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8125–8128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Kilpatrick M. W., Wells R. D. S1 nuclease recognizes DNA conformational junctions between left-handed helical (dT-dG n. dC-dA)n and contiguous right-handed sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1963–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Gaillard C., Prunell A. Helical periodicity of DNA, Poly(dA) . poly(dT) and poly(dA-dT). poly(dA-dT) in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehler E. E., Mahdavi V., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Intron positions are conserved in the 5' end region of myosin heavy-chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):468–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs J. W., Wagner R. W. Nuclease recognition of an alternating structure in a d(AT)14 plasmid insert. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3703–3716. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Renz M. Simple DNA sequences of Drosophila virilis isolated by screening with RNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 15;172(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Inokuchi H., Ohyama K., Ozeki H. Nucleotide sequence of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast DNA: a region possibly encoding three tRNAs and three proteins including a homologue of E. coli ribosomal protein S14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9551–9565. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Jones P. G., Sheldrick G. M., Salisbury S., Favello L., Shakked Z. DNA double helical fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):687–688. doi: 10.1038/273687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorlícková M., Kypr J. Conformational variability of poly(dA-dT).poly(dA-dT) and some other deoxyribonucleic acids includes a novel type of double helix. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Aug;3(1):67–83. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Peck L. J., Becherer K. DNA supercoiling and its effects on DNA structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):85–91. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Payne G., Varmus H. E. Proviral deletions and oncogene base-substitutions in insertionally mutagenized c-myc alleles may contribute to the progression of avian bursal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):843–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann L. M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the expressed gene and several processed pseudogenes for the mouse ribosomal protein L30 gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2518–2528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Paluh J. L., van Cleemput M., Moye W. S., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes TRP2 and TRP3 encoding bifunctional anthranilate synthase: indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3985–3992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]